Poster Session C
Sjögren’s syndrome
Session: (2177–2194) Sjögren’s Syndrome – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
2190: Saliclick: A Novel Technology for Minimal Invasive Salivary Gland Biopsy in Suspected Sjögren’s Syndrome
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- TH
Thomas Hügle, MD, PhD, MA
University Hospital Lausanne
Lausanne, SwitzerlandDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Thomas Hügle1, Diana Dan2 and Alexandre Dumusc3, 1Dept. of Rheumatology, University Hospital Lausanne (CHUV) and University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2Dept. of Rheumatology, University Hospital Lausanne (CHUV) and University Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, 3Dept. of Rheumatology, University Hospital Lausanne (CHUV) and University Lausanne, Switzerland, Lausanne, Switzerland
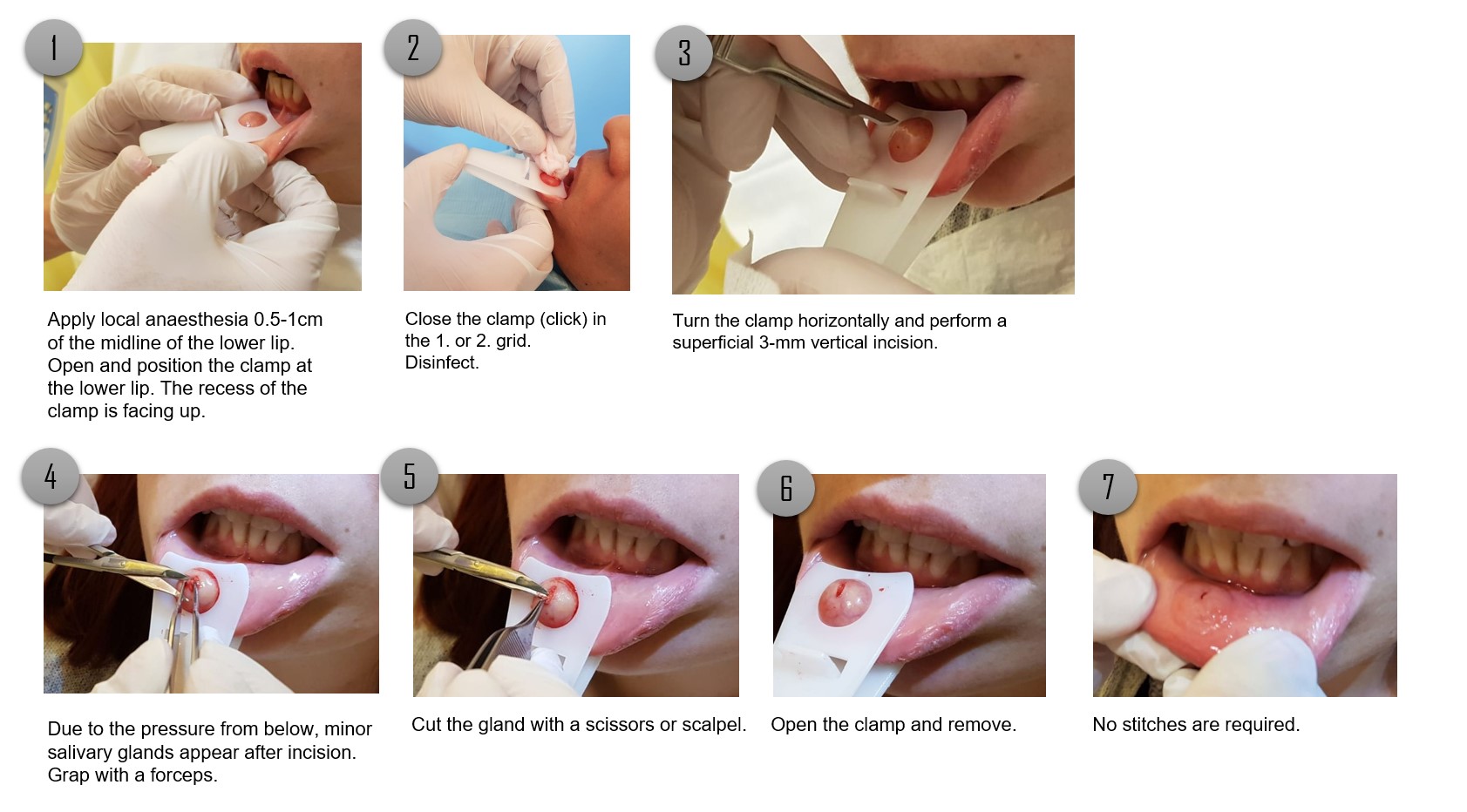
Background/Purpose: Labial minor salivary gland (MSG) biopsy is a major element in the diagnosis of Sjögren´s Syndrome and the exclusion of other pathologies, respectively. Transient local paraesthesia as a complication of MSG biopsy has been described in up to 11%. We recently developed a device in the form of a lip clamp exerting transcutaneous pressure on the salivary glands thus allowing a more superficial incision and less invasive procedure. In this study we report four years experience of MSG using this device in our rheumatology department.
Methods: Retrospective study of 114 MSG biopsies performed with the use of Saliclick (Curmed, Switzerland). For each MSG biopsy we recorded complications, salivary gland surface, intervention time, need of assistance and focus score.
Results: In 106 (95%) out of114 MSG biopsies, representative salivary gland material was obtained. No numbness was recorded. No stitches were needed. In 6 (5.2%) patients, moderate haemorrhage occurred which was controllable by intraoral pressure using a swab. 4 (3.5%) patients suffered from a vaso-vagal reaction. The mean (SD) duration of the intervention was 10.4 (3.5) min. 85% of the interventions could be performed by a rheumatologist without the technical assistance of another person. The mean glandular surface area was 5.9 mm2. A focal lymphocytic sialadenitis was reported in 21 patients (20%), with a focus score >1 for 62% of them.
Conclusion: MSG biopsy using Saliclick is a safe and rapid procedure for the diagnosis in Sjögren's Syndrome without observed numbness occurring in this study. The lack of technical assistance safed resources and the procedure was integrated more quickly into the clinical workflow.
T. Hügle: Atreon SA, 8, Curmed, 9, Eli Lilly, 6, Fresenius Kabi, 2, 5, Galapagos, 6, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 6, Janssen, 6, Merck/MSD, 6, Pfizer, 6; D. Dan: None; A. Dumusc: None.
Background/Purpose: Labial minor salivary gland (MSG) biopsy is a major element in the diagnosis of Sjögren´s Syndrome and the exclusion of other pathologies, respectively. Transient local paraesthesia as a complication of MSG biopsy has been described in up to 11%. We recently developed a device in the form of a lip clamp exerting transcutaneous pressure on the salivary glands thus allowing a more superficial incision and less invasive procedure. In this study we report four years experience of MSG using this device in our rheumatology department.
Methods: Retrospective study of 114 MSG biopsies performed with the use of Saliclick (Curmed, Switzerland). For each MSG biopsy we recorded complications, salivary gland surface, intervention time, need of assistance and focus score.
Results: In 106 (95%) out of114 MSG biopsies, representative salivary gland material was obtained. No numbness was recorded. No stitches were needed. In 6 (5.2%) patients, moderate haemorrhage occurred which was controllable by intraoral pressure using a swab. 4 (3.5%) patients suffered from a vaso-vagal reaction. The mean (SD) duration of the intervention was 10.4 (3.5) min. 85% of the interventions could be performed by a rheumatologist without the technical assistance of another person. The mean glandular surface area was 5.9 mm2. A focal lymphocytic sialadenitis was reported in 21 patients (20%), with a focus score >1 for 62% of them.
Conclusion: MSG biopsy using Saliclick is a safe and rapid procedure for the diagnosis in Sjögren's Syndrome without observed numbness occurring in this study. The lack of technical assistance safed resources and the procedure was integrated more quickly into the clinical workflow.

Figure 1. Step-by-step description of the lLabial minor salivary gland biopsy using the novel device 'Saliclick'.
T. Hügle: Atreon SA, 8, Curmed, 9, Eli Lilly, 6, Fresenius Kabi, 2, 5, Galapagos, 6, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 6, Janssen, 6, Merck/MSD, 6, Pfizer, 6; D. Dan: None; A. Dumusc: None.



