Poster Session A
Vasculitis
Session: (0673–0690) Vasculitis – ANCA-Associated Poster I: Treatment Outcomes
0681: Real-World Outcomes for Remission Induction in Working-Age Adults with Severe Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-associated Vasculitis
Sunday, November 12, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- IM
Itay Marmor, MD
Dana-Dwek Children’s Hospital
Hod Hasharon, IsraelDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Itay Marmor1, Katelin Nickel2, Matthew Keller2, Guy Hazan3, Kevin Baszis4, Anthony French5 and Mary Hartman2, 1Dana-Dwek Children's Hospital, Hod Hasharon, Israel, 2Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, 3Soroka University Medical Center, Beer Sheva, Israel, 4Washington Univ in St. Louis School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, 5Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO
Background/Purpose: Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV), including Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA) and Microscopic Polyangiitis (MPA), often manifests with life-threatening complications. Cyclophosphamide (CYC) and rituximab (RTX) are the mainstay of remission induction treatment in severe AAV, but their safety and efficacy have not been comprehensively compared in “real-world” settings.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using administrative data from the
2006–2019 IBM® MarketScan® Commercial Database. We identified working-age adults (age 18-64 years) with a new diagnosis of GPA/MPA, using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) version 9 or 10 codes, who received induction treatment with CYC or RTX. We used propensity score matching and a Cox proportional hazard model to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) for the first major disease relapse and severe infection.
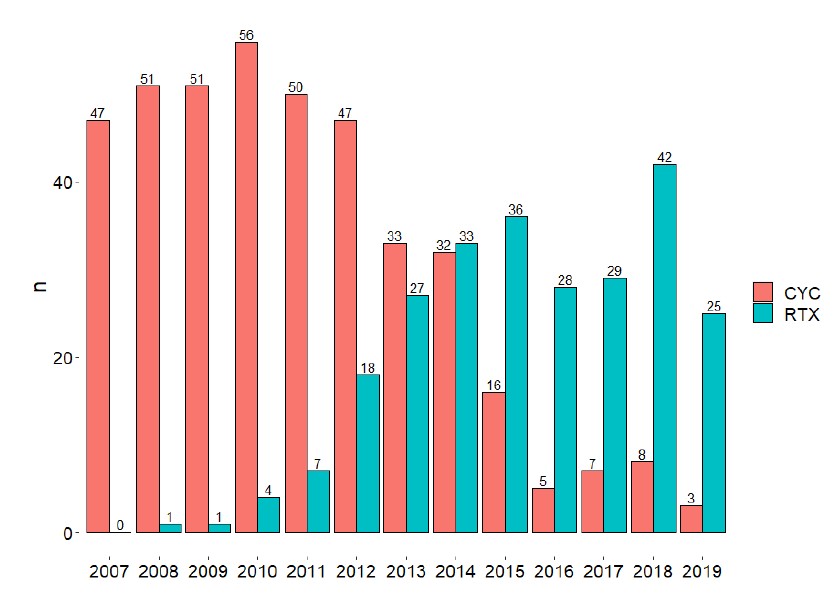
Results: We identified 657 patients, 406 (61.8%) of whom were treated with CYC and 251 (38.2%) with RTX. Patients in the CYC group had worse disease severity scores at baseline.
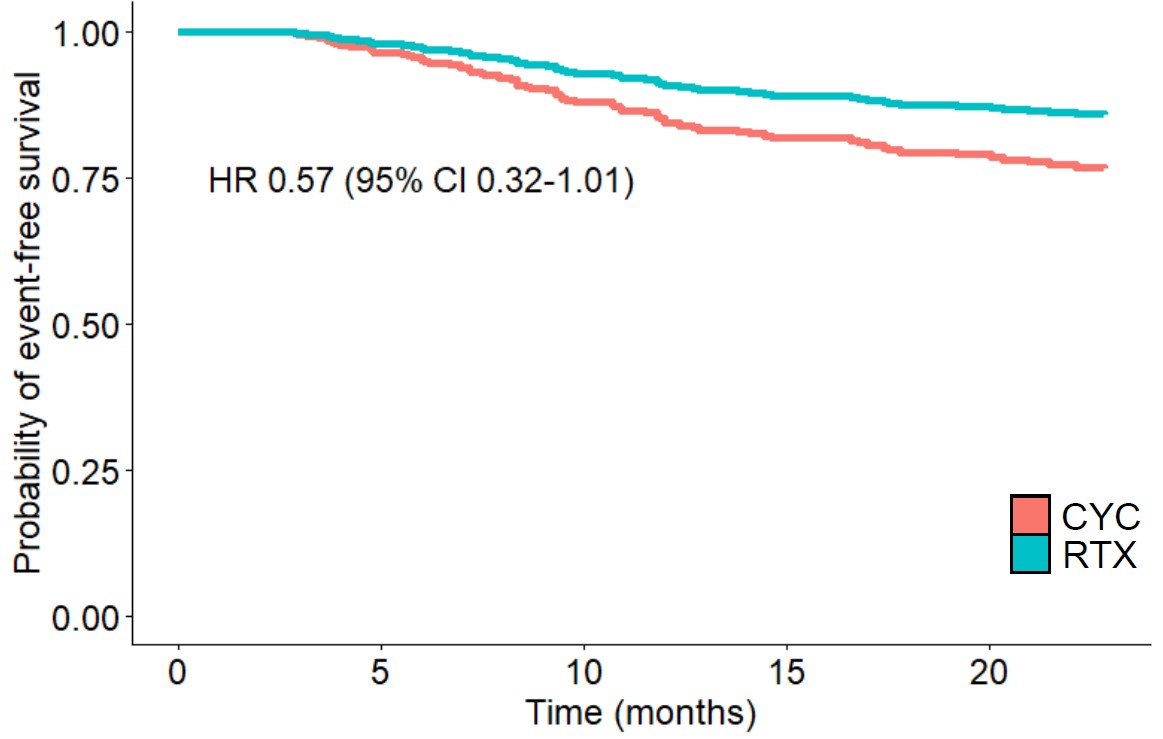
In the 24 months after induction, 146 (22.2%) patients experienced a major disease relapse and 129 patients (19.6%) had severe infection. Multivariate analysis with propensity score matching showed no significant differences between RTX and CYC in the likelihood of experiencing major relapse (HR 0.57, 95% CI 0.32-1.01) or severe infection (HR 0.63, 95% CI 0.30-1.02).
Conclusion: In a nationally representative sample of working-age adults, RTX was found to be comparable to CYC for remission induction treatment in severe AAV.
.jpg)
I. Marmor: None; K. Nickel: None; M. Keller: None; G. Hazan: None; K. Baszis: None; A. French: None; M. Hartman: None.
Background/Purpose: Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV), including Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA) and Microscopic Polyangiitis (MPA), often manifests with life-threatening complications. Cyclophosphamide (CYC) and rituximab (RTX) are the mainstay of remission induction treatment in severe AAV, but their safety and efficacy have not been comprehensively compared in “real-world” settings.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using administrative data from the
2006–2019 IBM® MarketScan® Commercial Database. We identified working-age adults (age 18-64 years) with a new diagnosis of GPA/MPA, using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) version 9 or 10 codes, who received induction treatment with CYC or RTX. We used propensity score matching and a Cox proportional hazard model to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) for the first major disease relapse and severe infection.
Results: We identified 657 patients, 406 (61.8%) of whom were treated with CYC and 251 (38.2%) with RTX. Patients in the CYC group had worse disease severity scores at baseline.
In the 24 months after induction, 146 (22.2%) patients experienced a major disease relapse and 129 patients (19.6%) had severe infection. Multivariate analysis with propensity score matching showed no significant differences between RTX and CYC in the likelihood of experiencing major relapse (HR 0.57, 95% CI 0.32-1.01) or severe infection (HR 0.63, 95% CI 0.30-1.02).
Conclusion: In a nationally representative sample of working-age adults, RTX was found to be comparable to CYC for remission induction treatment in severe AAV.

Absolute number of patients treated with each induction medication, by year. The data clearly shows a shift in practice over time, with RTX gradually becoming the medication of choice. CYC, cyclophosphamide; RTX, rituximab

Adjusted event-free survival for the primary outcomes, in the first 24 months following induction, by induction medication. 3A: Major relapse; 3B: Severe infection. Curves were plotted using multivariate Cox proportional hazards model, conducted following propensity score matching. CYC, cyclophosphamide; RTX, rituximab; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval
.jpg)
Multivariable-adjusted risk factors a for the primary outcomes
in the first 24 months following induction
in the first 24 months following induction
I. Marmor: None; K. Nickel: None; M. Keller: None; G. Hazan: None; K. Baszis: None; A. French: None; M. Hartman: None.



