Poster Session C
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Session: (2257–2325) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III
2296: Association Between EQ-5D-5L and SLEDAI Scores in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in the United States and Europe: A Real-world Survey
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- EI
Ebuwa Igho-Osagie, DrPH
Merck & Co. Inc.
North Wales, PA, United StatesDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Ebuwa Igho-Osagie1, Rezaul Khandker1, Jack Milligan2, Emily Goddard2 and Sophie Barlow2, 1Merck & Co. Inc., Rahway, NJ, 2Adelphi Real World, Bollington, United Kingdom
Background/Purpose: The EQ-5D-5L is validated for estimating health related quality of life (HRQoL) across a variety of different disease areas, including rheumatic diseases. However, its ability to effectively capture HRQoL in patients with complex conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is debated. While disease-specific instruments may more robustly quantify HRQoL and disease burden in these patients, they cannot be used for cross-disease comparisons. Divergence of results between disease-specific instruments and the EQ-5D-5L may indicate an inability of the latter to completely capture the impact of disease manifestation in patients with SLE. In this study, we measured the correlation between the EQ-5D-5L and the SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) – a disease-specific instrument used to quantify SLE disease activity and severity.
Methods: Data were drawn from the 2021 Adelphi Real World Lupus Disease Specific Programme (DSP)™, a cross-sectional survey with retrospective data collection. Rheumatologists in France, Germany, Italy, Spain, the United Kingdom and the United States provided demographic and clinical information for their next 5-6 consecutively consulting patients with SLE. SLEDAI scores were derived from physicians' clinical assessment of their SLE patients. The same patients were then invited to complete a questionnaire that included an EQ-5D-5L form. We assessed the correlation between EQ-5D-5L and SLEDAI scores, and EQ-5D-5L subdomains and SLEDAI scores using Pearson's and Spearman's correlations, respectively.
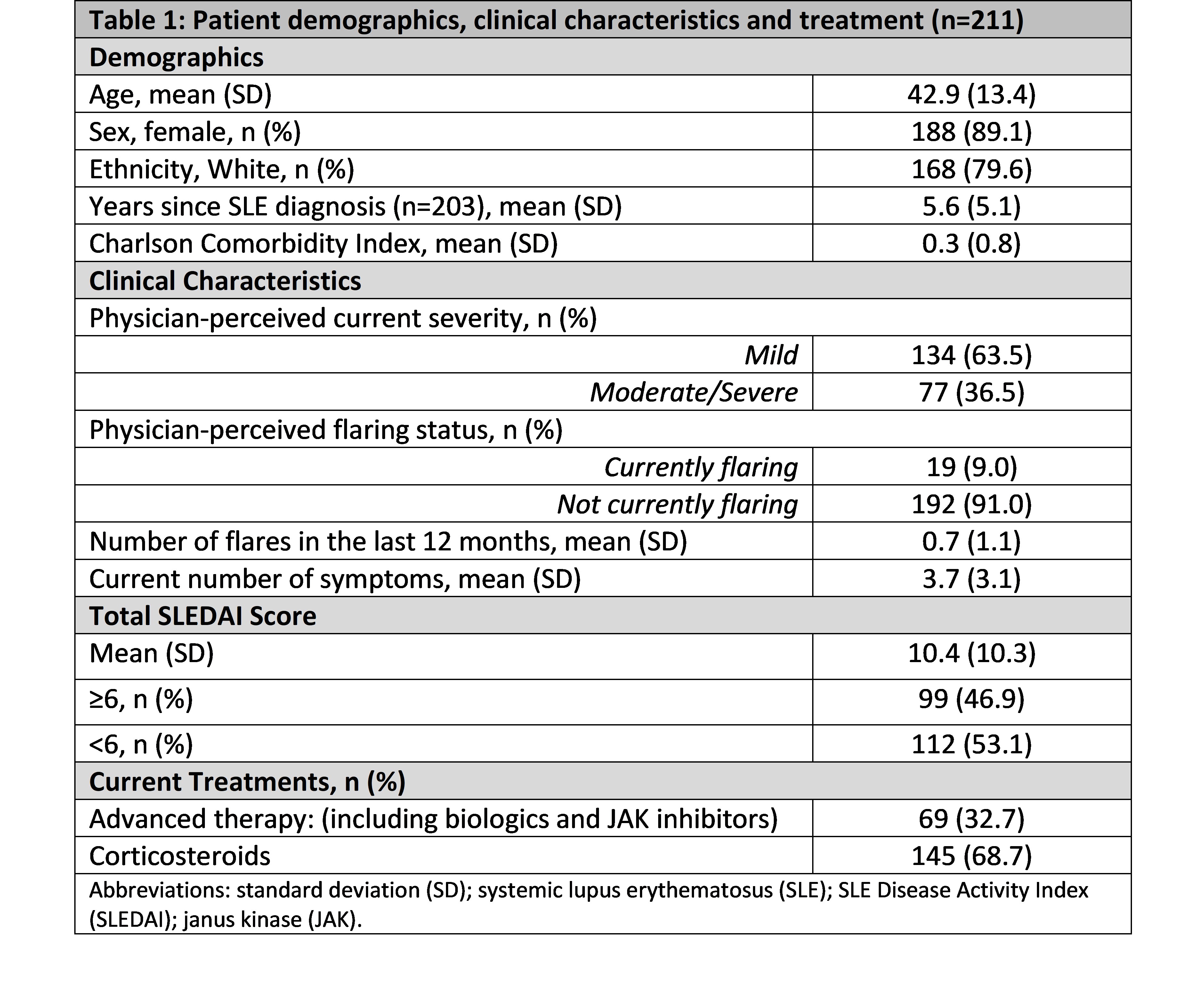
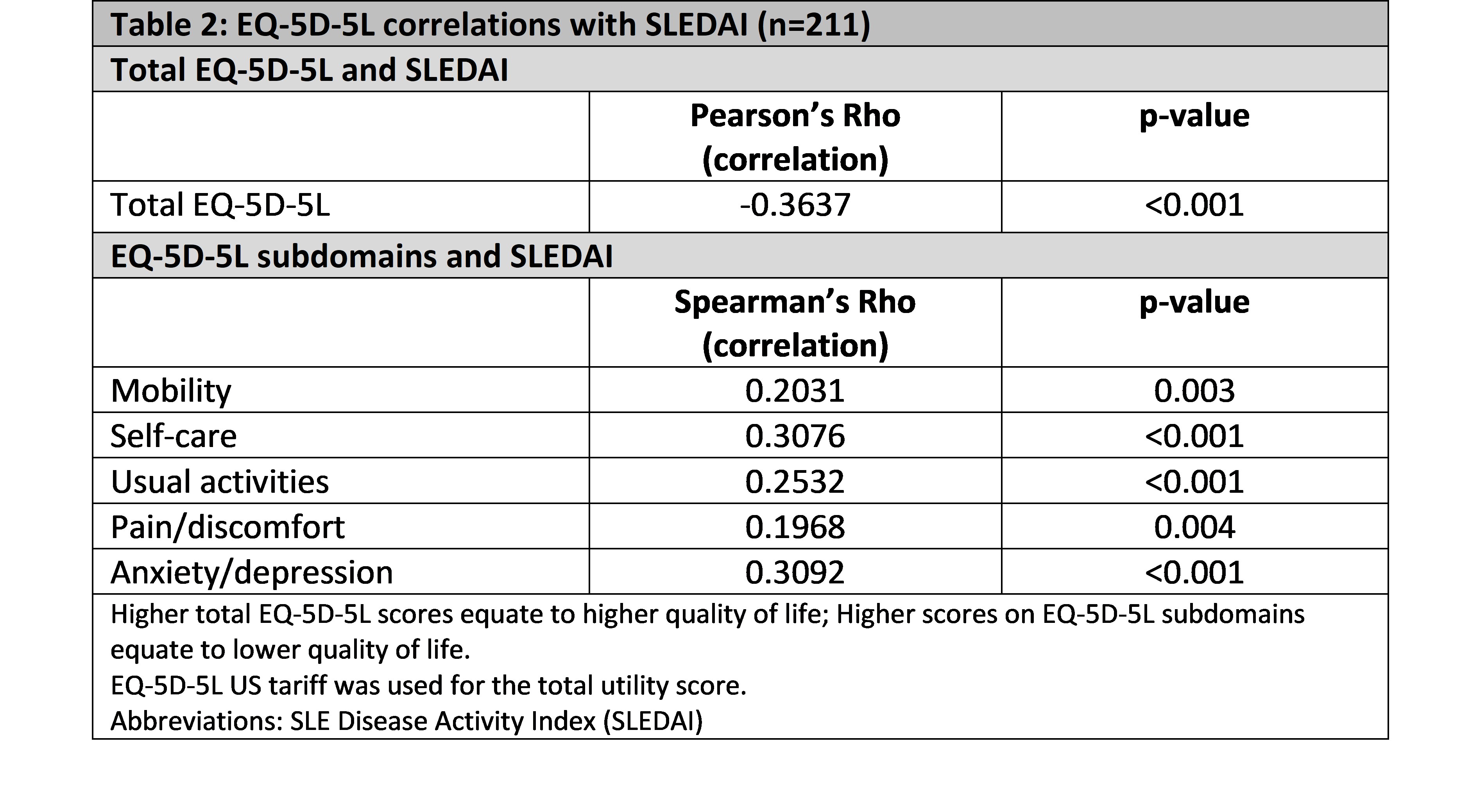
Results: A total of 211 patients were included in this analysis. Mean (SD) age was 42.9 (13.4) years, 89% of patients were female and 80% were White. The mean (SD) SLEDAI score was 10.4 (10.3) and mean (SD) EQ-5D-5L score was 0.75 (0.24). Pearson's Rho correlation between SLEDAI scores and total EQ-5D-5L was r=-0.3637 (p< 0.001) while Spearman's Rho correlations between SLEDAI scores and each EQ-5D domain were: Mobility r=0.2031 (p=0.003); Self-care r=0.3076 (p< 0.001); Usual activities r=0.2532 (p< 0.001); Pain/discomfort r=0.1968 (p=0.004); Anxiety/depression r=0.3092 (p< 0.001).
Conclusion: Weak correlations were observed between SLEDAI and EQ-5D-5L and between SLEDAI and the EQ-5D-5L subdomains, suggesting a patient's clinical status may not be fully reflected in the EQ-5D-5L. More sensitive disease-specific instruments or HRQoL estimation tools may be required to fully capture the burden of disease in patients with SLE.
E. Igho-Osagie: Merck/MSD, 3; R. Khandker: Merck/MSD, 3; J. Milligan: None; E. Goddard: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, Adelphi Real World, 3; S. Barlow: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, Adelphi Real World, 3.
Background/Purpose: The EQ-5D-5L is validated for estimating health related quality of life (HRQoL) across a variety of different disease areas, including rheumatic diseases. However, its ability to effectively capture HRQoL in patients with complex conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is debated. While disease-specific instruments may more robustly quantify HRQoL and disease burden in these patients, they cannot be used for cross-disease comparisons. Divergence of results between disease-specific instruments and the EQ-5D-5L may indicate an inability of the latter to completely capture the impact of disease manifestation in patients with SLE. In this study, we measured the correlation between the EQ-5D-5L and the SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) – a disease-specific instrument used to quantify SLE disease activity and severity.
Methods: Data were drawn from the 2021 Adelphi Real World Lupus Disease Specific Programme (DSP)™, a cross-sectional survey with retrospective data collection. Rheumatologists in France, Germany, Italy, Spain, the United Kingdom and the United States provided demographic and clinical information for their next 5-6 consecutively consulting patients with SLE. SLEDAI scores were derived from physicians' clinical assessment of their SLE patients. The same patients were then invited to complete a questionnaire that included an EQ-5D-5L form. We assessed the correlation between EQ-5D-5L and SLEDAI scores, and EQ-5D-5L subdomains and SLEDAI scores using Pearson's and Spearman's correlations, respectively.
Results: A total of 211 patients were included in this analysis. Mean (SD) age was 42.9 (13.4) years, 89% of patients were female and 80% were White. The mean (SD) SLEDAI score was 10.4 (10.3) and mean (SD) EQ-5D-5L score was 0.75 (0.24). Pearson's Rho correlation between SLEDAI scores and total EQ-5D-5L was r=-0.3637 (p< 0.001) while Spearman's Rho correlations between SLEDAI scores and each EQ-5D domain were: Mobility r=0.2031 (p=0.003); Self-care r=0.3076 (p< 0.001); Usual activities r=0.2532 (p< 0.001); Pain/discomfort r=0.1968 (p=0.004); Anxiety/depression r=0.3092 (p< 0.001).
Conclusion: Weak correlations were observed between SLEDAI and EQ-5D-5L and between SLEDAI and the EQ-5D-5L subdomains, suggesting a patient's clinical status may not be fully reflected in the EQ-5D-5L. More sensitive disease-specific instruments or HRQoL estimation tools may be required to fully capture the burden of disease in patients with SLE.


E. Igho-Osagie: Merck/MSD, 3; R. Khandker: Merck/MSD, 3; J. Milligan: None; E. Goddard: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, Adelphi Real World, 3; S. Barlow: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, Adelphi Real World, 3.



