Poster Session B
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (1264–1307) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
1273: Long-term Follow-up of Treated-to-target RA and UA: Results of the BeSt and IMPROVED Studies
Monday, November 13, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- IN
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Sascha Heckert1, Johanna Maria Maassen1, Isabell Nevins2, F. Fodili3, Margreet Steup-Beekman4, Thomas Huizinga1, Sytske Anne Bergstra1 and CF Allaart1, 1Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands, 2Leiden University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 3Stichting ReumaZorg ZWN, Roosendaal, Netherlands, 4Leiden University Medical Center, Den Haag, Netherlands
Background/Purpose: In 2 trials with an original follow-up of 5-10 years, patients with early arthritis were treated to target, resulting in low disease activity or remission in the majority of patients and limited radiographic progression. We invited former participants for a long-term follow-up ('RECALL') visit.
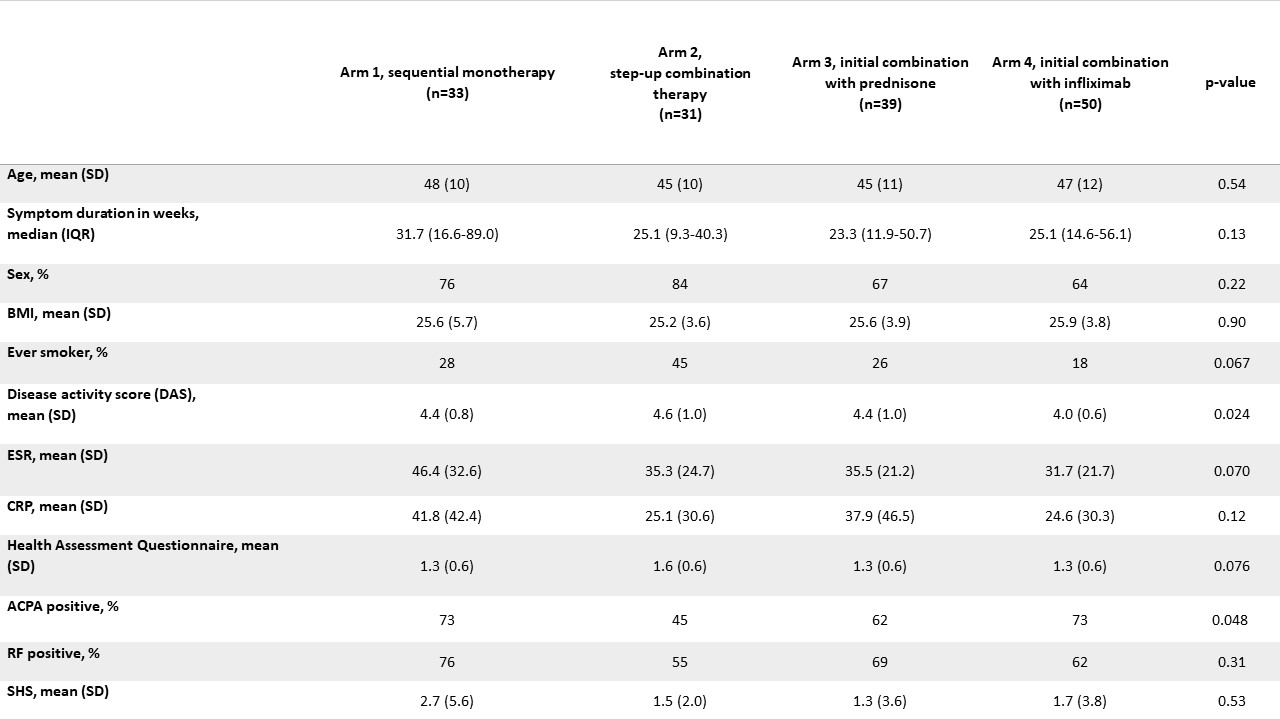
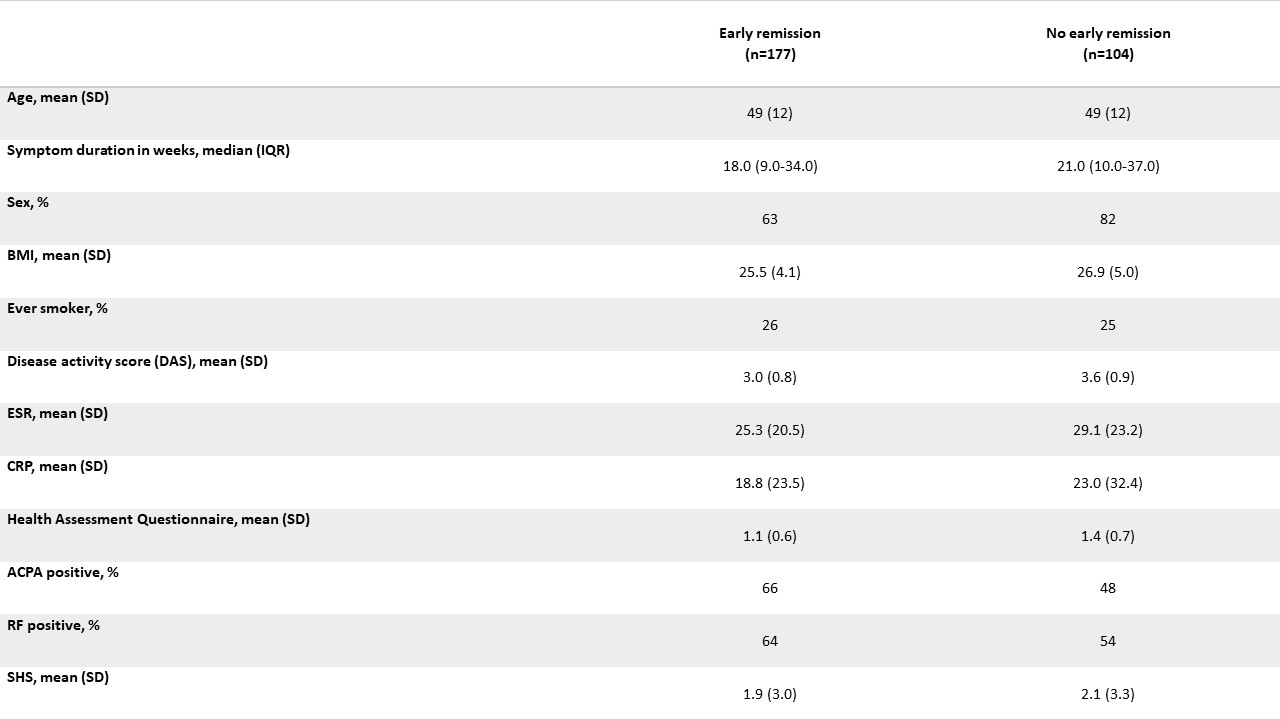
Methods: In BeSt (inclusion 2000-2002) 508 patients with early RA were randomized to: 1. Sequential DMARD monotherapy; 2. Step-up combination therapy; 3. Initial csDMARD combination therapy with prednisone or 4. Initial combination of MTX + infliximab, and treated-to-target DAS≤2.4 for 10 years. In IMPROVED (inclusion 2007-2010) 610 patients with early RA or UA received induction therapy with MTX + prednisone, with DAS< 1.6 as a treatment target. After 4 months 67% were in DAS remission (early remission). From 2019 to 2022 patients from both trials were invited for follow-up (after 20/12 years respectively). Outcomes were functional ability (HAQ), disease activity (3-component DAS) and radiographic damage (Sharp/Van der Heijde score, SHS, based on hands/feet X-rays of BeSt/IMPROVED at baseline & RECALL study visit, assessed by one reader (intrareader coefficient 0.98)). All outcomes had < 6% missing. In BeSt, SHS was compared between treatment arms with a generalized linear model, adjusted for unequally distributed patient characteristics across treatment arms (baseline DAS, ACPA; table 1). In IMPROVED, SHS was compared between patients that had been in early remission vs. not in early remission, adjusted for possible confounders (baseline DAS, ACPA, BMI).
Results: 45% (153/339) of alive BeSt patients participated (table 1). Their mean age at BeSt baseline was 46±11 years (non-participants/deceased: baseline age 58±13 years). At 20-year follow-up, median HAQ was 0.75, IQR 0.25-1.25; 0.54±0.7 lower than at baseline. Mean DAS was 1.5±0.6, with 137/151 (91%) of patients with DAS≤2.4 and 102/151 (68%) in DAS remission. Overall median SHS at RECALL visit was 13 (IQR 6-36) with a median progression of SHS 11 (IQR 5-30) since baseline. Compared to the other arms, SHS was lower in arm 4 (median SHS (IQR) 17 (8-58) in arm 1, 14 (3-28) in arm 2, 22 (7-42) in arm 3 and 9 (3-27) in arm 4). After adjusting for baseline differences this difference was statistically significant for arms 1 (p=0.02) and 3 (p=0.01), but not for arm 2 (p=0.16). 54% (282/523) of alive IMPROVED patients participated (table 2). Their mean age at IMPROVED baseline was 49±12 years (non-participants/deceased: 55±15 years). At 12-year follow-up, median HAQ was 0.50, IQR 0-1.0; 0.56±0.7 lower than at baseline. Mean DAS was 1.4±0.7, with 255/279 (91%) of patients with DAS≤2.4 and 189/279 (68%) in DAS remission. Overall median SHS was 8 (IQR 3-16) with a median SHS progression since baseline of 6 (IQR 3-13). Median SHS (IQR) was 10 (IQR 4-17) in the early remission group vs 6 (IQR 2-15) in patients that had not been in early remission. There was no statistically significant difference after adjusting for possible confounders (p=0.28).
Conclusion: 91% of patients who attended long term follow-up of BeSt/IMPROVED after respectively 20 and 12 years were in remission or low disease activity, with a median HAQ of 0.75/0.50 and clinically significant SHS progression of median 11/6 points.
S. Heckert: None; J. Maassen: None; I. Nevins: None; F. Fodili: None; M. Steup-Beekman: None; T. Huizinga: None; S. Bergstra: Pfizer, 5; C. Allaart: AbbVie/Abbott, 5.
Background/Purpose: In 2 trials with an original follow-up of 5-10 years, patients with early arthritis were treated to target, resulting in low disease activity or remission in the majority of patients and limited radiographic progression. We invited former participants for a long-term follow-up ('RECALL') visit.
Methods: In BeSt (inclusion 2000-2002) 508 patients with early RA were randomized to: 1. Sequential DMARD monotherapy; 2. Step-up combination therapy; 3. Initial csDMARD combination therapy with prednisone or 4. Initial combination of MTX + infliximab, and treated-to-target DAS≤2.4 for 10 years. In IMPROVED (inclusion 2007-2010) 610 patients with early RA or UA received induction therapy with MTX + prednisone, with DAS< 1.6 as a treatment target. After 4 months 67% were in DAS remission (early remission). From 2019 to 2022 patients from both trials were invited for follow-up (after 20/12 years respectively). Outcomes were functional ability (HAQ), disease activity (3-component DAS) and radiographic damage (Sharp/Van der Heijde score, SHS, based on hands/feet X-rays of BeSt/IMPROVED at baseline & RECALL study visit, assessed by one reader (intrareader coefficient 0.98)). All outcomes had < 6% missing. In BeSt, SHS was compared between treatment arms with a generalized linear model, adjusted for unequally distributed patient characteristics across treatment arms (baseline DAS, ACPA; table 1). In IMPROVED, SHS was compared between patients that had been in early remission vs. not in early remission, adjusted for possible confounders (baseline DAS, ACPA, BMI).
Results: 45% (153/339) of alive BeSt patients participated (table 1). Their mean age at BeSt baseline was 46±11 years (non-participants/deceased: baseline age 58±13 years). At 20-year follow-up, median HAQ was 0.75, IQR 0.25-1.25; 0.54±0.7 lower than at baseline. Mean DAS was 1.5±0.6, with 137/151 (91%) of patients with DAS≤2.4 and 102/151 (68%) in DAS remission. Overall median SHS at RECALL visit was 13 (IQR 6-36) with a median progression of SHS 11 (IQR 5-30) since baseline. Compared to the other arms, SHS was lower in arm 4 (median SHS (IQR) 17 (8-58) in arm 1, 14 (3-28) in arm 2, 22 (7-42) in arm 3 and 9 (3-27) in arm 4). After adjusting for baseline differences this difference was statistically significant for arms 1 (p=0.02) and 3 (p=0.01), but not for arm 2 (p=0.16). 54% (282/523) of alive IMPROVED patients participated (table 2). Their mean age at IMPROVED baseline was 49±12 years (non-participants/deceased: 55±15 years). At 12-year follow-up, median HAQ was 0.50, IQR 0-1.0; 0.56±0.7 lower than at baseline. Mean DAS was 1.4±0.7, with 255/279 (91%) of patients with DAS≤2.4 and 189/279 (68%) in DAS remission. Overall median SHS was 8 (IQR 3-16) with a median SHS progression since baseline of 6 (IQR 3-13). Median SHS (IQR) was 10 (IQR 4-17) in the early remission group vs 6 (IQR 2-15) in patients that had not been in early remission. There was no statistically significant difference after adjusting for possible confounders (p=0.28).
Conclusion: 91% of patients who attended long term follow-up of BeSt/IMPROVED after respectively 20 and 12 years were in remission or low disease activity, with a median HAQ of 0.75/0.50 and clinically significant SHS progression of median 11/6 points.

BeSt baseline characteristics of RECALL participants

IMPROVED baseline characteristics of RECALL participants
S. Heckert: None; J. Maassen: None; I. Nevins: None; F. Fodili: None; M. Steup-Beekman: None; T. Huizinga: None; S. Bergstra: Pfizer, 5; C. Allaart: AbbVie/Abbott, 5.



