Poster Session C
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Session: (2326–2351) SLE – Treatment Poster III
2345: Paired Kidney Biopsies from the AURORA 2 Study of Voclosporin in Active Lupus Nephritis
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- EY
Ernie Yap, MD (he/him/his)
Aurinia Pharmaceuticals
Long Island City, NY, United StatesDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Samir Parikh1, Salem Almaani2, Arnon Arazi3, Huijuan Song1, Pearlly Yan1, Estela Puchulu-Campanella1, Clint Abner4, Ernie Yap4, Krista Piper4, Robert B. Huizinga5 and Henry Leher4, 1Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, 2Ohio State University Medical Center, Columbus, OH, 3Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Melrose, MA, 4Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc., Edmonton, AB, Canada, 5Reformation Consulting Services, North Saanich, BC, Canada
Background/Purpose: Voclosporin is approved for the treatment of adults with active lupus nephritis. Addition of voclosporin to mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and low-dose glucocorticoids in the Phase 3 global AURORA 1 and AURORA 2 studies led to significantly earlier and greater reductions in proteinuria and an improved estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) slope over time.To characterize the long-term renal impact of voclosporin at the histologic level, we analyzed paired kidney biopsies from a subset of patients in these studies.
Methods: Patients in AURORA 1 had biopsy-proven lupus nephritis, urine protein creatinine ratio (UPCR) ≥1.5 g/g (≥2 g/g for Class V), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) >45 mL/min/1.73 m2. Patients were randomized to voclosporin or control for 1 year in AURORA 1 and continued the same blinded therapy for 2 additional years in AURORA 2; all patients received MMF and low-dose glucocorticoids. A subset of patients had a kidney biopsy prior to screening and a repeat biopsy after approximately 18-months of therapy. Histopathologic grading according to National Institutes of Health indices for lupus nephritis activity and chronicity was conducted by Arkana Laboratories. Efficacy outcomes and measures of renal function over time, including eGFR were assessed.
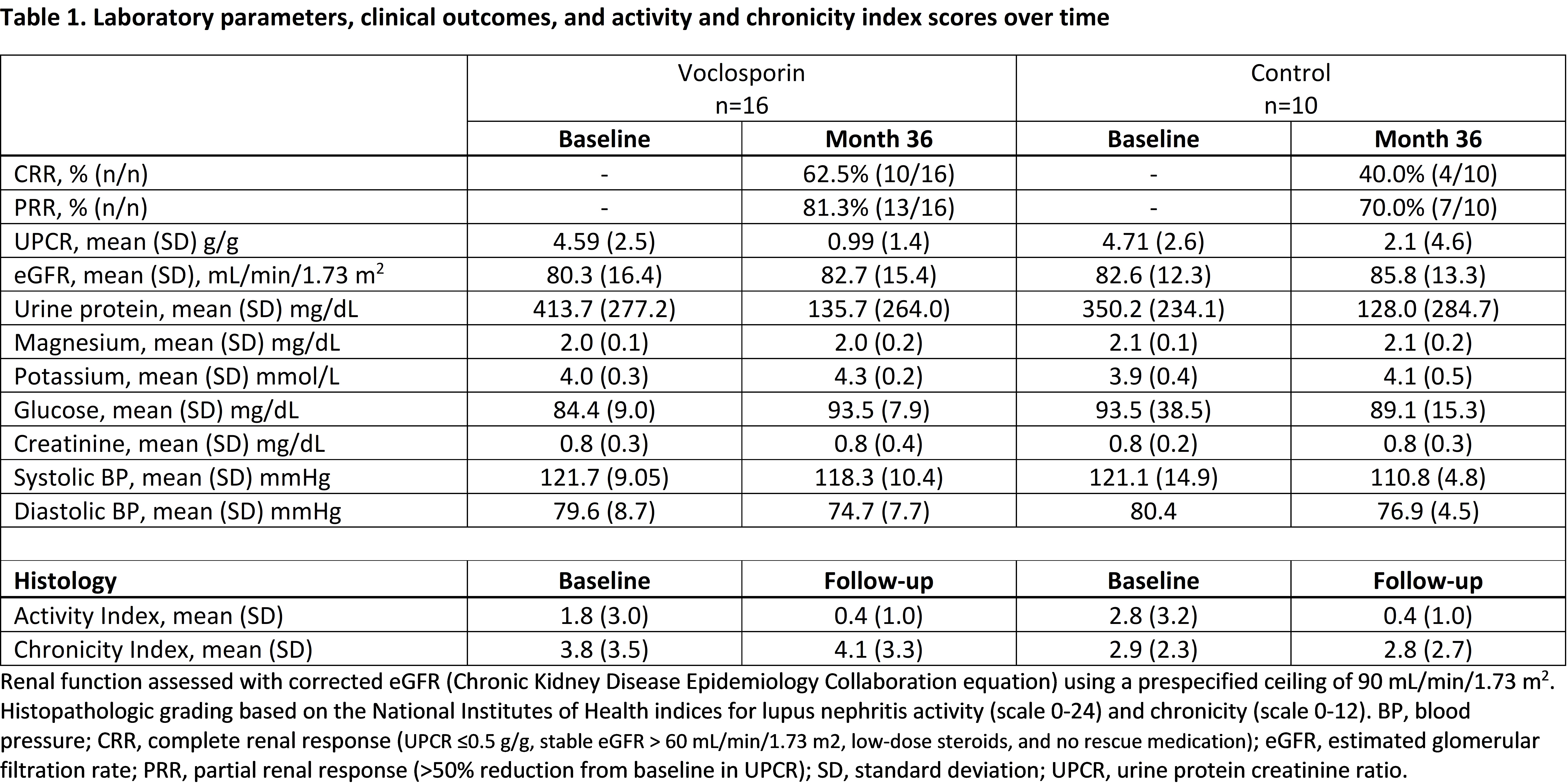
Results: Paired biopsy samples were collected from sixteen patients in the voclosporin arm and ten patients in the control arm. Baseline mean activity scores were similar between arms, with scores improving with treatment in both arms (Table 1). Mean chronicity scores were also similar between arms at baseline and remained stable over time in most patients. Measures of renal function remained stable in both arms over the 3-year follow-up. Voclosporin-treated patients had numerically greater mean reductions from baseline in UPCR year-on-year compared to patients in the control arm, although the difference was not statistically significant. On-going research involving the above patients and others from AURORA 2 using multiplex immunohistochemistry and RNA-sequencing has been performed, and data are currently being analyzed.
Conclusion: As expected, mean activity scores improved in both treatment arms. Importantly, exposure to voclosporin was not associated with chronic injury, with the mean index remaining stable at follow-up. Similar to the overall population, patients treated with voclosporin saw greater reductions in UPCR over 3 years of treatment; safety outcomes from this small subgroup were also consistent with outcomes in AURORA 1. Multiplex immunohistochemistry and sequencing data will further illuminate the cellular and molecular underpinnings of disease and response to treatment.
S. Parikh: Alexion, 2, Aurinia, 2, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, Kezar life sciences, 2; S. Almaani: Amgen, 2, Aurinia, 2, Chemocentryx, 2, Kezar, 2, Otsuka, 2; A. Arazi: None; H. Song: None; P. Yan: None; E. Puchulu-Campanella: None; C. Abner: Aurinia Pharma, 3; E. Yap: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, 3, 11; K. Piper: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc., 3, 11; R. Huizinga: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, 2, 9, 10; H. Leher: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc., 3, 11.
Background/Purpose: Voclosporin is approved for the treatment of adults with active lupus nephritis. Addition of voclosporin to mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and low-dose glucocorticoids in the Phase 3 global AURORA 1 and AURORA 2 studies led to significantly earlier and greater reductions in proteinuria and an improved estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) slope over time.To characterize the long-term renal impact of voclosporin at the histologic level, we analyzed paired kidney biopsies from a subset of patients in these studies.
Methods: Patients in AURORA 1 had biopsy-proven lupus nephritis, urine protein creatinine ratio (UPCR) ≥1.5 g/g (≥2 g/g for Class V), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) >45 mL/min/1.73 m2. Patients were randomized to voclosporin or control for 1 year in AURORA 1 and continued the same blinded therapy for 2 additional years in AURORA 2; all patients received MMF and low-dose glucocorticoids. A subset of patients had a kidney biopsy prior to screening and a repeat biopsy after approximately 18-months of therapy. Histopathologic grading according to National Institutes of Health indices for lupus nephritis activity and chronicity was conducted by Arkana Laboratories. Efficacy outcomes and measures of renal function over time, including eGFR were assessed.
Results: Paired biopsy samples were collected from sixteen patients in the voclosporin arm and ten patients in the control arm. Baseline mean activity scores were similar between arms, with scores improving with treatment in both arms (Table 1). Mean chronicity scores were also similar between arms at baseline and remained stable over time in most patients. Measures of renal function remained stable in both arms over the 3-year follow-up. Voclosporin-treated patients had numerically greater mean reductions from baseline in UPCR year-on-year compared to patients in the control arm, although the difference was not statistically significant. On-going research involving the above patients and others from AURORA 2 using multiplex immunohistochemistry and RNA-sequencing has been performed, and data are currently being analyzed.
Conclusion: As expected, mean activity scores improved in both treatment arms. Importantly, exposure to voclosporin was not associated with chronic injury, with the mean index remaining stable at follow-up. Similar to the overall population, patients treated with voclosporin saw greater reductions in UPCR over 3 years of treatment; safety outcomes from this small subgroup were also consistent with outcomes in AURORA 1. Multiplex immunohistochemistry and sequencing data will further illuminate the cellular and molecular underpinnings of disease and response to treatment.

S. Parikh: Alexion, 2, Aurinia, 2, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, Kezar life sciences, 2; S. Almaani: Amgen, 2, Aurinia, 2, Chemocentryx, 2, Kezar, 2, Otsuka, 2; A. Arazi: None; H. Song: None; P. Yan: None; E. Puchulu-Campanella: None; C. Abner: Aurinia Pharma, 3; E. Yap: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, 3, 11; K. Piper: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc., 3, 11; R. Huizinga: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, 2, 9, 10; H. Leher: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc., 3, 11.



