Poster Session A
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) including psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Session: (0483–0509) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: PsA
0494: Levels of Atherosclerotic Index of Plasma and Triglyceride Glucose Index in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis and Carotid Plaque
Sunday, November 12, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- RA
Rosa Arvizu-Rivera, MD
Hospital Universitario \"Dr. José Eleuterio Gonzalez\"
Escobedo, Federal District, MexicoDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Dionicio A. Galarza-Delgado1, Iris Colunga1, José Ramón Azpiri-López1, Valeria Gonzalez-Gonzalez2, Rosa Arvizu-Rivera3, Victor Beltran4, Angel Arias Peralta5 and Jesus Alberto Cardenas-De la Garza6, 1Hospital Universitario UANL, Monterrey, Mexico, 2Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, Monterrey, Mexico, 3Hospital Universitario \"Dr. José Eleuterio Gonzalez\", Escobedo, Mexico, 4Rheumatology Service Hospital Universitario "Dr. José Eleuterio González", Monterrey, Mexico, 5Medicine Faculty, Universidad Autonoma De Nuevo Leon, Monterrey, Mexico, 6Hospital Universitario "Dr. José Eleuterio González", San Nicolas, Mexico
Background/Purpose: Triglyceride Glucose Index (TyG) is a surrogate marker positively correlated with atherosclerotic burden in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Atherosclerotic index of plasma (AIP) levels have not been evaluated in patients with subclinical atherosclerosis and PsA. The objective was to compare levels of AIP and TGI between PsA-patients with and without carotid plaque (CP).
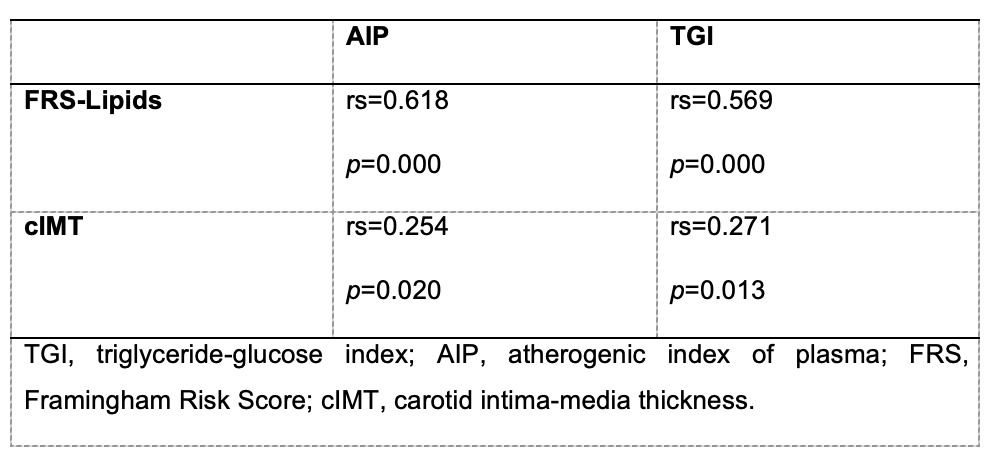
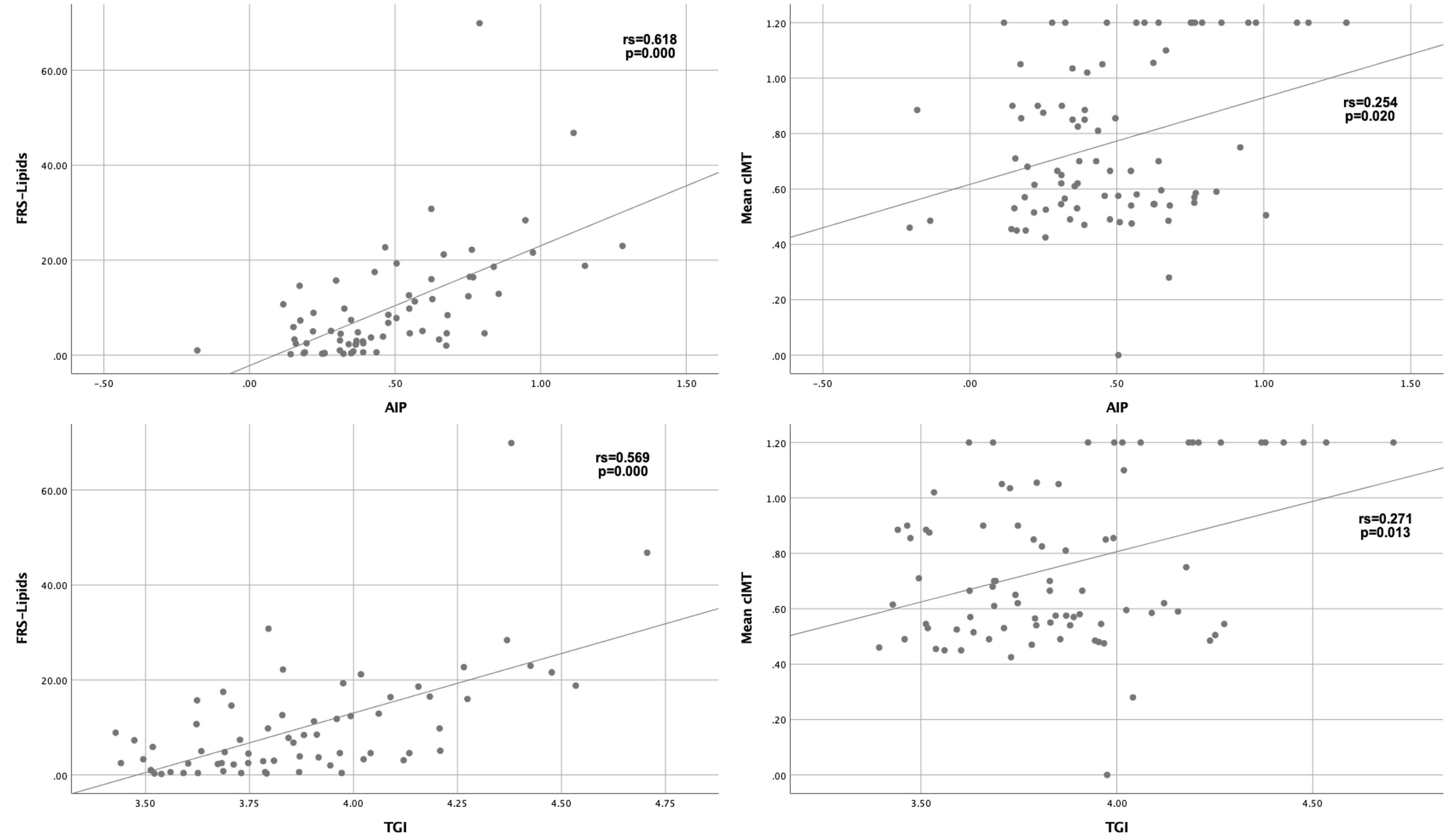
Methods: Cross-sectional study that included PsA-patients aged 40 to 75 years old who fulfilled the 2006 Classification Criteria for PsA. Patients with previous cardiovascular disease were excluded. Carotid ultrasound was performed on all study participants. The presence of carotid plaque (CP) was defined as diffuse carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) ≥1.2 mm or focal thickness ≥0.5 mm. Subclinical atherosclerosis was defined as the presence of CP or an increased cIMT (≥0.8mm). Cardiovascular disease risk was evaluated using the algorithm: FRS-Lipids. AIP was defined by Log (TG/HDL-C) mg/dL. TGI was defined by Log (Fasting triglyceride (mg/dl) x fasting glucose (mg/dl)/2. The distribution between groups was assessed with the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Comparisons with Chi-square or Fisher's exact test and Student's t-test or Mann Whitney's U-test, accordingly. The correlation between the AIP, TGI, cIMT, and FRS-Lipids was assessed by Spearman's correlation coefficient. A value of p≤0.05 was considered statistically significant.
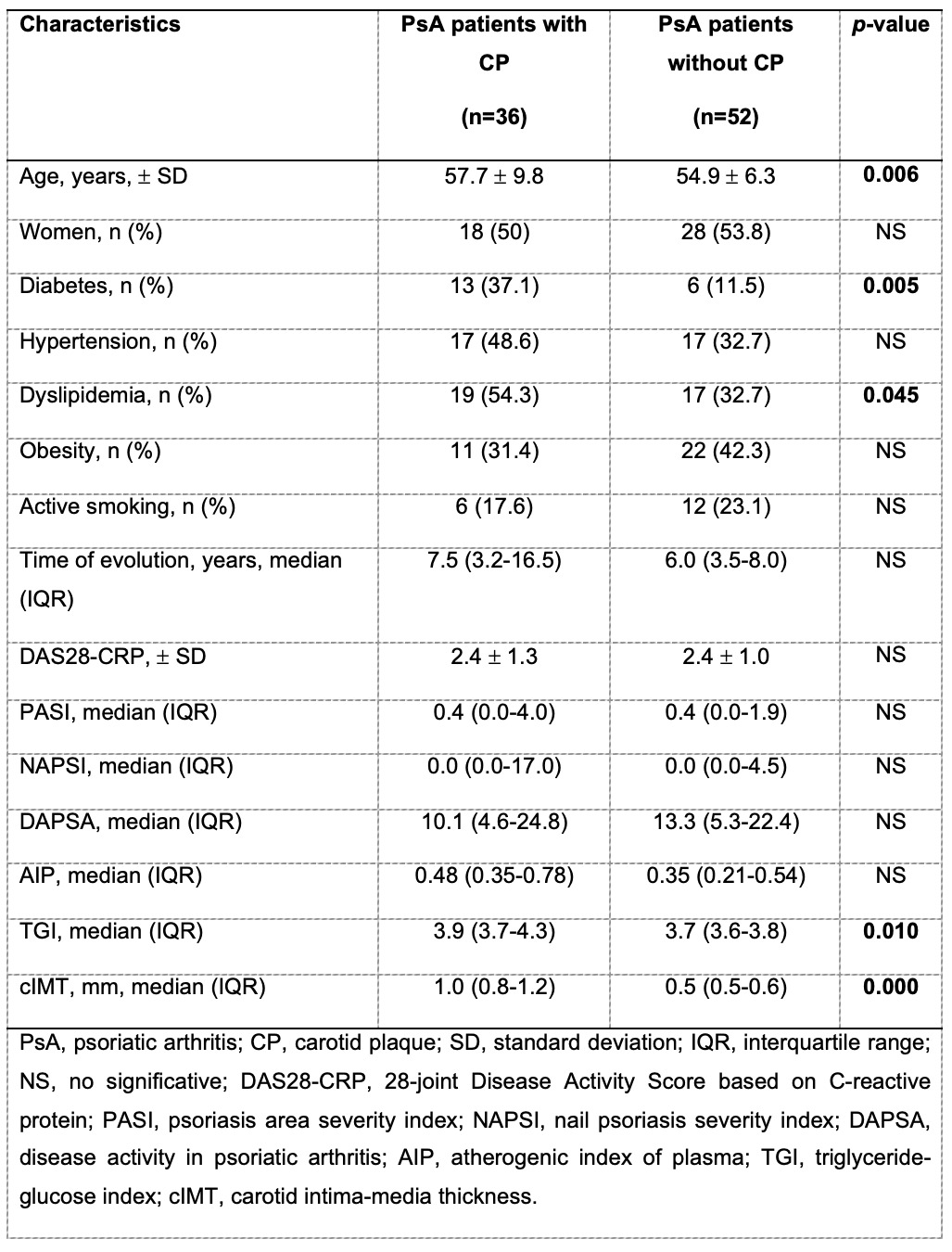
Results: A total of 88 patients with PsA were included, mostly women (n=46, 52.3%), the mean age was 53 ± 11.3, median disease duration of PsA was 5.0 (3.0-10.7) years. Median AIP was 0.44 (0.31-0.66) and TGI 3.8 (3.6-4.0) of all patients included. The most prevalent cardiovascular risk factor was dyslipidemia (n= 36, 41.4%). Patients with carotid plaque and PsA presented higher TyG compared to the group without carotid plaque (p=0.010). (Table 1).
Conclusion: AIP is not elevated in patients with PsA and subclinical atherosclerosis. However, TyG levels are increased in PsA-patients and CP. Prospective studies are needed to evaluate the performance of these surrogate markers to predict CV events in these patients.
D. Galarza-Delgado: None; I. Colunga: None; J. Azpiri-López: None; V. Gonzalez-Gonzalez: None; R. Arvizu-Rivera: None; V. Beltran: None; A. Arias Peralta: None; J. Cardenas-De la Garza: None.
Background/Purpose: Triglyceride Glucose Index (TyG) is a surrogate marker positively correlated with atherosclerotic burden in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Atherosclerotic index of plasma (AIP) levels have not been evaluated in patients with subclinical atherosclerosis and PsA. The objective was to compare levels of AIP and TGI between PsA-patients with and without carotid plaque (CP).
Methods: Cross-sectional study that included PsA-patients aged 40 to 75 years old who fulfilled the 2006 Classification Criteria for PsA. Patients with previous cardiovascular disease were excluded. Carotid ultrasound was performed on all study participants. The presence of carotid plaque (CP) was defined as diffuse carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) ≥1.2 mm or focal thickness ≥0.5 mm. Subclinical atherosclerosis was defined as the presence of CP or an increased cIMT (≥0.8mm). Cardiovascular disease risk was evaluated using the algorithm: FRS-Lipids. AIP was defined by Log (TG/HDL-C) mg/dL. TGI was defined by Log (Fasting triglyceride (mg/dl) x fasting glucose (mg/dl)/2. The distribution between groups was assessed with the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Comparisons with Chi-square or Fisher's exact test and Student's t-test or Mann Whitney's U-test, accordingly. The correlation between the AIP, TGI, cIMT, and FRS-Lipids was assessed by Spearman's correlation coefficient. A value of p≤0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: A total of 88 patients with PsA were included, mostly women (n=46, 52.3%), the mean age was 53 ± 11.3, median disease duration of PsA was 5.0 (3.0-10.7) years. Median AIP was 0.44 (0.31-0.66) and TGI 3.8 (3.6-4.0) of all patients included. The most prevalent cardiovascular risk factor was dyslipidemia (n= 36, 41.4%). Patients with carotid plaque and PsA presented higher TyG compared to the group without carotid plaque (p=0.010). (Table 1).
Conclusion: AIP is not elevated in patients with PsA and subclinical atherosclerosis. However, TyG levels are increased in PsA-patients and CP. Prospective studies are needed to evaluate the performance of these surrogate markers to predict CV events in these patients.

Table 1. Demographic characteristics.

Table 2. Association between cardiovascular algorithm, cIMT and index.

Figure 1. Scatterplots of the association between cardiovascular algorithm, cIMT and index.
D. Galarza-Delgado: None; I. Colunga: None; J. Azpiri-López: None; V. Gonzalez-Gonzalez: None; R. Arvizu-Rivera: None; V. Beltran: None; A. Arias Peralta: None; J. Cardenas-De la Garza: None.



