Poster Session C
Vasculitis
Session: (2370–2386) Vasculitis – ANCA-Associated Poster III: Biomarkers & Renal Outcomes
2375: Clinical Characteristics of ANCA-associated Vasculitis with High Levels of Serum Interleukin 7
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- SF
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Shoichi Fukui1, Haruna Matsuo2, Kanako Kojima3, Shota Kurushima1, Tohru Michitsuji4, Yoshika Tsuji5, Toshimasa Shimizu3, Masataka Umeda3, Remi Sumiyoshi5, Takashi Igawa1, Tomohiro Koga5, Shin-ya Kawashiri1, Naoki Iwamoto1, Tomoki Origuchi1 and Atsushi Kawakami1, 1Nagasaki University, Nagasaki, Japan, 2Nagasaki University, Nagasaki City, Japan, 3Department of Immunology and Rheumatology, Nagasaki University Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Nagasaki, Japan, 4Department of Immunology and Rheumatology, Division of Advanced Preventive Medical Sciences, Nagasaki University Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Nagasaki, Japan, 5Department of Immunology and Rheumatology, Division of Advanced Preventive Medical Sciences, Nagasaki University, Nagasaki, Japan
Background/Purpose: Interleukin 7 (IL-7) is a hematopoietic growth factor produced by stromal cells in the bone marrow and thymus, which is indispensable in maintaining immune cells. The transcriptome analysis using CD8 positive T cells demonstrated genes involved in the IL-7 receptor pathway were the poor prognostic factor in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) (McKinney EF, Nat Med 2010;16:586–91). However, the clinical utility of the serum IL-7 levels in AAV is unknown. We aimed to elucidate the clinical characteristics of patients with AAV with high serum IL-7 levels.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 60 patients newly diagnosed with AAV (granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA)) from March 2010 to April 2022 with preserved sera. We collected medical records from baseline variables at diagnosis, including clinical symptoms, laboratory data, treatments, and outcomes. Multiplex cytokine and chemokine bead assays were performed using preserved serum supernatants. Serum samples from 101 healthy donors were used to define the normal serum IL-7 levels. We compared clinical indices between the patients with and without high levels of IL-7 defined by the median levels of serum IL-7.
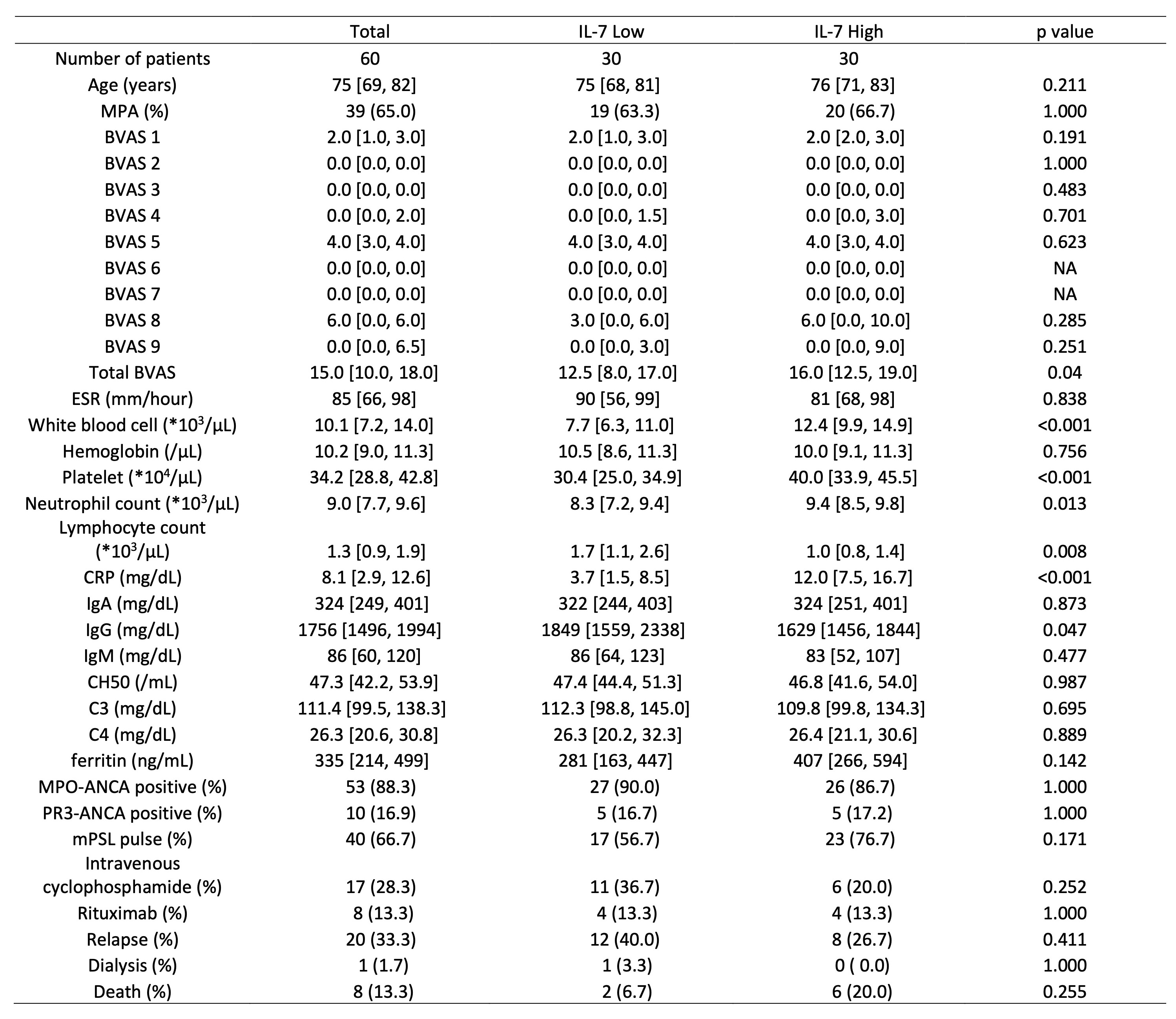
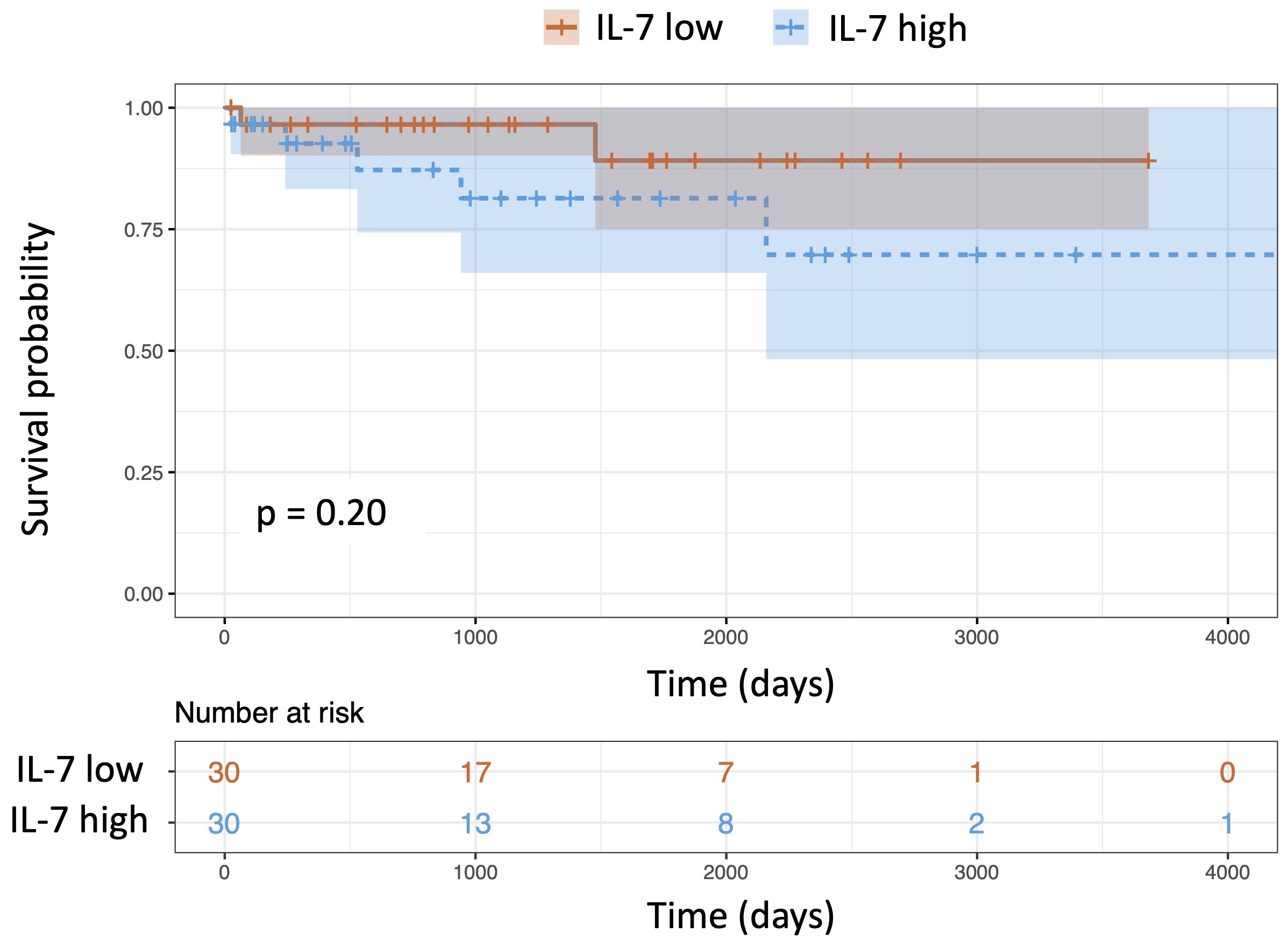
Results: The median serum levels of IL-7 were 8.3pg/mL (IQR: 5.3pg/mL - 15.1pg/mL) and 22.4pg/mL (IQR: 11.9pg/mL - 46.6pg/mL) in healthy donors and patients with AAV, respectively. The median levels of IL-7 (22.4pg/mL) divided the patients with AAV into two groups (30 patients for each group). The IL-7 high group had significantly higher total Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS), higher white blood cell count, higher neutrophil count, higher platelet count, higher CRP level, lower lymphocyte count, and lower IgG levels compared to the IL-7 low group (Table). The serum levels of IL-7 correlated with the total BVAS score significantly (ρ=0.28 (Spearman's rank correlation coefficient), p=0.028). No significant differences were shown in the type of ANCA (MPO-ANCA or PR3-ANCA) and the diseases (GPA or MPA). There were no differences in the treatments (initial prednisolone dose, methylprednisolone pulse therapy, intravenous cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) and the prognosis (relapse and death). The log-rank test demonstrated no significant differences in the survival rate (p=0.20, Figure).
Conclusion: The high serum levels of IL-7 at diagnosis demonstrated the high disease activity and distinct character with higher white blood cell count, platelet count, and CRP levels in AAV.
S. Fukui: None; H. Matsuo: None; K. Kojima: None; S. Kurushima: None; T. Michitsuji: None; Y. Tsuji: None; T. Shimizu: None; M. Umeda: None; R. Sumiyoshi: None; T. Igawa: None; T. Koga: None; S. Kawashiri: None; N. Iwamoto: None; T. Origuchi: None; A. Kawakami: None.
Background/Purpose: Interleukin 7 (IL-7) is a hematopoietic growth factor produced by stromal cells in the bone marrow and thymus, which is indispensable in maintaining immune cells. The transcriptome analysis using CD8 positive T cells demonstrated genes involved in the IL-7 receptor pathway were the poor prognostic factor in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) (McKinney EF, Nat Med 2010;16:586–91). However, the clinical utility of the serum IL-7 levels in AAV is unknown. We aimed to elucidate the clinical characteristics of patients with AAV with high serum IL-7 levels.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 60 patients newly diagnosed with AAV (granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA)) from March 2010 to April 2022 with preserved sera. We collected medical records from baseline variables at diagnosis, including clinical symptoms, laboratory data, treatments, and outcomes. Multiplex cytokine and chemokine bead assays were performed using preserved serum supernatants. Serum samples from 101 healthy donors were used to define the normal serum IL-7 levels. We compared clinical indices between the patients with and without high levels of IL-7 defined by the median levels of serum IL-7.
Results: The median serum levels of IL-7 were 8.3pg/mL (IQR: 5.3pg/mL - 15.1pg/mL) and 22.4pg/mL (IQR: 11.9pg/mL - 46.6pg/mL) in healthy donors and patients with AAV, respectively. The median levels of IL-7 (22.4pg/mL) divided the patients with AAV into two groups (30 patients for each group). The IL-7 high group had significantly higher total Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS), higher white blood cell count, higher neutrophil count, higher platelet count, higher CRP level, lower lymphocyte count, and lower IgG levels compared to the IL-7 low group (Table). The serum levels of IL-7 correlated with the total BVAS score significantly (ρ=0.28 (Spearman's rank correlation coefficient), p=0.028). No significant differences were shown in the type of ANCA (MPO-ANCA or PR3-ANCA) and the diseases (GPA or MPA). There were no differences in the treatments (initial prednisolone dose, methylprednisolone pulse therapy, intravenous cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) and the prognosis (relapse and death). The log-rank test demonstrated no significant differences in the survival rate (p=0.20, Figure).
Conclusion: The high serum levels of IL-7 at diagnosis demonstrated the high disease activity and distinct character with higher white blood cell count, platelet count, and CRP levels in AAV.

Table: Clinical characteristics of AAV with low and high levels of serum IL-7

Figure: Survival provability of AAV with low and high levels of serum IL-7
S. Fukui: None; H. Matsuo: None; K. Kojima: None; S. Kurushima: None; T. Michitsuji: None; Y. Tsuji: None; T. Shimizu: None; M. Umeda: None; R. Sumiyoshi: None; T. Igawa: None; T. Koga: None; S. Kawashiri: None; N. Iwamoto: None; T. Origuchi: None; A. Kawakami: None.



