Poster Session B
Periodic fever syndromes, autoinflammatory diseases, Still’s disease and MAS/HLH
Session: (1124–1154) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster II
1130: Interobserver Reliability and Sensitivity to Change of a Composite Ocular Inflammatory Activity Index: UVEDAI
Monday, November 13, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- MD
Marta Domínguez, PhD
Sociedad Española de Reumatología
Madrid, SpainDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Esperanza Pato1, Lara Borrego-Sanz2, Marta Domínguez3, Fernando Alonso4, Fayna Rodríguez-Gonazález5, Marta Tejera-Santana5, María del Mar Esteban-Ortega6, Isabel García-Lozano7, Lucia Martinez-Costa8, Samuel Gonzalez-Ocampo8, Maite Sainz de la Maza9, Aina Moll-Udina9, Zulema Plaza10, Alejandro Fonollosa-Calduch11, Joseba Artaraz11, Teresa Díaz-Valle12, María Gurrea-Almela12, David Diaz-Valle13 and Rosalía Méndez-Fernández13, 1Hospital Clínico San Carlos, Rheumatology, Madrid, Spain, 2Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Ophthalmology, Madrid, Spain, 3Sociedad Española de Reumatología, Madrid, Spain, 4Spanish Society of Rheumatology, Madrid, Spain, 5Hospital Doctor Negrín, Ophthalmology, Gran Canaria, Spain, 6Hospital Infanta Sofia, Madrid, Spain, 7Hospital Infanta Sofia, Ophthalmology, Madrid, Spain, 8Hospital Doctor Peset, Ophthalmology, Valencia, Spain, 9Hospital Clinic of Barcelona, Ophthalmology, Barcelona, Spain, 10Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 11Hospital de Cruces, Ophthalmology, Bilbao, Spain, 12Hospital De Móstoles, Ophthalmology, Madrid, Spain, 13Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Madrid, Spain
Background/Purpose: Standardized and validated outcome measures of disease activity are lacking in the treatment and assessment of uveitis, making it difficult to compare efficacy and response to treatment. In 2014, this working group developed a composite index of ocular inflammatory activity: UVEDAI (1). The index was validated in a subsequent study conducted in 2019. The objective to this study was to determine the interobserver reliability and to demonstrate the sensitivity to change of the UVEDAI index in patients with anterior and non-anterior uveitis who undergo pharmacological treatment.
Methods: The design is an observational, longitudinal, prospective study in 7 Spanish hospitals. Patients over 18 years of age diagnosed with active uveitis were included. A complete baseline visit was performed by two ophthalmologists who determined ocular inflammatory activity with the UVEDAI index. Ophthalmologist 1 made a new visit at 4 weeks to determine the change in the level of uveal inflammatory activity using the UVEDAI index. The interobserver reliability analysis was performed by calculating the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) with the values of the UVEDAI index obtained by ophthalmologist 1 and ophthalmologist 2 in the most inflamed eye at the baseline visit. Sensitivity to change in the UVEDAI index was assessed at 4 weeks from the start of pharmacological treatment by determining the Clinically Relevant Change defined as a change in UVEDAI of 0.8 points between the baseline visit and the 4-week visit.
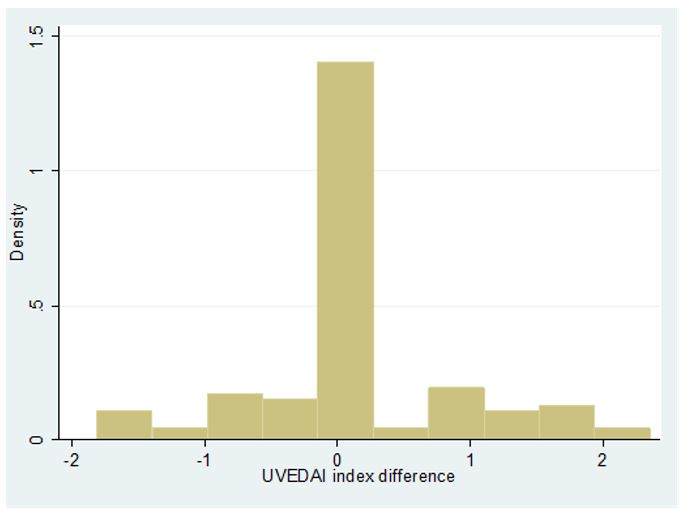
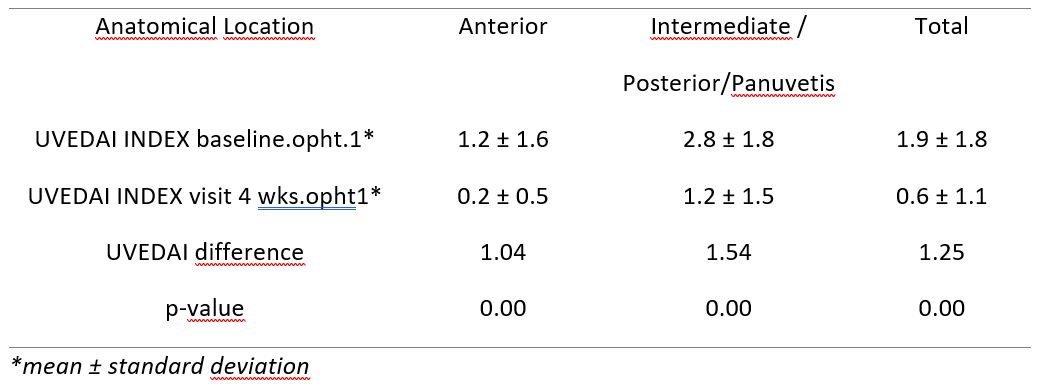
Results: A total of 111 patients were included (54.1% male). The mean age at the time of the visit was 49.9 years. 36.9% of uveitis were idiopathic uveitis and 58.6% were anterior uveitis. The UVEDAI value was calculated from the score obtained in the 7 variables of the index. The mean value recorded in the most inflamed eye at the baseline visit by ophthalmologist 1 was 1.9 (1.2 anterior uveitis and 2.8 intermediate/posterior uveitis). The ICC for the UVEDAI value was 0.9 and when compared the mean UVEDAI values obtained by the two ophthalmologists for the most inflamed eye at the baseline visit no statistically significant differences were found (p-value >0.05), neither for the total sample nor differentiating by anatomical location. As for sensitivity of UVEDAI change, statistically significant differences (p-value=0.00) were found when comparing the mean values of the index measured by ophthalmologist 1 at the baseline visit and at 4 weeks, both in the overall sample and differentiating by anatomic location of uveitis. In all cases, the index value decreased significantly by more than 1 point at the 4-week visit after pharmacological treatment.
Conclusion: The interobserver reliability of the UVEDAI was high in the total sample and in the different variables. Furthermore, the index was sensitive in determining the change in inflammatory activity after treatment in both anterior and intermediate/posterior uveitis. We believe it is an index of activity that could be used both in routine clinical practice and in clinical studies and trials to compare results objectively
1: Pato-Cour E et al. Development of an activity disease score in patients with uveitis (UVEDAI). Rheumatol Int. 2017
E. Pato: None; L. Borrego-Sanz: None; M. Domínguez: None; F. Alonso: None; F. Rodríguez-Gonazález: None; M. Tejera-Santana: None; M. Esteban-Ortega: None; I. García-Lozano: None; L. Martinez-Costa: None; S. Gonzalez-Ocampo: None; M. Sainz de la Maza: None; A. Moll-Udina: None; Z. Plaza: None; A. Fonollosa-Calduch: None; J. Artaraz: None; T. Díaz-Valle: None; M. Gurrea-Almela: None; D. Diaz-Valle: None; R. Méndez-Fernández: None.
Background/Purpose: Standardized and validated outcome measures of disease activity are lacking in the treatment and assessment of uveitis, making it difficult to compare efficacy and response to treatment. In 2014, this working group developed a composite index of ocular inflammatory activity: UVEDAI (1). The index was validated in a subsequent study conducted in 2019. The objective to this study was to determine the interobserver reliability and to demonstrate the sensitivity to change of the UVEDAI index in patients with anterior and non-anterior uveitis who undergo pharmacological treatment.
Methods: The design is an observational, longitudinal, prospective study in 7 Spanish hospitals. Patients over 18 years of age diagnosed with active uveitis were included. A complete baseline visit was performed by two ophthalmologists who determined ocular inflammatory activity with the UVEDAI index. Ophthalmologist 1 made a new visit at 4 weeks to determine the change in the level of uveal inflammatory activity using the UVEDAI index. The interobserver reliability analysis was performed by calculating the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) with the values of the UVEDAI index obtained by ophthalmologist 1 and ophthalmologist 2 in the most inflamed eye at the baseline visit. Sensitivity to change in the UVEDAI index was assessed at 4 weeks from the start of pharmacological treatment by determining the Clinically Relevant Change defined as a change in UVEDAI of 0.8 points between the baseline visit and the 4-week visit.
Results: A total of 111 patients were included (54.1% male). The mean age at the time of the visit was 49.9 years. 36.9% of uveitis were idiopathic uveitis and 58.6% were anterior uveitis. The UVEDAI value was calculated from the score obtained in the 7 variables of the index. The mean value recorded in the most inflamed eye at the baseline visit by ophthalmologist 1 was 1.9 (1.2 anterior uveitis and 2.8 intermediate/posterior uveitis). The ICC for the UVEDAI value was 0.9 and when compared the mean UVEDAI values obtained by the two ophthalmologists for the most inflamed eye at the baseline visit no statistically significant differences were found (p-value >0.05), neither for the total sample nor differentiating by anatomical location. As for sensitivity of UVEDAI change, statistically significant differences (p-value=0.00) were found when comparing the mean values of the index measured by ophthalmologist 1 at the baseline visit and at 4 weeks, both in the overall sample and differentiating by anatomic location of uveitis. In all cases, the index value decreased significantly by more than 1 point at the 4-week visit after pharmacological treatment.
Conclusion: The interobserver reliability of the UVEDAI was high in the total sample and in the different variables. Furthermore, the index was sensitive in determining the change in inflammatory activity after treatment in both anterior and intermediate/posterior uveitis. We believe it is an index of activity that could be used both in routine clinical practice and in clinical studies and trials to compare results objectively
1: Pato-Cour E et al. Development of an activity disease score in patients with uveitis (UVEDAI). Rheumatol Int. 2017

Interobserver Reliability: Differences obtained in the UVEDAI index score by ophthalmologist 1 and 2 at the baseline visit

Sensitive to Change: Mean value and difference in UVEDAI index value measured by ophthalmologist 1 in the active eye at baseline and at 4 weeks
E. Pato: None; L. Borrego-Sanz: None; M. Domínguez: None; F. Alonso: None; F. Rodríguez-Gonazález: None; M. Tejera-Santana: None; M. Esteban-Ortega: None; I. García-Lozano: None; L. Martinez-Costa: None; S. Gonzalez-Ocampo: None; M. Sainz de la Maza: None; A. Moll-Udina: None; Z. Plaza: None; A. Fonollosa-Calduch: None; J. Artaraz: None; T. Díaz-Valle: None; M. Gurrea-Almela: None; D. Diaz-Valle: None; R. Méndez-Fernández: None.



