Poster Session C
Fibrosing rheumatic diseases (scleroderma, MCTD, IgG4-related disease, scleroderma mimics)
Session: (2352–2369) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III: Translational Science
2359: Reversal of the Activation State of Pro-fibrotic CD206 Positive Macrophages by Therapeutic Peptide AUR300 in Systemic Sclerosis
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- RS
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Sandra Lopez1, Bahja Ahmed Abdi1, Linda Lei1, Anas Al-Oweidi1, Claire Macfadyen1, Lydia Nagib1, Sarah Ive1, Anshul Kumar1, Teresa Collins1, Jennifer Cross2, Christopher Denton1, David Abraham1, Clayton Yates3, Charles Garvin4, Henry Lopez4, George Martin5 and Richard Stratton1, 1University College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc., Rockford, MD, 3Tuskegee University, Tuskegee, AL, 4Riptide Bioscience Inc., Valejo, CA, 5Riptide Bioscience Inc., Bethesda, MD
Background/Purpose: A spectrum of macrophage activation is seen in human pathologic conditions; M2-like CD206 positive macrophages are pro-fibrotic and proresolution, while M1-like macrophages are proinflammatory, as identified by polarisation in vitro. CD206 positive macrophages are under study as potential targets for inflammatory fibrotic conditions including systemic sclerosis (SSc). We investigated SSc lesional macrophages by single cell profiling and Akoya Multiplex immunochemistry and evaluated the effects of AUR300, a novel peptide therapeutic that targets M2 macrophages via CD206, the mannose receptor.
Methods: Suction blister fluid-derived cells from lesional skin were profiled by 10X RNAseq matched to AKOYA antibody staining to characterise the tissue resident immune cells, including the CD206 positive macrophages of interest (n=12 SSc patients and controls).Tissue culture modelling with patients' blood monocyte-derived macrophages and disease fibroblasts (n=6 SSc cell lines), as well as bleomycin induced lung fibrosis as a model of organ involvement, were used to determine efficacy and mechanism of action of the therapeutic AUR300 peptide.Soluble CD206 (sCD206) (n=140 SSc and n=80 healthy control (HC) plasma samples) and cellular CD206 (n=17 SSc, n=9 HC macrophage lines) were investigated as potential biomarkers of SSc disease activity.
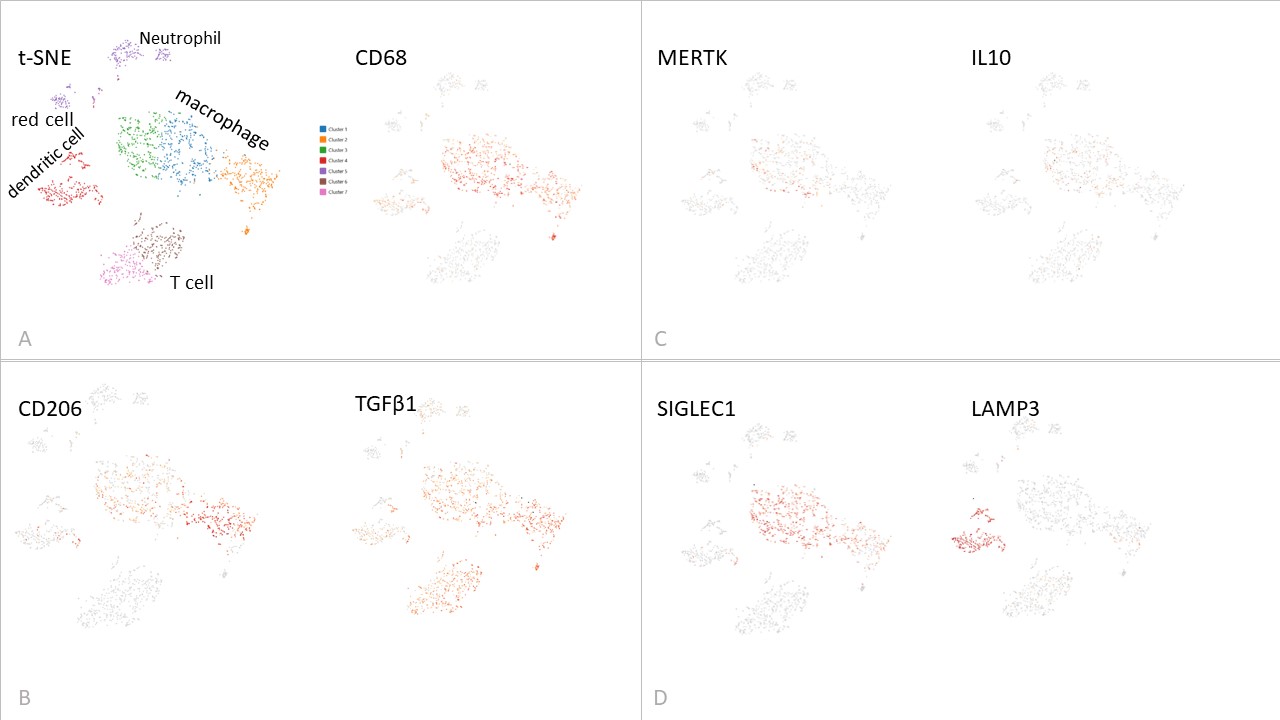
Results: CD206 positive macrophages were found in a spectrum of activation states varying from MERTK high CD206 low IL10 expressing regulatory cells, to CD206 high MERTK negative TGFβ expressing pathogenic cells (Figure 1) implicated in cross talk with fibroblasts, in the affected tissue and model systems. Exposure to disease microenvironments enhanced CD206 levels and triggered IL-6 release, reversed by the therapeutic AUR300 peptide (p < 0.05 for CD206, p< 0.0013 for IL-6, p< 0.018 for gel contraction, for effect of 10 µM AUR300) (Figure 2), which also attenuated inflammation and fibrosis in the bleomycin lung fibrosis model.Cross-talk with disease fibroblasts involved cytokines (IL-6, TSP-1) and growth factors (TGFβ and PDGF-BB) acting in concert. CD206 was elevated in plasma (HC 552±25, lcSSc 521±32, dcSSc 645±32, sCD206 pg/ml mean±SEM, P< 0.026 for dcSSc), tissue fluid (HC 31±3, SSc 48±6, pg/ml P< 0.041) and cells (HC 628, 485-729, SSc 663, 294-1932, median, range, fluorescence, P NS) as a biomarker, linked to severe resistant disease (highest in anti-Scl70 group).
Conclusion: In disease tissue, CD206 positive macrophages represent a spectrum of activation states, from pro-resolving MERTK IL-10 expressing cells, to pathogenic cells releasing profibrotic cytokines and growth factors in activating microenvironments. AUR300 reverses the activation state in SSc cell-based and murine in vivo models and represents a potential therapeutic for patients with strong CD206 positive signatures.
.jpg)
S. Lopez: None; B. Ahmed Abdi: None; L. Lei: None; A. Al-Oweidi: None; C. Macfadyen: None; L. Nagib: None; S. Ive: None; A. Kumar: None; T. Collins: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc., 3; J. Cross: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc., 3; C. Denton: AbbVie, 2, Acceleron, 2, Arxx Therapeutics, 5, Bayer, 2, Boehringer-Ingelheim, 2, 6, Corbus, 2, 6, CSL Behring, 2, 5, GlaxoSmithKline, 2, 5, Horizon Therapeutics, 2, Inventiva, 2, 5, Janssen, 6, Roche, 2, Sanofi, 2, Servier, 5; D. Abraham: None; C. Yates: Riptide Bioscience Inc., 4; C. Garvin: Riptide Bioscience Inc., 4; H. Lopez: Riptide Bioscience Inc., 4; G. Martin: Riptide Bioscience Inc., 4; R. Stratton: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc., 5, Riptide Bioscience Inc., 5.
Background/Purpose: A spectrum of macrophage activation is seen in human pathologic conditions; M2-like CD206 positive macrophages are pro-fibrotic and proresolution, while M1-like macrophages are proinflammatory, as identified by polarisation in vitro. CD206 positive macrophages are under study as potential targets for inflammatory fibrotic conditions including systemic sclerosis (SSc). We investigated SSc lesional macrophages by single cell profiling and Akoya Multiplex immunochemistry and evaluated the effects of AUR300, a novel peptide therapeutic that targets M2 macrophages via CD206, the mannose receptor.
Methods: Suction blister fluid-derived cells from lesional skin were profiled by 10X RNAseq matched to AKOYA antibody staining to characterise the tissue resident immune cells, including the CD206 positive macrophages of interest (n=12 SSc patients and controls).Tissue culture modelling with patients' blood monocyte-derived macrophages and disease fibroblasts (n=6 SSc cell lines), as well as bleomycin induced lung fibrosis as a model of organ involvement, were used to determine efficacy and mechanism of action of the therapeutic AUR300 peptide.Soluble CD206 (sCD206) (n=140 SSc and n=80 healthy control (HC) plasma samples) and cellular CD206 (n=17 SSc, n=9 HC macrophage lines) were investigated as potential biomarkers of SSc disease activity.
Results: CD206 positive macrophages were found in a spectrum of activation states varying from MERTK high CD206 low IL10 expressing regulatory cells, to CD206 high MERTK negative TGFβ expressing pathogenic cells (Figure 1) implicated in cross talk with fibroblasts, in the affected tissue and model systems. Exposure to disease microenvironments enhanced CD206 levels and triggered IL-6 release, reversed by the therapeutic AUR300 peptide (p < 0.05 for CD206, p< 0.0013 for IL-6, p< 0.018 for gel contraction, for effect of 10 µM AUR300) (Figure 2), which also attenuated inflammation and fibrosis in the bleomycin lung fibrosis model.Cross-talk with disease fibroblasts involved cytokines (IL-6, TSP-1) and growth factors (TGFβ and PDGF-BB) acting in concert. CD206 was elevated in plasma (HC 552±25, lcSSc 521±32, dcSSc 645±32, sCD206 pg/ml mean±SEM, P< 0.026 for dcSSc), tissue fluid (HC 31±3, SSc 48±6, pg/ml P< 0.041) and cells (HC 628, 485-729, SSc 663, 294-1932, median, range, fluorescence, P NS) as a biomarker, linked to severe resistant disease (highest in anti-Scl70 group).
Conclusion: In disease tissue, CD206 positive macrophages represent a spectrum of activation states, from pro-resolving MERTK IL-10 expressing cells, to pathogenic cells releasing profibrotic cytokines and growth factors in activating microenvironments. AUR300 reverses the activation state in SSc cell-based and murine in vivo models and represents a potential therapeutic for patients with strong CD206 positive signatures.

Figure 1 Single cell RNAseq of blister fluid derived cells from anti-Scl70 positive SSc patient. (A) Tissue derived immune cell populations and pan-macrophage marker CD68. (B) Pro-fibrotic CD206 cells. (C) Possible regulatory macrophages expressing MERTK and IL10. (D) Distinct tissue macrophage (SIGLEC1) and dendritic cell (LAMP3) cell populations.
.jpg)
Figure 2 Effect of AUR300 on SSc macrophage activity in tissue culture models systems. (A) SSc blood monocyte-derived macrophage cultures were activated by stimulation with BzATP (0.1mM) with or without addition of AUR300 (10µM) which supressed the induction of IL-6 release. (B) In SSc macrophage-fibroblast co-cultures, macrophage induced fibroblast gel contraction was suppressed by the AUR300 compound (10µM). (AUR=AUR300 10µM, F= SSc fibroblasts, M=SSc macrophages,).
S. Lopez: None; B. Ahmed Abdi: None; L. Lei: None; A. Al-Oweidi: None; C. Macfadyen: None; L. Nagib: None; S. Ive: None; A. Kumar: None; T. Collins: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc., 3; J. Cross: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc., 3; C. Denton: AbbVie, 2, Acceleron, 2, Arxx Therapeutics, 5, Bayer, 2, Boehringer-Ingelheim, 2, 6, Corbus, 2, 6, CSL Behring, 2, 5, GlaxoSmithKline, 2, 5, Horizon Therapeutics, 2, Inventiva, 2, 5, Janssen, 6, Roche, 2, Sanofi, 2, Servier, 5; D. Abraham: None; C. Yates: Riptide Bioscience Inc., 4; C. Garvin: Riptide Bioscience Inc., 4; H. Lopez: Riptide Bioscience Inc., 4; G. Martin: Riptide Bioscience Inc., 4; R. Stratton: Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc., 5, Riptide Bioscience Inc., 5.



