Poster Session A
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Session: (0543–0581) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
0556: Classical Complement Activation in Lupus Nephritis Correlates with Disease Biomarkers: Results from Two Observational Studies
Sunday, November 12, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- EC
Edmund Chang, PhD
Annexon Biosciences
Brisbane, CA, United StatesDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Edmund Chang1, Julian Low1, Noosha Yousefpour1, Min Bao1, Jeannette Osterloh1, Qing Chang1, Dean Artis1, Henk-Andre Kroon1, Yaisa Andrews-Zwilling1, Maria Dall'Era2, Ted Yednock1 and Ann Mongan1, 1Annexon Biosciences, Brisbane, CA, 2University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is an autoantibody-mediated disease that can activate C1q and the classical complement pathway. Pathogenic anti-C1q antibodies (PACAs) are often present, amplifying classical pathway inflammation and contributing to progressive kidney damage. Elevated C4d and reduced C4 are markers of classical complement activation and consumption, respectively. For LN patients in the CLUES/UCSF Study, C4d/C4 ratio positively correlated with PACAs and urine protein-creatinine ratio (UPCR). To validate this correlation, the Sanguine Bio study was conducted.
Methods: Samples were collected from 40 LN patients (plus 20 healthy controls) from the CLUES/UCSF Study and 24 LN patients (plus 10 healthy controls) from Sanguine Bio. In the CLUES/UCSF Study, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) diagnoses were confirmed by study physicians according to either of the following definitions: (a) meeting ≥4 of the 11 ACR revised classification criteria for SLE as defined in 1982 and updated in 1997 or (b) meeting 3 of the 11 ACR criteria along with having SLE confirmed by a study rheumatologist. Complement activation and consumption (C4d, C4), exploratory biomarkers in plasma and urine, and UPCR were evaluated.
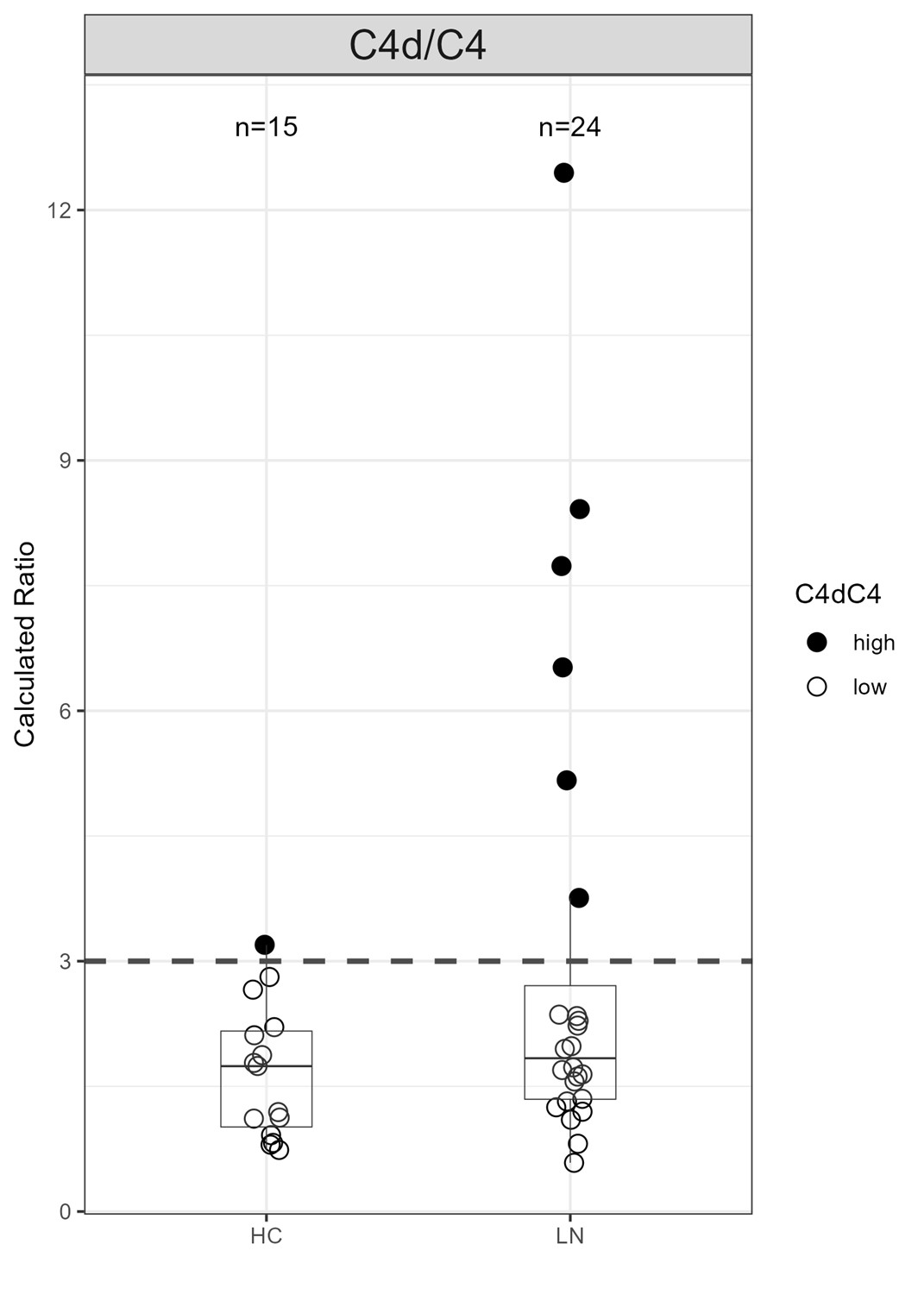
Results: Sanguine Bio samples from a subset of LN patients demonstrated elevated C4d/C4 compared to healthy controls, indicating classical complement pathway activation (Figure). Urinary biomarkers of LN correlated with C4d/C4 ratio in these patients.
Conclusion: In these LN patients, C4d/C4 ratios were elevated and correlated with LN biomarkers in blood and urine, supporting classical complement activity. These data support an ongoing, phase 1b study of ANX009 with the goal of assessing safety, tolerability, and pharmacodynamics of repeat doses of subcutaneous ANX009 with standard of care in adults with LN. ANX009 is an anti-C1q antigen binding fragment targeting LN patients with evidence of classical complement activity (elevated C4d/C4).
E. Chang: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; J. Low: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; N. Yousefpour: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; M. Bao: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8, Roche/Genentech, 3, 8; J. Osterloh: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8, FibroGen, Inc., 3; Q. Chang: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; D. Artis: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; H. Kroon: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; Y. Andrews-Zwilling: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; M. Dall'Era: Annexon Biosciences, 2, 5, AstraZeneca, 2, Aurinia, 2, Biogen, 2, GlaxoSmithKlein, 2, 5, Pfizer, 2; T. Yednock: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; A. Mongan: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8.
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is an autoantibody-mediated disease that can activate C1q and the classical complement pathway. Pathogenic anti-C1q antibodies (PACAs) are often present, amplifying classical pathway inflammation and contributing to progressive kidney damage. Elevated C4d and reduced C4 are markers of classical complement activation and consumption, respectively. For LN patients in the CLUES/UCSF Study, C4d/C4 ratio positively correlated with PACAs and urine protein-creatinine ratio (UPCR). To validate this correlation, the Sanguine Bio study was conducted.
Methods: Samples were collected from 40 LN patients (plus 20 healthy controls) from the CLUES/UCSF Study and 24 LN patients (plus 10 healthy controls) from Sanguine Bio. In the CLUES/UCSF Study, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) diagnoses were confirmed by study physicians according to either of the following definitions: (a) meeting ≥4 of the 11 ACR revised classification criteria for SLE as defined in 1982 and updated in 1997 or (b) meeting 3 of the 11 ACR criteria along with having SLE confirmed by a study rheumatologist. Complement activation and consumption (C4d, C4), exploratory biomarkers in plasma and urine, and UPCR were evaluated.
Results: Sanguine Bio samples from a subset of LN patients demonstrated elevated C4d/C4 compared to healthy controls, indicating classical complement pathway activation (Figure). Urinary biomarkers of LN correlated with C4d/C4 ratio in these patients.
Conclusion: In these LN patients, C4d/C4 ratios were elevated and correlated with LN biomarkers in blood and urine, supporting classical complement activity. These data support an ongoing, phase 1b study of ANX009 with the goal of assessing safety, tolerability, and pharmacodynamics of repeat doses of subcutaneous ANX009 with standard of care in adults with LN. ANX009 is an anti-C1q antigen binding fragment targeting LN patients with evidence of classical complement activity (elevated C4d/C4).

Figure. A Subset of Patients with LN Demonstrated Elevated C4d/C4 Over Healthy Controls
E. Chang: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; J. Low: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; N. Yousefpour: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; M. Bao: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8, Roche/Genentech, 3, 8; J. Osterloh: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8, FibroGen, Inc., 3; Q. Chang: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; D. Artis: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; H. Kroon: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; Y. Andrews-Zwilling: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; M. Dall'Era: Annexon Biosciences, 2, 5, AstraZeneca, 2, Aurinia, 2, Biogen, 2, GlaxoSmithKlein, 2, 5, Pfizer, 2; T. Yednock: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8; A. Mongan: Annexon Biosciences, 3, 8.



