Poster Session A
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Session: (0582–0608) SLE – Treatment Poster I
0589: A Comparative Evaluation of IgA2 Anti-dsDNA Antibodies and Clinical Outcome in Two Clinical Trials of Belimumab After Rituximab in SLE
Sunday, November 12, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- MS
Muhammad RA Shipa, MBBS, MRCP (he/him/his)
University College London
LONDON, United KingdomDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Muhammad RA Shipa1, Daniel McCluskey1, Laura Cooney2 and Michael Ehrenstein1, 1University College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Immune Tolerance Network, Seattle, WA
Background/Purpose: We have shown that serum IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody levels is a biomarker of response to belimumab after rituximab in SLE (BEAT-lupus trial) (1). We sought to confirm these findings in the CALIBRATE trial where 43 patients with lupus nephritis refractory to conventional therapy were randomised to receive either rituximab, cyclophosphamide, and then belimumab (RCB) for 48 weeks, or rituximab and cyclophosphamide (RC) (2).
Methods: All patients met the ACR classification criteria for SLE. Serum IgG, IgA1 and IgA2 anti-DNA antibodies were assayed by ELISA. We performed a post-hoc modified intention to treat analysis of the CALIBRATE trial so that the clinical outcome data could be matched with the BEAT-lupus trial.
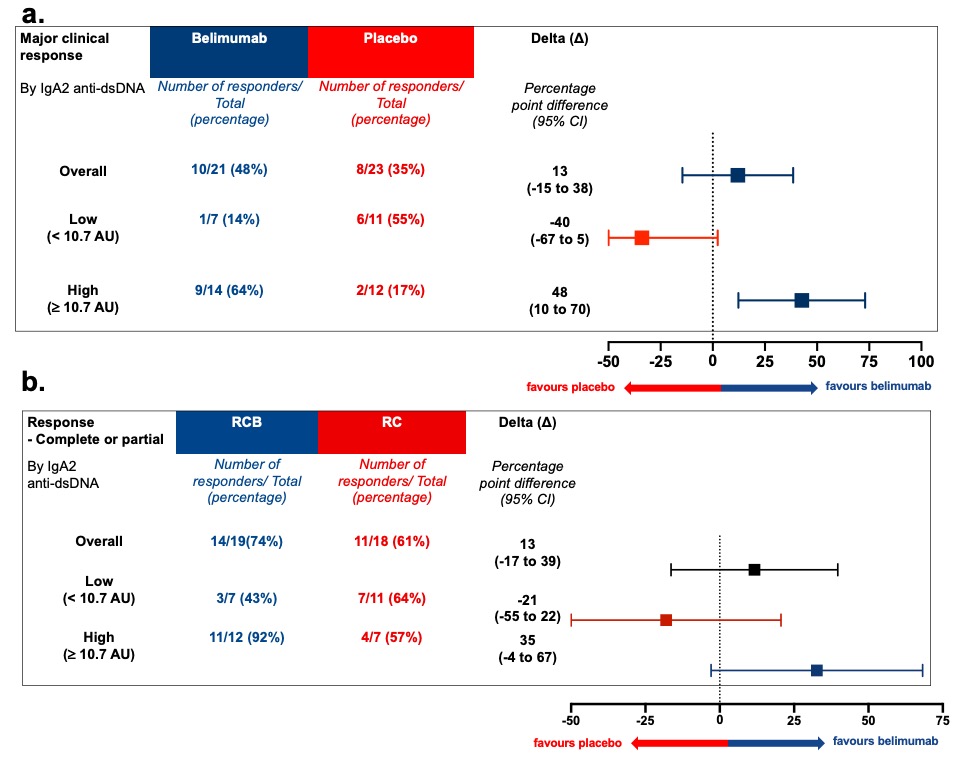
Results: The intention-to-treat analysis of both the BEAT-lupus and CALIBRATE trials revealed a 13% difference in outcome at 1 year favouring belimumab after rituximab compared to rituximab. This difference increased to 35% in those patients in the CALIBRATE trial with elevated serum levels of IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies, the corresponding value in the BEAT-lupus trial was a 48% difference (1) (Figure 1a-b).
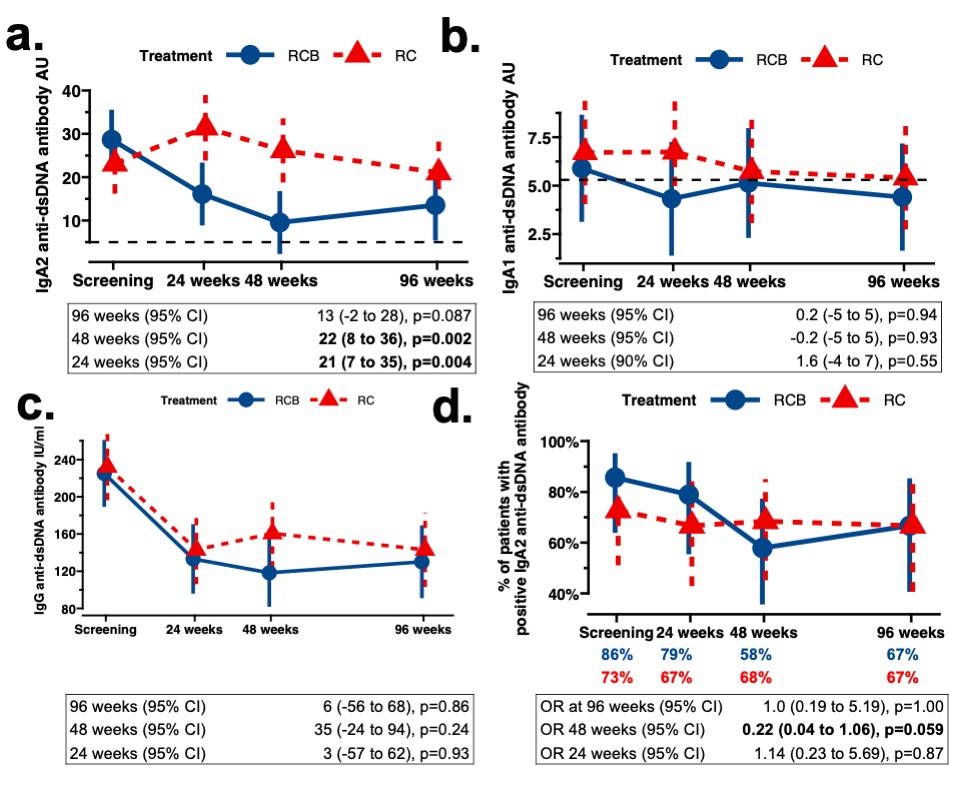
Matching previously published data from the BEAT-LUPUS trial (1), serum IgA2, but not IgA1, anti-dsDNA antibodylevels decreased at 48 weeks only in patients who received belimumab (p=0.002) (Figure 2a-b). Serum IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies increased after cessation of belimumab therapy. There was no significant difference in serum IgG anti-DNA antibody levels between the two arms of the CALIBRATE trial (Figure 2c). Serum IgA1 anti-dsDNA antibody levels in the CALIBRATE trial were less than IgA2 anti-DNA antibody levels and remained close to healthy control values, consistent with our previous observation that the former is low in lupus nephritis (1).
At baseline, 18/21 patients (86%) in the RCB group and 16/22 patients (73%) in the RC group were positive for serum IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies. The percentage of patients with positive IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies reduced to 58% in the RCB group at 48 weeks (Figure 2d). The odds ratio of reversion to seronegativity in belimumab treated patients with positive IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies was 0.22 at 48 weeks (95% CI 0.04–1.06; p=0.059); a similar sero-reversion rate was noted in the belimumab arm of the BEAT-LUPUS trial (1).
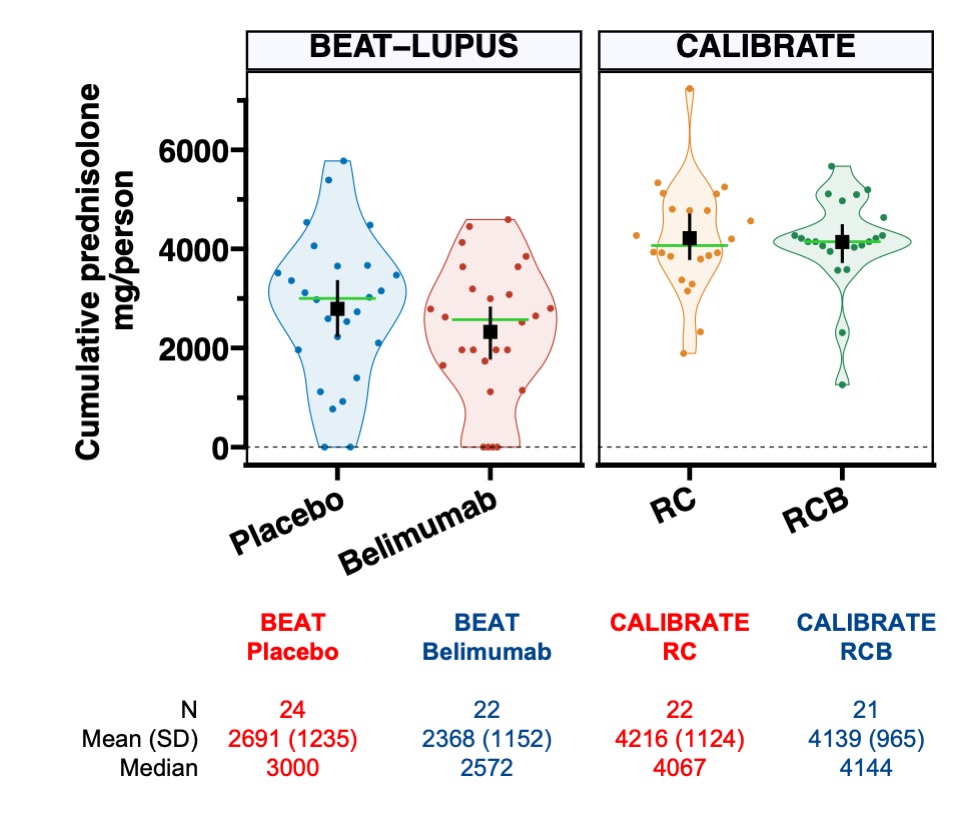
The overall response rate in the CALIBRATE trial (74% - RCB arm, 61% - RC arm) was higher than the BEAT-LUPUS trial (48% - belimumab arm, 35% - placebo arm). Patients in the CALIBRATE trial received almost twice as much prednisolone in the first 48 weeks compared to the BEAT-LUPUS trial (Figure 3) which could reflect the slightly different patient populations (CALIBRATE- refractory lupus nephritis; BEAT-lupus – refractory lupus: 20/52 patients had lupus nephritis) and explain the difference in outcome.
Conclusion: Data from two independent trials confirm IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody levels as a predictive biomarker of response to belimumab after rituximab in SLE. Cessation of belimumab therapy after rituximab led to a rise in IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody levels providing a mechanistic rationale for continuation of therapy. Reference-
1. Shipa, M. et al. The Lancet rheumatology.2022;5: e24
2. Atisha-Fregoso, Y et.al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73:121
M. Shipa: None; D. McCluskey: None; L. Cooney: None; M. Ehrenstein: GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 2.
Background/Purpose: We have shown that serum IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody levels is a biomarker of response to belimumab after rituximab in SLE (BEAT-lupus trial) (1). We sought to confirm these findings in the CALIBRATE trial where 43 patients with lupus nephritis refractory to conventional therapy were randomised to receive either rituximab, cyclophosphamide, and then belimumab (RCB) for 48 weeks, or rituximab and cyclophosphamide (RC) (2).
Methods: All patients met the ACR classification criteria for SLE. Serum IgG, IgA1 and IgA2 anti-DNA antibodies were assayed by ELISA. We performed a post-hoc modified intention to treat analysis of the CALIBRATE trial so that the clinical outcome data could be matched with the BEAT-lupus trial.
Results: The intention-to-treat analysis of both the BEAT-lupus and CALIBRATE trials revealed a 13% difference in outcome at 1 year favouring belimumab after rituximab compared to rituximab. This difference increased to 35% in those patients in the CALIBRATE trial with elevated serum levels of IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies, the corresponding value in the BEAT-lupus trial was a 48% difference (1) (Figure 1a-b).
Matching previously published data from the BEAT-LUPUS trial (1), serum IgA2, but not IgA1, anti-dsDNA antibodylevels decreased at 48 weeks only in patients who received belimumab (p=0.002) (Figure 2a-b). Serum IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies increased after cessation of belimumab therapy. There was no significant difference in serum IgG anti-DNA antibody levels between the two arms of the CALIBRATE trial (Figure 2c). Serum IgA1 anti-dsDNA antibody levels in the CALIBRATE trial were less than IgA2 anti-DNA antibody levels and remained close to healthy control values, consistent with our previous observation that the former is low in lupus nephritis (1).
At baseline, 18/21 patients (86%) in the RCB group and 16/22 patients (73%) in the RC group were positive for serum IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies. The percentage of patients with positive IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies reduced to 58% in the RCB group at 48 weeks (Figure 2d). The odds ratio of reversion to seronegativity in belimumab treated patients with positive IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies was 0.22 at 48 weeks (95% CI 0.04–1.06; p=0.059); a similar sero-reversion rate was noted in the belimumab arm of the BEAT-LUPUS trial (1).
The overall response rate in the CALIBRATE trial (74% - RCB arm, 61% - RC arm) was higher than the BEAT-LUPUS trial (48% - belimumab arm, 35% - placebo arm). Patients in the CALIBRATE trial received almost twice as much prednisolone in the first 48 weeks compared to the BEAT-LUPUS trial (Figure 3) which could reflect the slightly different patient populations (CALIBRATE- refractory lupus nephritis; BEAT-lupus – refractory lupus: 20/52 patients had lupus nephritis) and explain the difference in outcome.
Conclusion: Data from two independent trials confirm IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody levels as a predictive biomarker of response to belimumab after rituximab in SLE. Cessation of belimumab therapy after rituximab led to a rise in IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody levels providing a mechanistic rationale for continuation of therapy. Reference-
1. Shipa, M. et al. The Lancet rheumatology.2022;5: e24
2. Atisha-Fregoso, Y et.al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73:121

Figure 1a-b - Patients with high baseline serum IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody levels were more likely to respond at 1 year to belimumab after rituximab compared to rituximab therapy: (a) BEAT-LUPUS and (b) CALIBRATE trial. Baseline serum IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody levels were categorised into high or low levels (the optimal cut-point was derived from the Area under the Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve (AUROC) analysis (= 10.7 arbitrary units/AUs). RCB = belimumab after rituximab and cyclophosphamide, RC = rituximab and cyclophosphamide

Figure 2a-d - Belimumab after rituximab decreased serum IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody levels compared to rituximab therapy (CALIBRATE trial). Longitudinal change of (a) serum IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies, (b) serum IgA1 anti-dsDNA antibodies, and (c) serum IgG anti-dsDNA antibodies stratified by treatment i.e., RCB = belimumab after rituximab and cyclophosphamide versus RC = no belimumab after rituximab and cyclophosphamide. A generalised longitudinal linear mixed-effect model was fitted with random patient effect to account for clustering by patients and fixed effect of treatment group intercepting with trial times and adjusted for screening IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody values, age, gender, and concomitant prednisolone (yes or no) to calculate expected difference at 24, 48, and 96 weeks. Estimated mean with 95% confidence intervals (95%CIs) are shown; p values are provided. The horizontal black dotted lines where shown indicate upper limit of normal (3 standard deviation above the mean of healthy control samples). (d) Proportion of patients who were positive† for IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies at each time point. Odds ratio (OR) of seronegative reversion for IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies at each time points with RCB (if positive for IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibodies at baseline) compared to RC group. †Positivity of IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody was defined as 3 standard deviations above the mean values of healthy control samples (=5.4 arbitrary units).

Figure 3 – Cumulative dose of prednisolone in the CALIBRATE and BEAT-lupus trials. Cumulative dose of prednisolone in the treatment arms in the BEAT-LUPUS and CALIBRATE trials over 52 and 48 weeks, respectfully. The black boxes and lines indicate mean values with 95% confidence interval, green horizontal lines indicate median values.
RCB = belimumab after rituximab and cyclophosphamide.
RC = no belimumab after rituximab and cyclophosphamide.
RCB = belimumab after rituximab and cyclophosphamide.
RC = no belimumab after rituximab and cyclophosphamide.
M. Shipa: None; D. McCluskey: None; L. Cooney: None; M. Ehrenstein: GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 2.



