Poster Session A
Infection-related rheumatic syndromes
Session: (0196–0228) Infection-related Rheumatic Disease Poster
0212: The Impact of Immunosuppression on the Humoral Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines in SLE
Sunday, November 12, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- RS
Rebecca Sadun, MD, PhD
Duke University
Durham, NC, United StatesDisclosure(s): No financial relationships with ineligible companies to disclose
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Rebecca Sadun1, Dan Crair2, Emmanuel B Walter3, Jennifer Rogers1, Megan Clowse4, Amanda Eudy5, Kai Sun1, Jayanth Doss1, Lisa Criscione-Schreiber6, Sarah Valencia2 and M. Anthony Moody6, 1Duke University, Durham, NC, 2Duke Human Vaccine Institute, Durham, NC, 3Duke Human Vaccine Institute, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, NC, 4Duke University, Chapel Hill, NC, 5Duke University, Raleigh, NC, 6Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, NC
Background/Purpose: The ACR's COVID-19 Vaccine Guidance recommends all patients with rheumatic diagnoses be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2. The predominant SARS-CoV-2 vaccines used in the United States are based on mRNA technology. Little is known about the immunogenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with SLE, many of whom are on immune suppressing medications. This study sought to determine the humoral immunogenicity of two doses of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines made by Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech in SLE patients, stratified by immunosuppression.
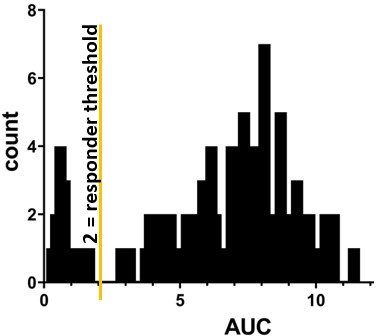
Methods: We obtained biobanked serum from SLE patients and healthy control patients whose blood was drawn 14-180 days following dose #2 of a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. ELISA was performed using anti-wild-type spike protein ectodomain S1+S2. Area under the curve (AUC) was calculated for each individual. An AUC threshold of 2.0 was established to distinguish between responders and non-responders (Figure 1).
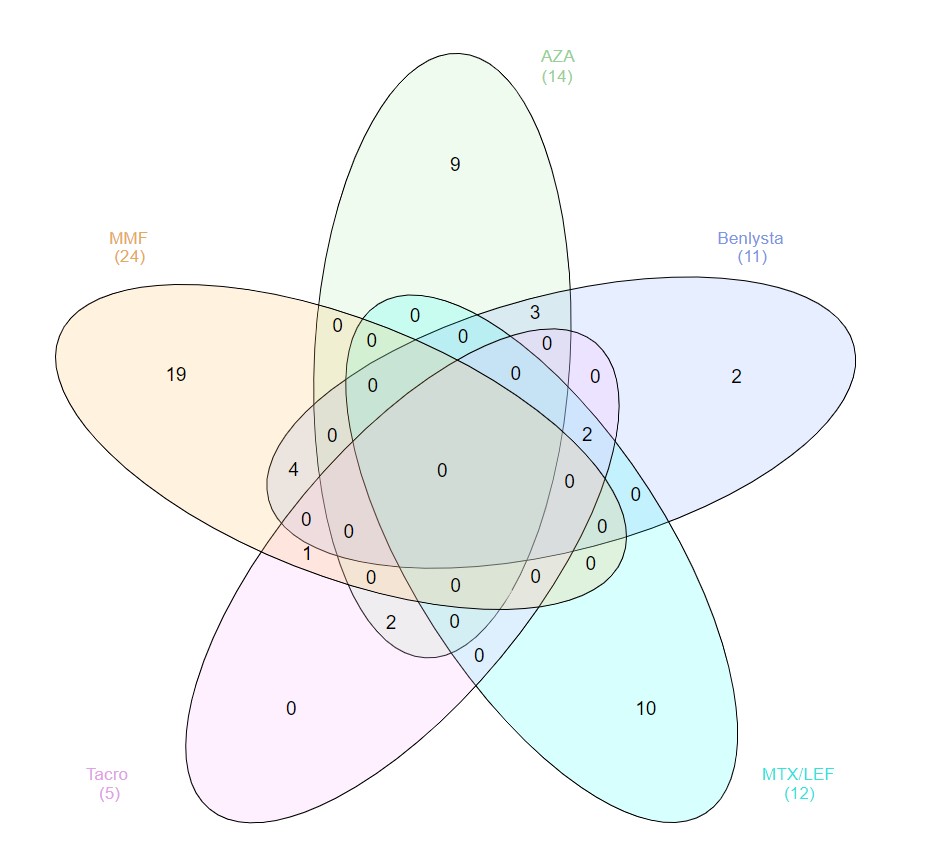
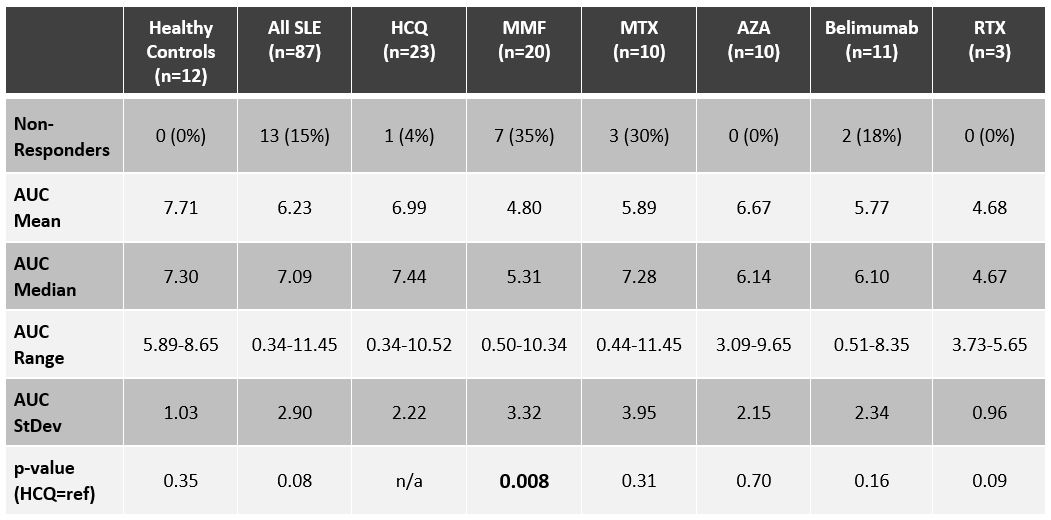
Results: Of the SLE patients (n=87), 23 (26%) were on no SLE therapy or HCQ monotherapy, 44 (51%) were on a DMARD and ≤7.5mg of prednisone, and 20 (23%) patients were on a biologic (rituximab=3, belimumab=11) and/or high-dose prednisone. Figure 2 depicts concomitant use of DMARDs and belimumab. As summarized in Table 1, the AUC for SLE patients was not significantly lower than for healthy controls (n=12): median AUC of 7.09 (range 0.34-11.45) versus 7.30 (range 5.89-8.65). The median AUC for SLE patients on no lupus medications or hydroxychloroquine monotherapy was 7.44 (range 0.34-10.52), with only one patient (4%) being classified as a non-responder. Ten (23%) of the SLE patients on DMARDs were non-responders, with mycophenolate and methotrexate having the biggest impact on AUC: seven (35%) of the patients on mycophenolate were non-responders (AUC median = 5.31; p=0.008), and 30% of the patients on methotrexate were non-responders (AUC median = 7.28; p=0.31). Three (15%) of the SLE patients on biologics and/or high-dose prednisone were non-responders, including two of the 11 belimumab patients (18%), one of whom was on concomitant mycophenolate, and the other on high-dose prednisone (20 mg daily). All three rituximab patients were classified as responders, although the median AUC (4.67) and mean AUC (4.68) were the lowest of any medication (range 3.73-5.65). The number of days between dose #2 and serum sample collection did not correlate with AUCs: the 13 non-responders were on average 66 days out from dose #2, whereas responders were on average 80 days out from dose #2.
Conclusion: SLE patients on certain immune suppressing medications, most notably mycophenolate, produce less SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike antibodies after receiving two doses of an mRNA vaccine. Neutralization assays and cell-based studies are necessary to understand the full picture of vaccine immunogenicity in SLE; nevertheless, decreased serologic response in SLE patients on certain medications should prompt studies exploring whether holding medications like mycophenolate will enhance the immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 and other vaccines.
R. Sadun: None; D. Crair: None; E. Walter: Clinetic, 5, Iliad Biotechnologies, 2, Moderna, 5, Najit biotechnologies, 5, Pfizer, 5, Sequiris, 5, Vaxcyte, 1; J. Rogers: Amgen, 2, Ampel Biosolutions, 1, AstraZeneca, 6, Aurinia, 1, Eli Lilly, 1, Exagen, 5, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 2, Immunovant, 2, 5; M. Clowse: Exagen, 5, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 2, 5, Immunovant, 5, UCB, 2, 5; A. Eudy: Amgen, 2, Exagen, 5, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 5, Immunovant, 5, Pfizer, 5; K. Sun: AstraZeneca, 6; J. Doss: None; L. Criscione-Schreiber: GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 5, UCB, 5; S. Valencia: None; M. Moody: None.
Background/Purpose: The ACR's COVID-19 Vaccine Guidance recommends all patients with rheumatic diagnoses be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2. The predominant SARS-CoV-2 vaccines used in the United States are based on mRNA technology. Little is known about the immunogenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with SLE, many of whom are on immune suppressing medications. This study sought to determine the humoral immunogenicity of two doses of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines made by Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech in SLE patients, stratified by immunosuppression.
Methods: We obtained biobanked serum from SLE patients and healthy control patients whose blood was drawn 14-180 days following dose #2 of a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. ELISA was performed using anti-wild-type spike protein ectodomain S1+S2. Area under the curve (AUC) was calculated for each individual. An AUC threshold of 2.0 was established to distinguish between responders and non-responders (Figure 1).
Results: Of the SLE patients (n=87), 23 (26%) were on no SLE therapy or HCQ monotherapy, 44 (51%) were on a DMARD and ≤7.5mg of prednisone, and 20 (23%) patients were on a biologic (rituximab=3, belimumab=11) and/or high-dose prednisone. Figure 2 depicts concomitant use of DMARDs and belimumab. As summarized in Table 1, the AUC for SLE patients was not significantly lower than for healthy controls (n=12): median AUC of 7.09 (range 0.34-11.45) versus 7.30 (range 5.89-8.65). The median AUC for SLE patients on no lupus medications or hydroxychloroquine monotherapy was 7.44 (range 0.34-10.52), with only one patient (4%) being classified as a non-responder. Ten (23%) of the SLE patients on DMARDs were non-responders, with mycophenolate and methotrexate having the biggest impact on AUC: seven (35%) of the patients on mycophenolate were non-responders (AUC median = 5.31; p=0.008), and 30% of the patients on methotrexate were non-responders (AUC median = 7.28; p=0.31). Three (15%) of the SLE patients on biologics and/or high-dose prednisone were non-responders, including two of the 11 belimumab patients (18%), one of whom was on concomitant mycophenolate, and the other on high-dose prednisone (20 mg daily). All three rituximab patients were classified as responders, although the median AUC (4.67) and mean AUC (4.68) were the lowest of any medication (range 3.73-5.65). The number of days between dose #2 and serum sample collection did not correlate with AUCs: the 13 non-responders were on average 66 days out from dose #2, whereas responders were on average 80 days out from dose #2.
Conclusion: SLE patients on certain immune suppressing medications, most notably mycophenolate, produce less SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike antibodies after receiving two doses of an mRNA vaccine. Neutralization assays and cell-based studies are necessary to understand the full picture of vaccine immunogenicity in SLE; nevertheless, decreased serologic response in SLE patients on certain medications should prompt studies exploring whether holding medications like mycophenolate will enhance the immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 and other vaccines.

Figure 1. Histogram depicting the distribution of anti-spike antibody areas under the curve (AUC) in SLE patients (n=87), which formed the basis for establishing the responder threshold of 2.0, at which 13 SLE patients (15%) were determined to be non-responsive.

Figure 2. Concomitant use of belimumab (Benlysta) and DMARDs (AZA=azathioprine; LEF=leflunomide; MTX=methotrexate, MMF=mycophenolate; Tacro=tacrolimus).

Table 1. Serologic responses, quantified as areas under the curve (AUC) for healthy controls, patients on insignificant immunosuppression (HCQ group encompasses patients on no medication or hydroxychloroquine monotherapy), and patients on a variety of immune suppressing medications (MMF=mycophenolate; MTX=methotrexate (n=9) and leflunomide (n=1); AZA=azathioprine; RTX=rituximab). Many of the patients on belimumab were also on >10 mg of prednisone daily. P-values were calculated in reference to the HCQ group.
R. Sadun: None; D. Crair: None; E. Walter: Clinetic, 5, Iliad Biotechnologies, 2, Moderna, 5, Najit biotechnologies, 5, Pfizer, 5, Sequiris, 5, Vaxcyte, 1; J. Rogers: Amgen, 2, Ampel Biosolutions, 1, AstraZeneca, 6, Aurinia, 1, Eli Lilly, 1, Exagen, 5, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 2, Immunovant, 2, 5; M. Clowse: Exagen, 5, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 2, 5, Immunovant, 5, UCB, 2, 5; A. Eudy: Amgen, 2, Exagen, 5, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 5, Immunovant, 5, Pfizer, 5; K. Sun: AstraZeneca, 6; J. Doss: None; L. Criscione-Schreiber: GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 5, UCB, 5; S. Valencia: None; M. Moody: None.



