Poster Session C
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) including psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Session: (2227–2256) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III: SpA
2228: Early Improvement in 3 Visual Analogue Scale (3VAS)/4VAS Predicts Reduced Rates of Radiographic Change in Bio-naive Active Psoriatic Arthritis Patients Receiving Guselkumab Treatment
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall

Laura Coates, MD, PhD
University of Oxford
Oxford, United KingdomDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
William R Tillett1, Laura Coates2, marijn vis3, Enrique Soriano4, Joseph F. Merola5, Miriam Zimmermann6, May Shawi7, Mohamed Sharaf8, Peter Nash9 and Philip Helliwell10, 1Department of Rheumatology, Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Bath, United Kingdom, 2University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, 3Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 4Rheumatology Section, Internal Medicine Services, Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, and University Institute Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 5Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, 6Immunology, Janssen Medical Affairs, LLC, Zug, Switzerland, 7Immunology, Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Titusville, NJ, 8Immunology, Janssen MEA, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 9School of Medicine, Griffith University, Brisbane, Australia, 10University of Leeds, Leeds, United Kingdom
Background/Purpose: Guselkumab (GUS), a fully human IL-23p19 subunit inhibitor, was shown to reduce mean changes in radiographic progression vs placebo (PBO) by week (W)24 and to be associated with low rates of radiographic progression through W100 among GUS-treated patients (pts) with PsA, irrespective of dosing regimen (every [Q] 4W or Q8W). Furthermore, earlier clinical response predicted improved long-term radiographic outcome in GUS-treated pts with active PsA. The recently developed 3 Visual Analogue Scale (3VAS) and 4VAS scores are the first short multidimensional composite measures specifically for use in PsA routine clinical care. Here we determined whether early improvement in 3VAS/4VAS predicts radiographic change through W100.
Methods: DISCOVER-2 included bio-naive pts with active PsA (≥5 swollen and ≥5 tender joint counts [SJC/TJC]; CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL) randomized (1:1:1) to GUS 100 mg Q4W; GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, then Q8W; or PBO with crossover to GUS 100 mg Q4W at W24. In the current analysis, only pts randomized to GUS (Q4W and Q8W) were included (N=493). Response at W8 was defined as achievement of low disease activity (LDA) in 3VAS (≤3.4), 4VAS (≤3.5), routine assessment of pt index data 3 (RAPID3; ≤6), Disease Activity in PsA (DAPSA; ≤14), and PsA Disease Activity Score (PASDAS; ≤3.2). Association of W8 response with change from baseline (BL) to W100 in total PsA-modified van der Heijde-Sharp (vdH-S) score was assessed with the independent samples t-test and generalized linear models adjusting for known BL determinants of radiographic progression (vdH-S score, age, gender, and CRP). Pairwise correlations and agreement in LDA classification between the endpoints were assessed with Pearson's correlation coefficient and the kappa statistic, respectively.
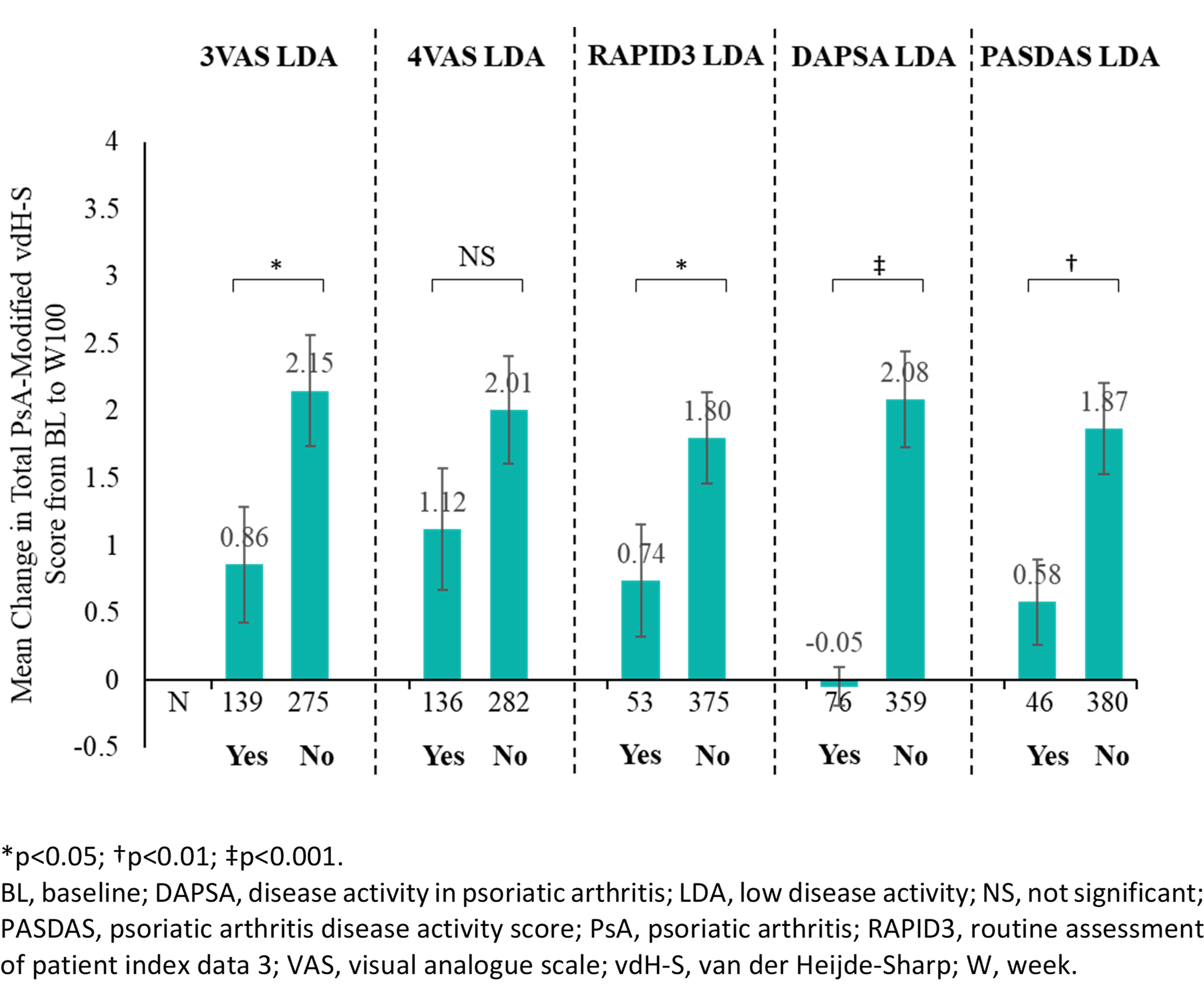
Results: Among GUS-treated pts not meeting the respective endpoints at BL, 32.9%, 31.6%, 12.4%, 17.8%, and 10.8% achieved LDA in 3VAS, 4VAS, RAPID3, DAPSA, and PASDAS, respectively, at W8. LDA achievement in 3VAS (0.86 vs 2.15, p=0.03), RAPID3 LDA (0.74 vs 1.80, p=0.049), DAPSA LDA (-0.05 vs 2.08, p< 0.001), and PASDAS LDA (0.58 vs 1.87, p=0.006) at W8 were associated with significantly less radiographic progression through W100 (Figure). For 4VAS, achievement of remission (≤2.1; 0.71 vs 1.84, p=0.045), but not LDA (1.12 vs 2.01, p=0.142), was also associated with improved radiographic outcome. In multivariate analyses, improved response to GUS treatment at W8 in all endpoints assessed was associated with numerically less radiographic progression through W100. At W8, 3VAS and 4VAS showed strong correlations with RAPID3 (r3VAS=0.787; r4VAS=0.877) and PASDAS (r3VAS=0.795; r4VAS=0.790) and moderate correlations with DAPSA (r3VAS=0.466; r4VAS=0.524), whereas fair to moderate agreement (kappa range: 0.325-0.545) in LDA classification was noted.
Conclusion: Approximately one-third of GUS-treated pts achieved early response (W8 LDA) in 3VAS/4VAS, which was associated with reduced rates of radiographic change, as was early response in the other outcomes assessed. These results suggest that, in addition to their usefulness in assessing disease activity in routine clinical care, 3VAS and 4VAS, the former being more sensitive, may predict long-term radiographic changes.
W. Tillett: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Amgen, 2, 5, 6, Celgene, 2, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, 6, GSK, 2, 5, 6, Janssen, 2, 5, 6, MSD, 2, 5, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Ovo Pharma, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, UCB Pharma, 2, 5, 6; L. Coates: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Amgen, 2, 5, 6, Biogen, 6, Bristol Myers Squibb, 2, Celgene, 2, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, 6, Galapagos, 2, 6, Gilead Sciences, 2, 6, GSK, 6, Janssen, 2, 5, 6, Medac, 6, MoonLake, 2, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer Inc, 2, 5, 6, UCB, 2, 5, 6; m. vis: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Amgen, 2, 5, 6, Dutch Arthritis Foundation, 2, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, 6, Janssen, 2, 5, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, UCB, 2, 5, 6; E. Soriano: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Amgen, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb, 6, Eli Lilly, 6, Janssen, 2, 5, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 5, 6, Roche, 2, 5, 6, UCB, 5, 6; J. Merola: AbbVie, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Amgen, 2, Biogen, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Bristol Myers Squibb, 2, Dermavant, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Eli Lilly, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Janssen, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, LEO Pharma, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Novartis, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Pfizer, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Regeneron, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Sanofi, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Sun Pharmaceuticals, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, UCB Pharma, 12, Consultant and/or investigator; M. Zimmermann: Janssen, 3, Johnson & Johnson, 11; M. Shawi: Immunology Global Medical Affairs, Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson, 3, Johnson & Johnson, 11; M. Sharaf: Janssen, 3, Johnson & Johnson, 11; P. Nash: AbbVie, 5, 6, Bristol Myers Squibb, 5, 6, Celgene, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 5, 6, Galapagos, 5, 6, GSK, 5, 6, Janssen, 5, 6, Novartis, 5, 6, Pfizer Inc, 5, 6; P. Helliwell: Janssen, 12, fees for educational services, Novartis, 12, fees for educational services.
Background/Purpose: Guselkumab (GUS), a fully human IL-23p19 subunit inhibitor, was shown to reduce mean changes in radiographic progression vs placebo (PBO) by week (W)24 and to be associated with low rates of radiographic progression through W100 among GUS-treated patients (pts) with PsA, irrespective of dosing regimen (every [Q] 4W or Q8W). Furthermore, earlier clinical response predicted improved long-term radiographic outcome in GUS-treated pts with active PsA. The recently developed 3 Visual Analogue Scale (3VAS) and 4VAS scores are the first short multidimensional composite measures specifically for use in PsA routine clinical care. Here we determined whether early improvement in 3VAS/4VAS predicts radiographic change through W100.
Methods: DISCOVER-2 included bio-naive pts with active PsA (≥5 swollen and ≥5 tender joint counts [SJC/TJC]; CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL) randomized (1:1:1) to GUS 100 mg Q4W; GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, then Q8W; or PBO with crossover to GUS 100 mg Q4W at W24. In the current analysis, only pts randomized to GUS (Q4W and Q8W) were included (N=493). Response at W8 was defined as achievement of low disease activity (LDA) in 3VAS (≤3.4), 4VAS (≤3.5), routine assessment of pt index data 3 (RAPID3; ≤6), Disease Activity in PsA (DAPSA; ≤14), and PsA Disease Activity Score (PASDAS; ≤3.2). Association of W8 response with change from baseline (BL) to W100 in total PsA-modified van der Heijde-Sharp (vdH-S) score was assessed with the independent samples t-test and generalized linear models adjusting for known BL determinants of radiographic progression (vdH-S score, age, gender, and CRP). Pairwise correlations and agreement in LDA classification between the endpoints were assessed with Pearson's correlation coefficient and the kappa statistic, respectively.
Results: Among GUS-treated pts not meeting the respective endpoints at BL, 32.9%, 31.6%, 12.4%, 17.8%, and 10.8% achieved LDA in 3VAS, 4VAS, RAPID3, DAPSA, and PASDAS, respectively, at W8. LDA achievement in 3VAS (0.86 vs 2.15, p=0.03), RAPID3 LDA (0.74 vs 1.80, p=0.049), DAPSA LDA (-0.05 vs 2.08, p< 0.001), and PASDAS LDA (0.58 vs 1.87, p=0.006) at W8 were associated with significantly less radiographic progression through W100 (Figure). For 4VAS, achievement of remission (≤2.1; 0.71 vs 1.84, p=0.045), but not LDA (1.12 vs 2.01, p=0.142), was also associated with improved radiographic outcome. In multivariate analyses, improved response to GUS treatment at W8 in all endpoints assessed was associated with numerically less radiographic progression through W100. At W8, 3VAS and 4VAS showed strong correlations with RAPID3 (r3VAS=0.787; r4VAS=0.877) and PASDAS (r3VAS=0.795; r4VAS=0.790) and moderate correlations with DAPSA (r3VAS=0.466; r4VAS=0.524), whereas fair to moderate agreement (kappa range: 0.325-0.545) in LDA classification was noted.
Conclusion: Approximately one-third of GUS-treated pts achieved early response (W8 LDA) in 3VAS/4VAS, which was associated with reduced rates of radiographic change, as was early response in the other outcomes assessed. These results suggest that, in addition to their usefulness in assessing disease activity in routine clinical care, 3VAS and 4VAS, the former being more sensitive, may predict long-term radiographic changes.

Mean Change in Total PsA-Modified vdH-S Score from BL to W100 by Achievement of LDA in Outcomes of Interest
W. Tillett: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Amgen, 2, 5, 6, Celgene, 2, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, 6, GSK, 2, 5, 6, Janssen, 2, 5, 6, MSD, 2, 5, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Ovo Pharma, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, UCB Pharma, 2, 5, 6; L. Coates: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Amgen, 2, 5, 6, Biogen, 6, Bristol Myers Squibb, 2, Celgene, 2, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, 6, Galapagos, 2, 6, Gilead Sciences, 2, 6, GSK, 6, Janssen, 2, 5, 6, Medac, 6, MoonLake, 2, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer Inc, 2, 5, 6, UCB, 2, 5, 6; m. vis: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Amgen, 2, 5, 6, Dutch Arthritis Foundation, 2, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, 6, Janssen, 2, 5, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, UCB, 2, 5, 6; E. Soriano: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Amgen, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb, 6, Eli Lilly, 6, Janssen, 2, 5, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 5, 6, Roche, 2, 5, 6, UCB, 5, 6; J. Merola: AbbVie, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Amgen, 2, Biogen, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Bristol Myers Squibb, 2, Dermavant, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Eli Lilly, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Janssen, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, LEO Pharma, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Novartis, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Pfizer, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Regeneron, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Sanofi, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, Sun Pharmaceuticals, 12, Consultant and/or investigator, UCB Pharma, 12, Consultant and/or investigator; M. Zimmermann: Janssen, 3, Johnson & Johnson, 11; M. Shawi: Immunology Global Medical Affairs, Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson, 3, Johnson & Johnson, 11; M. Sharaf: Janssen, 3, Johnson & Johnson, 11; P. Nash: AbbVie, 5, 6, Bristol Myers Squibb, 5, 6, Celgene, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 5, 6, Galapagos, 5, 6, GSK, 5, 6, Janssen, 5, 6, Novartis, 5, 6, Pfizer Inc, 5, 6; P. Helliwell: Janssen, 12, fees for educational services, Novartis, 12, fees for educational services.



