Poster Session C
Pain syndromes, fibromyalgia and regional musculoskeletal disorders
Session: (1827–1839) Fibromyalgia & Other Clinical Pain Syndromes Poster
1829: Blood-derived Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Diagnostic Biomarker in Fibromyalgia Syndrome
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- GH
Gilad Halpert, PhD
CAHIM SHEBA MEDICAL CENTER
Tel Hashomer, IsraelDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Gilad Halpert, Daniel Yechiali, liel Katbi, Eri Govrin, Boris Guilbord, Ori Segal and Howard AMITAL, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel
Background/Purpose: The Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) is a global chronic pain condition, which affects approximately 2–6% of the population. The underlying mechanism of FMS is unclear and there is no specific lab test to confirm the diagnosis of FMS. There is an unmet need regarding the development of a precise diagnostic marker for FMS. Previous studies had demonstrated that small extracellular vesicles (sEVs), are involved in: intercellular communications and in the pathogenesis of inflammatory/autoimmune diseases. Recently, an autoimmune origin had been suggested for the development of FMS. In the current study, we aimed to characterize sEVs derived from blood of FMS patients and to explore a potential change in the expression of key proteins in these vesicles as compared to healthy controls.
Methods: sEVs have been isolated from the plasma of women diagnosed with primary FMS (n=9) vs. Age matched healthy women (n=9), using size exclusion chromatography technique. Characterization of these sEVs have been conducted using nanoparticle tracking analysis, transition electron microscopy and western blot analysis. The protein profile of these sEVs have been explored using proteomics analysis.
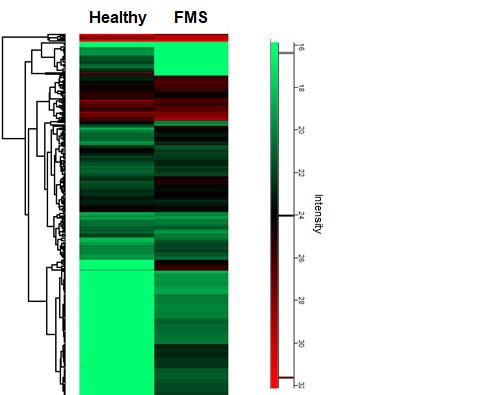
Results: We found changes in the expression of various proteins in sEVs derived from plasma of FMS as compared to healthy controls (Figure 1), among them: immunological- (e.g. Complement component 1q), neurological- (e.g. Cofilin-1), ribosomal protein assembly- (e.g. Nucleophosmin) and oxidative stress- (e.g. Superoxide dismutase) related proteins.
Conclusion: Our results potentially shed a light on the importance of sEVs in the pathophysiology of FMS and their potential to serve as a new diagnostic biomarker candidate in FMS.
G. Halpert: None; D. Yechiali: None; l. Katbi: None; E. Govrin: None; B. Guilbord: None; O. Segal: None; H. AMITAL: Janssen, 5.
Background/Purpose: The Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) is a global chronic pain condition, which affects approximately 2–6% of the population. The underlying mechanism of FMS is unclear and there is no specific lab test to confirm the diagnosis of FMS. There is an unmet need regarding the development of a precise diagnostic marker for FMS. Previous studies had demonstrated that small extracellular vesicles (sEVs), are involved in: intercellular communications and in the pathogenesis of inflammatory/autoimmune diseases. Recently, an autoimmune origin had been suggested for the development of FMS. In the current study, we aimed to characterize sEVs derived from blood of FMS patients and to explore a potential change in the expression of key proteins in these vesicles as compared to healthy controls.
Methods: sEVs have been isolated from the plasma of women diagnosed with primary FMS (n=9) vs. Age matched healthy women (n=9), using size exclusion chromatography technique. Characterization of these sEVs have been conducted using nanoparticle tracking analysis, transition electron microscopy and western blot analysis. The protein profile of these sEVs have been explored using proteomics analysis.
Results: We found changes in the expression of various proteins in sEVs derived from plasma of FMS as compared to healthy controls (Figure 1), among them: immunological- (e.g. Complement component 1q), neurological- (e.g. Cofilin-1), ribosomal protein assembly- (e.g. Nucleophosmin) and oxidative stress- (e.g. Superoxide dismutase) related proteins.
Conclusion: Our results potentially shed a light on the importance of sEVs in the pathophysiology of FMS and their potential to serve as a new diagnostic biomarker candidate in FMS.

Figure 1: Heatmap visualization of protein expression profiles, in blood-derived small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) isolated from FMS patients vs. healthy controls, identified by proteomics analysis.
G. Halpert: None; D. Yechiali: None; l. Katbi: None; E. Govrin: None; B. Guilbord: None; O. Segal: None; H. AMITAL: Janssen, 5.



