Poster Session C
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (2095–2140) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
2130: Prevalence and Risk Factors of Pneumocystis Jirovecii Colonization in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors and Tocilizumab
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- YH
Yi-Min Huang, MD
National Taiwan University Hospital Cancer Center
Taipei City, TaiwanDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Yi-Min Huang1, Chieh-An Chuang2, Jui-Hung Kao2, Yen-Chun Lin2, Jen-Hao Chen3, Chiao-Feng Cheng4, Cheng-Hsun Lu4, Yu-Min Kuo4, Chieh-Yu Shen4, Chin-Hsiu Liu5, Ko-Jen Li4, Song-Chou Hsieh4, Jung-Yien Chien4 and Po-Ren Hsueh4, 1National Taiwan University Cancer Center, Taipei City, Taiwan, 2National Taiwan University Hospital Yunlin Branch, Yunlin, Taiwan, 3National Taiwan University Cancer Center, Taipei, Taiwan, 4National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan, 5National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are susceptible toPneumocystis jiroveciicolonization and prone to develop life-threateningPneumocystispneumonia (PCP). An increased risk ofP. jiroveciicolonization and PCP was found in RA patients treated with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors. However, the impact of other biologics onP. jiroveciicolonization remains unrecognized. This study aims to investigate the prevalence and risk factors ofP. jiroveciicolonization in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with TNF inhibitors and tocilizumab.
Methods: We enrolled the patients with RA, who were treated with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs), TNF inhibitors, and tocilizumab between March 2022 to February 2023. The patients with acute respiratory symptoms were excluded.P. jiroveciipolymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays of induced sputum, nasal swab, and oral wash were performed. Factors associated withP. jiroveciicolonization were evaluated.
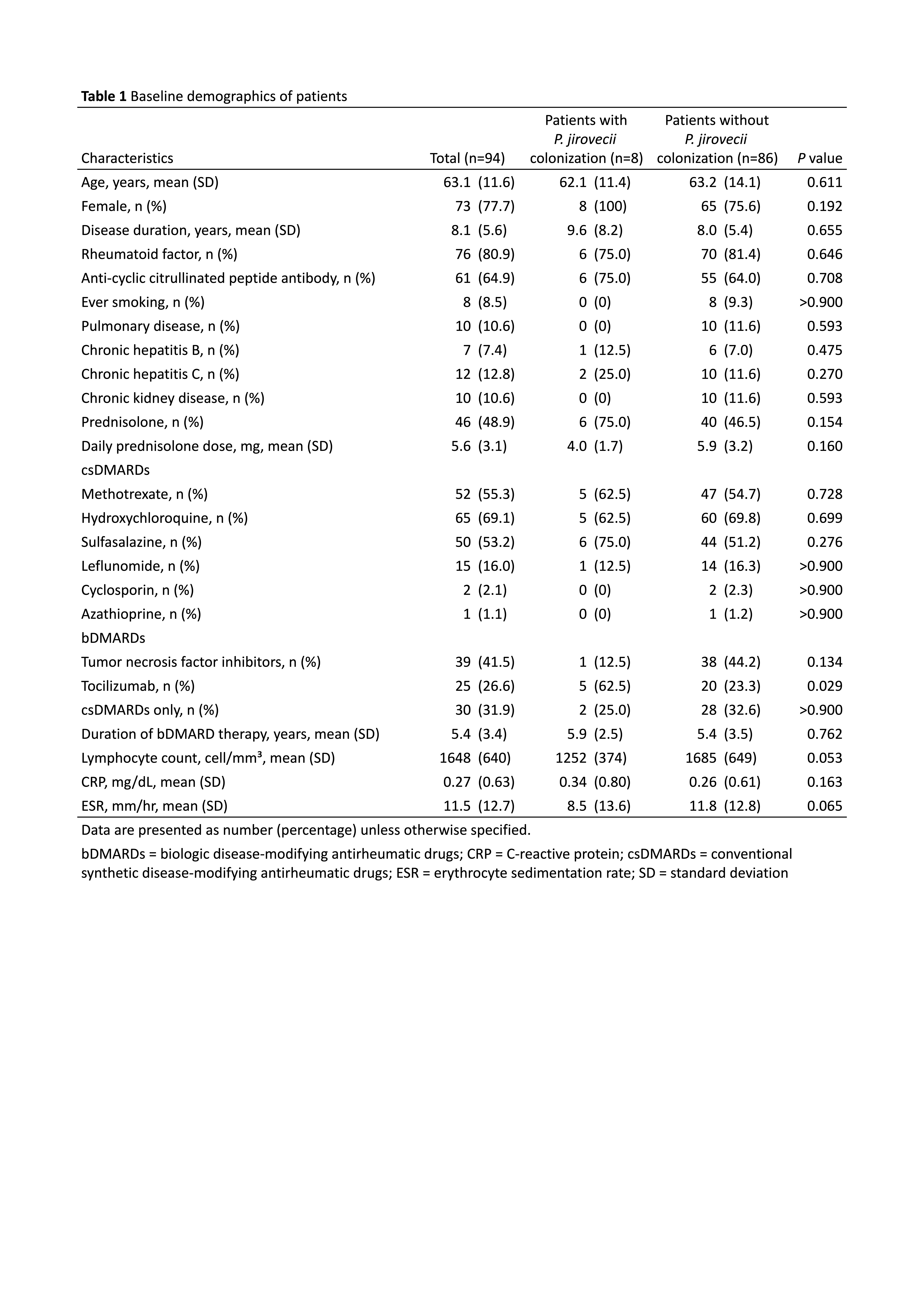
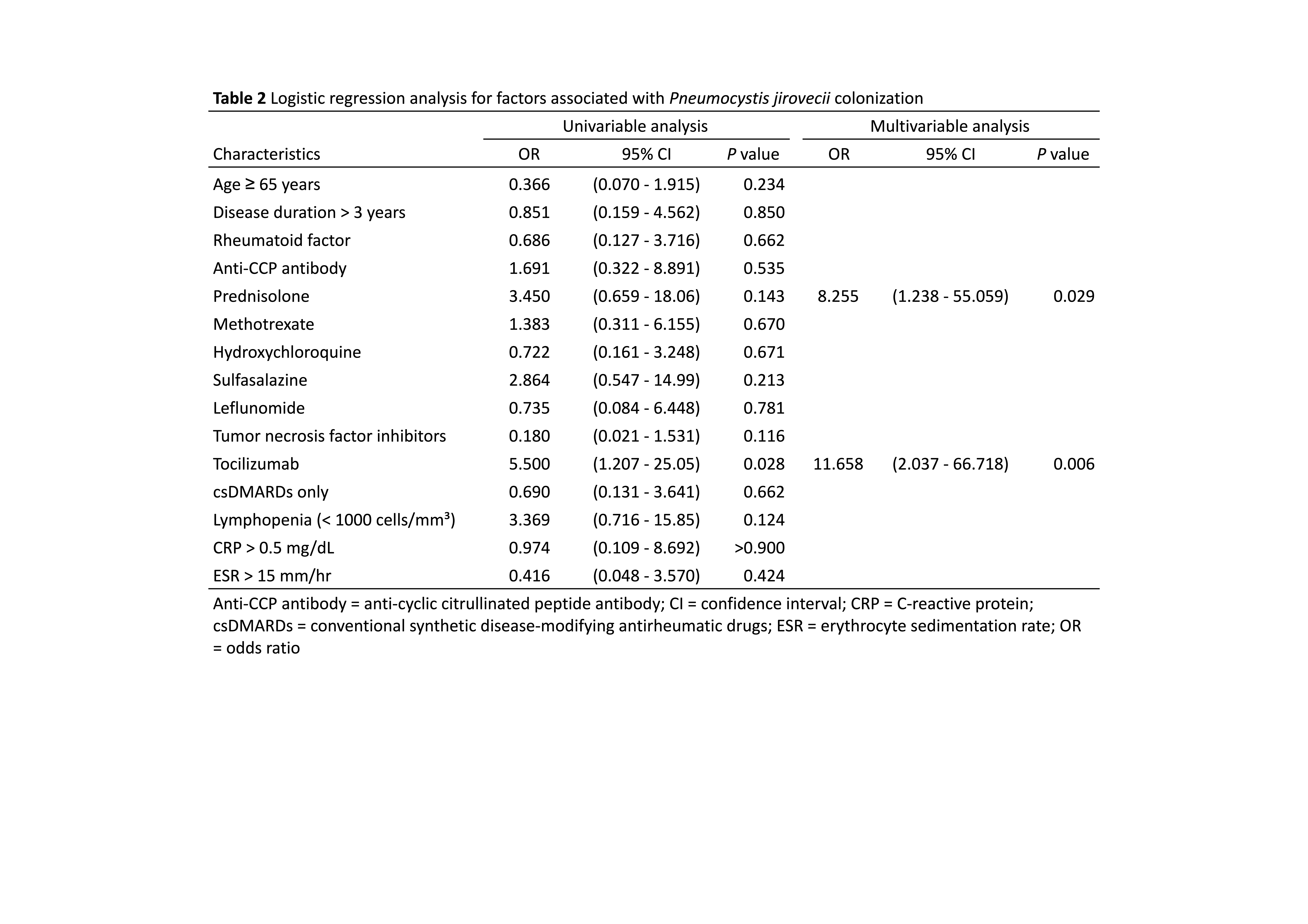
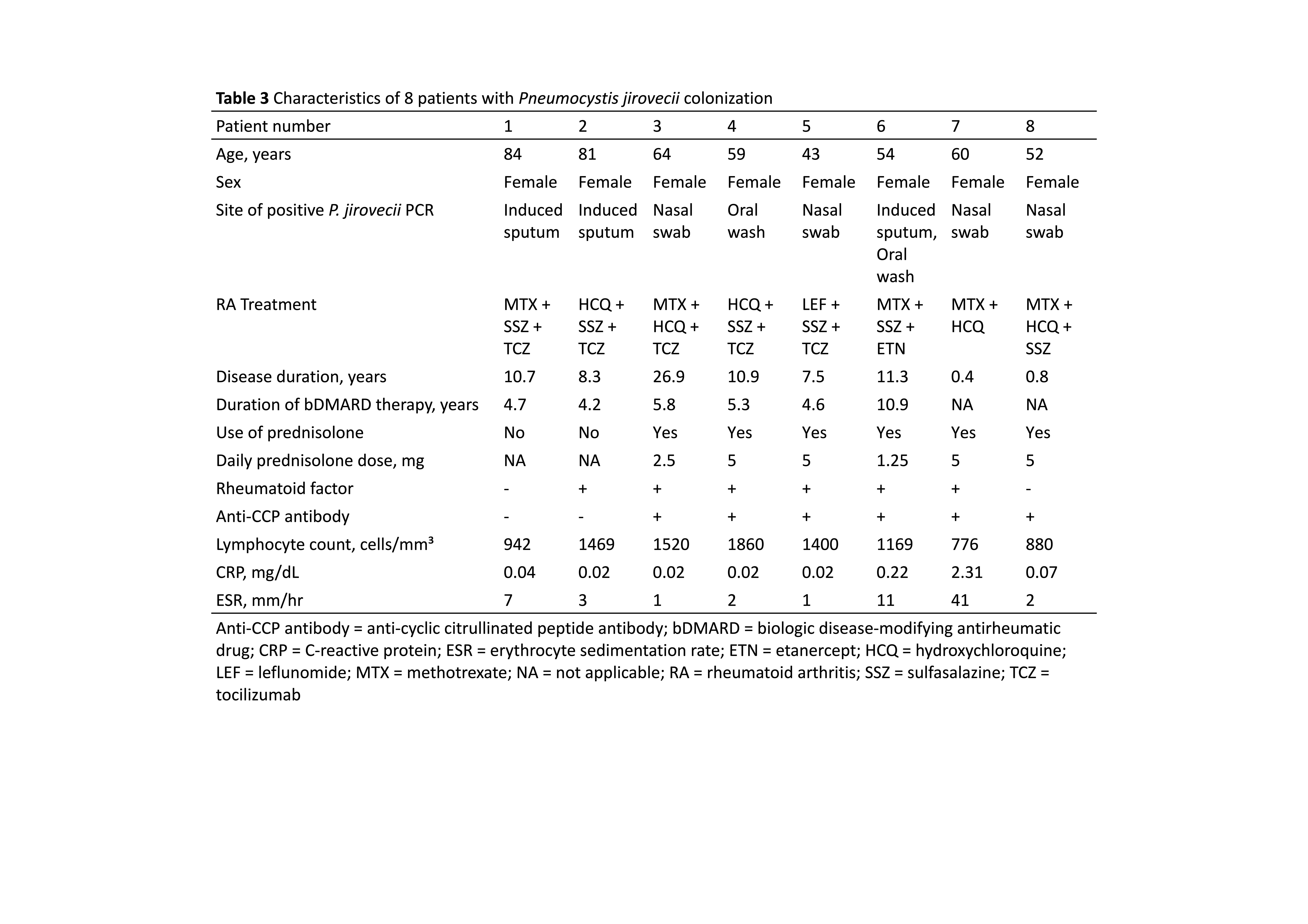
Results: A total of 94 patients with RA were included, and none of these patients received chemoprophylaxis for PCP.P. jiroveciicolonization was found in 8 (8.5%) patients, and positiveP. jiroveciiPCR was detected in 3 (3.2%) specimens of induced sputum, 4 (4.2%) in nasal swabs, and 2 (2.1%) in oral washes. One patient exhibited positiveP.jirovecii PCR in both induced sputum and oral wash samples. The mean (standard deviation, SD) age was 63.1 (11.6) years, and 73 (77.7%) patients were female. There were 39 (41.5%) patients treated with TNF inhibitors, 25 (26.6%) with tocilizumab, and 30 (31.9%) with csDMARDs only. In the TNF inhibitors group, 21 (53.8%) patients were treated with etanercept, 11 (28.2%) with adalimumab, 6 (15.4%) with golimumab, and 1 (2.6%) with certolizumab. One (2.6%) patient in the TNF inhibitors group hadP. jiroveciicolonization, 5 (20.0%) patients in the tocilizumab group, and 2 (6.7%) patients in the csDMARDs group. The chi-square test revealed a significant difference among TNF inhibitors, tocilizumab, and csDMARDs groups (chi-square = 6.141;P= 0.046). Patients withP. jiroveciicolonization had a higher rate of tocilizumab use (62.5% vs. 23.3%,P= 0.029), a numerically higher rate of prednisolone use (75.0% vs. 23.3%,P= 0.154), and a numerically lower lymphocyte count (1252 vs. 1685 cell/mm³;P= 0.053)than patients withoutP. jiroveciicolonization (Table 1). In the backward multivariable logistic regression analysis, tocilizumab (OR 11.658; 95% CI 2.037-66.718;P= 0.006) and prednisolone (OR 8.255; 95% CI 1.238-55.059;P= 0.029) were independent risk factors ofP. jiroveciicolonization (Table 2). The detailed characteristics of the 8 patients withP. jiroveciicolonization were outlined in Table 3, and no PCP was observed during the study period.
Conclusion: We demonstrated the prevalence ofP. jiroveciicolonization in RA by the combined sampling of the induced sputum, nasal swab, and oral wash. Tocilizumab and prednisolone might be associated witha higher risk ofP. jiroveciicolonization in patients with RA.
Y. Huang: None; C. Chuang: None; J. Kao: None; Y. Lin: None; J. Chen: None; C. Cheng: None; C. Lu: None; Y. Kuo: None; C. Shen: None; C. Liu: None; K. Li: None; S. Hsieh: None; J. Chien: None; P. Hsueh: None.
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are susceptible toPneumocystis jiroveciicolonization and prone to develop life-threateningPneumocystispneumonia (PCP). An increased risk ofP. jiroveciicolonization and PCP was found in RA patients treated with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors. However, the impact of other biologics onP. jiroveciicolonization remains unrecognized. This study aims to investigate the prevalence and risk factors ofP. jiroveciicolonization in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with TNF inhibitors and tocilizumab.
Methods: We enrolled the patients with RA, who were treated with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs), TNF inhibitors, and tocilizumab between March 2022 to February 2023. The patients with acute respiratory symptoms were excluded.P. jiroveciipolymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays of induced sputum, nasal swab, and oral wash were performed. Factors associated withP. jiroveciicolonization were evaluated.
Results: A total of 94 patients with RA were included, and none of these patients received chemoprophylaxis for PCP.P. jiroveciicolonization was found in 8 (8.5%) patients, and positiveP. jiroveciiPCR was detected in 3 (3.2%) specimens of induced sputum, 4 (4.2%) in nasal swabs, and 2 (2.1%) in oral washes. One patient exhibited positiveP.jirovecii PCR in both induced sputum and oral wash samples. The mean (standard deviation, SD) age was 63.1 (11.6) years, and 73 (77.7%) patients were female. There were 39 (41.5%) patients treated with TNF inhibitors, 25 (26.6%) with tocilizumab, and 30 (31.9%) with csDMARDs only. In the TNF inhibitors group, 21 (53.8%) patients were treated with etanercept, 11 (28.2%) with adalimumab, 6 (15.4%) with golimumab, and 1 (2.6%) with certolizumab. One (2.6%) patient in the TNF inhibitors group hadP. jiroveciicolonization, 5 (20.0%) patients in the tocilizumab group, and 2 (6.7%) patients in the csDMARDs group. The chi-square test revealed a significant difference among TNF inhibitors, tocilizumab, and csDMARDs groups (chi-square = 6.141;P= 0.046). Patients withP. jiroveciicolonization had a higher rate of tocilizumab use (62.5% vs. 23.3%,P= 0.029), a numerically higher rate of prednisolone use (75.0% vs. 23.3%,P= 0.154), and a numerically lower lymphocyte count (1252 vs. 1685 cell/mm³;P= 0.053)than patients withoutP. jiroveciicolonization (Table 1). In the backward multivariable logistic regression analysis, tocilizumab (OR 11.658; 95% CI 2.037-66.718;P= 0.006) and prednisolone (OR 8.255; 95% CI 1.238-55.059;P= 0.029) were independent risk factors ofP. jiroveciicolonization (Table 2). The detailed characteristics of the 8 patients withP. jiroveciicolonization were outlined in Table 3, and no PCP was observed during the study period.
Conclusion: We demonstrated the prevalence ofP. jiroveciicolonization in RA by the combined sampling of the induced sputum, nasal swab, and oral wash. Tocilizumab and prednisolone might be associated witha higher risk ofP. jiroveciicolonization in patients with RA.

Table 1 Baseline demographics of patients

Table 2 Logistic regression analysis for factors associated with Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization

Table 3 Characteristics of 8 patients with Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization
Y. Huang: None; C. Chuang: None; J. Kao: None; Y. Lin: None; J. Chen: None; C. Cheng: None; C. Lu: None; Y. Kuo: None; C. Shen: None; C. Liu: None; K. Li: None; S. Hsieh: None; J. Chien: None; P. Hsueh: None.



