Poster Session B
Periodic fever syndromes, autoinflammatory diseases, Still’s disease and MAS/HLH
Session: (1124–1154) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster II
1154: Clinical Presentation of IgG4-Related Disease. Single Referral Hospital Experience and Literature Review
Monday, November 13, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- FL
Fernando López-Gutierrez, PhD
Rheumatology, Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla
Santander, SpainDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Fernando López1, Javier Loricera2 and Ricardo Blanco3, 1Rheumatology, Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, Santander, Spain, 2Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, Santander, Spain, 3Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, IDIVAL, Santander, Spain
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an inflammatory and fibrosing entity with very heterogeneous clinical manifestations. It was recognized as a new disease entity only 12 years ago. Its pathogenesis remains unknown, clinical features are heterogeneous and unspecific, and recently released classification criteria are invaluable in early recognition of the disease. Therefore, regrettably IgG4 related disease continues underdiagnosed. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical characteristics of patients diagnosed with IgG4-RD in a single University Hospital as well as to compare it with other large series.
Methods: Study of patients from a referral hospital and literature review of cases diagnosed with IgG4-RD. Diagnosis was made accordingly to these criteria: a) Okazaki; b) Umehara; c) ACR/EULAR 2020; and/or d) clinical, laboratory and imaging suggestive findings (ref. 1-3). For the literature review, we searched PubMed and the Cochrane library from its inception until 30 April 2023, selecting those series with the largest number of patients
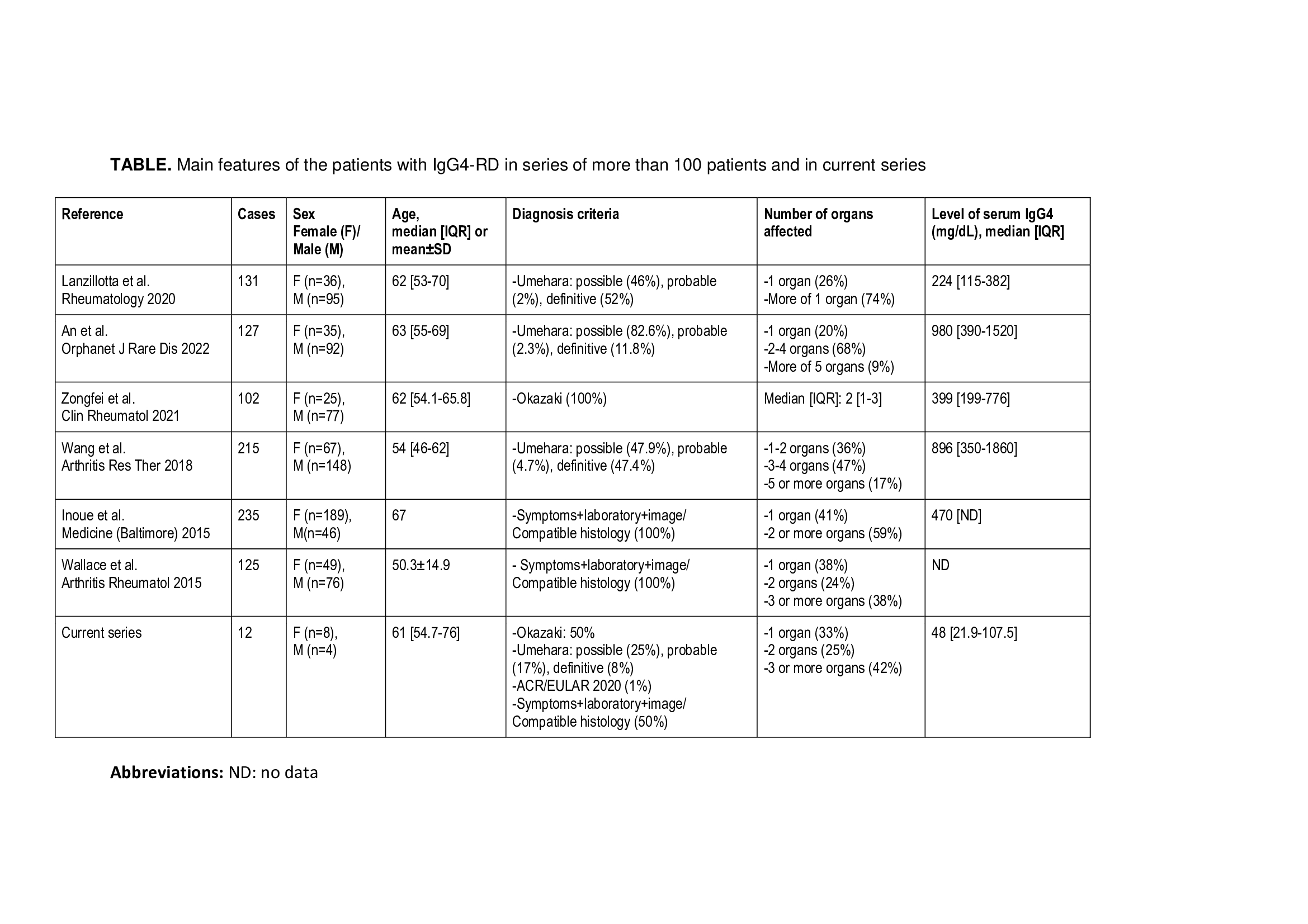
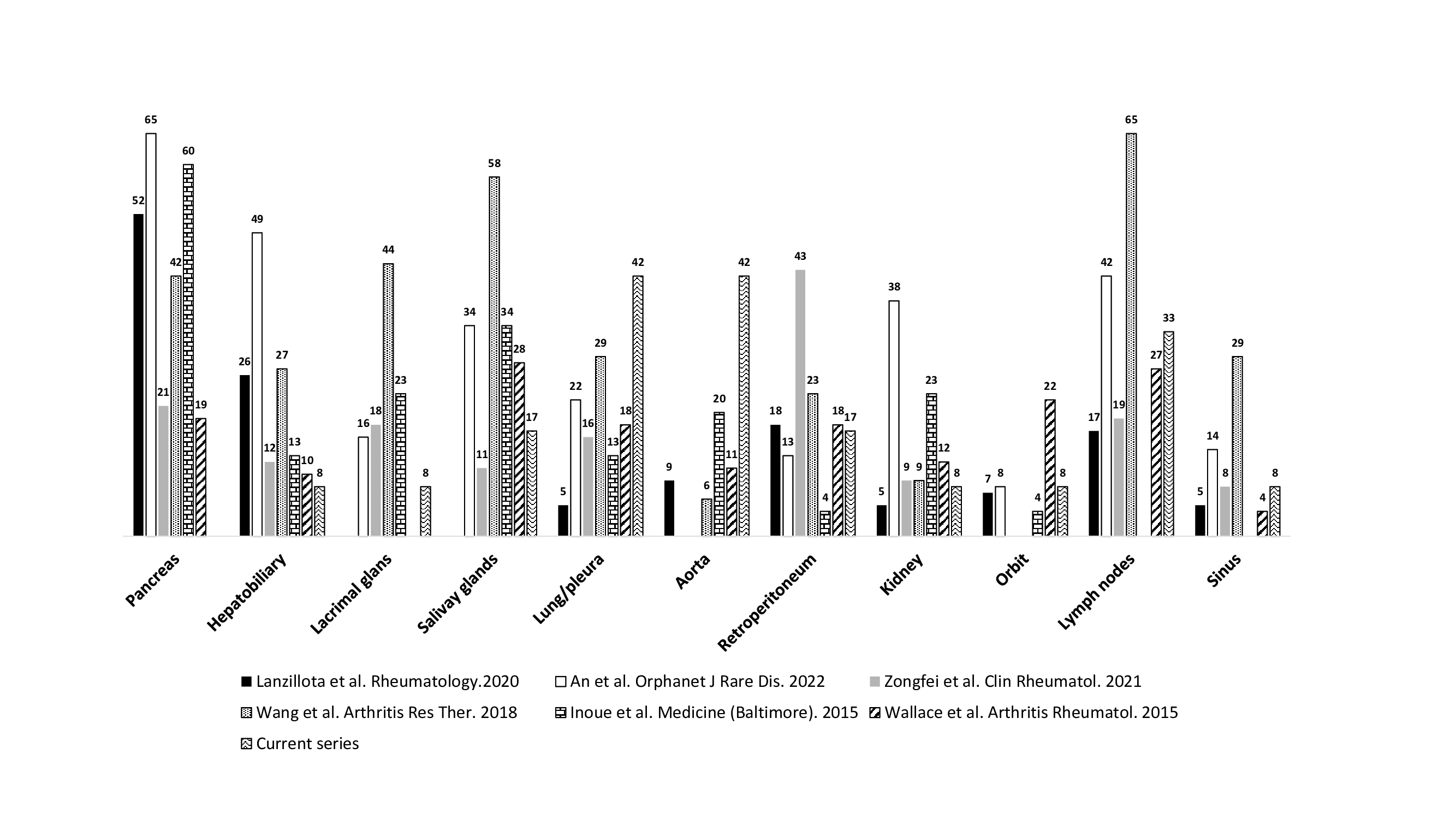
Results: We include 12 patients (8 females/4 males) (mean±SD age; 62.4±15.5 years) diagnosed with IgG4-RD. The organs affected at diagnosis were: aorta (n=5), pleura/lung (n=5), lymph nodes (n=4), salivary glands (n=2), retroperitoneum (n=2), pericardium (n=2), lacrimal glands (n=1), bile duct (n=1), kidney (n=1), orbit (n=1), subglottis (n=1), mesentery (n=1), maxillary sinuses (n=1). IgG4 values were increased in 2 (17%) patients (median [IQR]; 250.5 [201.0-300.1] mg/dL) (normal value < 135 mg/dL). Blood plasmablasts were increased in 8 (67%) patients (median; 808 [767-1152] cells/mL) (normal values < 653 cells/mL). In the literature review, 6 series of more than 100 patients each were selected. The main data from the different series are listed in table. The figure shows the most frequently affected organs in the different series. The pancreas was one of the most frequently involved. In contrast, in our series, aortic involvement and lung/pleura were the most frequent.
Conclusion: IgG4-RD is a very heterogeneous disease with involvement of virtually every organ of the anatomy, usually presenting with involvement of more than one organ. Despite the name of the entity, serum IgG4 is not always elevated.
References:
F. López: None; J. Loricera: None; R. Blanco: AbbVie, 5, 6, Amgen, 6, AstraZeneca, 2, BMS, 6, Eli Lilly, 6, Galapagos, 2, 6, Janssen, 2, 6, MSD, 6, Novartis, 2, 6, Pfizer, 2, 6, Roche, 5, 6, Sanofi, 6.
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an inflammatory and fibrosing entity with very heterogeneous clinical manifestations. It was recognized as a new disease entity only 12 years ago. Its pathogenesis remains unknown, clinical features are heterogeneous and unspecific, and recently released classification criteria are invaluable in early recognition of the disease. Therefore, regrettably IgG4 related disease continues underdiagnosed. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical characteristics of patients diagnosed with IgG4-RD in a single University Hospital as well as to compare it with other large series.
Methods: Study of patients from a referral hospital and literature review of cases diagnosed with IgG4-RD. Diagnosis was made accordingly to these criteria: a) Okazaki; b) Umehara; c) ACR/EULAR 2020; and/or d) clinical, laboratory and imaging suggestive findings (ref. 1-3). For the literature review, we searched PubMed and the Cochrane library from its inception until 30 April 2023, selecting those series with the largest number of patients
Results: We include 12 patients (8 females/4 males) (mean±SD age; 62.4±15.5 years) diagnosed with IgG4-RD. The organs affected at diagnosis were: aorta (n=5), pleura/lung (n=5), lymph nodes (n=4), salivary glands (n=2), retroperitoneum (n=2), pericardium (n=2), lacrimal glands (n=1), bile duct (n=1), kidney (n=1), orbit (n=1), subglottis (n=1), mesentery (n=1), maxillary sinuses (n=1). IgG4 values were increased in 2 (17%) patients (median [IQR]; 250.5 [201.0-300.1] mg/dL) (normal value < 135 mg/dL). Blood plasmablasts were increased in 8 (67%) patients (median; 808 [767-1152] cells/mL) (normal values < 653 cells/mL). In the literature review, 6 series of more than 100 patients each were selected. The main data from the different series are listed in table. The figure shows the most frequently affected organs in the different series. The pancreas was one of the most frequently involved. In contrast, in our series, aortic involvement and lung/pleura were the most frequent.
Conclusion: IgG4-RD is a very heterogeneous disease with involvement of virtually every organ of the anatomy, usually presenting with involvement of more than one organ. Despite the name of the entity, serum IgG4 is not always elevated.
References:
- Okazaki K et al. Int J Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22690221
- Umehara H, et al. Mod Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 21881964
- Wallace ZS et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31793250

Main features of the patients with IgG4-RD in series of more than 100 patients and in current series

F. López: None; J. Loricera: None; R. Blanco: AbbVie, 5, 6, Amgen, 6, AstraZeneca, 2, BMS, 6, Eli Lilly, 6, Galapagos, 2, 6, Janssen, 2, 6, MSD, 6, Novartis, 2, 6, Pfizer, 2, 6, Roche, 5, 6, Sanofi, 6.



