Abstract Session
Myopathic rheumatic diseases (polymyositis, dermatomyositis, inclusion body myositis)
Session: Abstracts: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science I (2461–2466)
2465: Clonally Expanded B Cells in Anti-Histidyl-tRNA Synthetase Syndrome Patients Exhibit an Autoreactive-Prone Memory Phenotype and Bind Jo-1 Autoantigen
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
3:00 PM - 3:10 PM PT
Location: Room 25A-C
- LB
Lindsay Bass, BS (she/her/hers)
Vanderbilt University
Nashville, TN, United StatesDisclosure information not submitted.
Presenting Author(s)
Lindsay Bass1, Dena Liu1, Alberto Cisneros2, Jennifer Young-Glazer2, Leslie Crofford3, Erin Wilfong2 and Rachel Bonami2, 1Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, 2Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, 3Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Melbourne, AR
Background/Purpose: Anti-histidyl-tRNA synthetase syndrome (Jo-1 ARS) is defined by the presence of autoantibodies against histidyl tRNA synthetase (Jo-1). Clinically, Jo-1 ARS can involve multiple tissues including muscle, lung, skin, and joints. Previously, we identified that Jo-1 binding B cells show skewing towards specific phenotypic subsets in the peripheral blood of Jo-1 ARS patients, but the mechanisms that promote B cell recognition of Jo-1 autoantigen are unknown.
Methods: Five patients with active anti-Jo-1 ARS were identified from the Vanderbilt MYSTIC cohort (VUMC IRB 141415). We isolated live CD19+ B cells from cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) using fluorescence activated cytometry sorting. Five-thousand cells were targeted for sequencing per sample. Single cell RNA-Seq, V(D)J sequencing, and Cite-Seq were performed using the 10X Chromium platform (5’-RNA, V(D)J, and CITE-Seq) de-multiplexed and processed using the CellRanger pipeline and analyzed with Seurat v4.0.0. V(D)J gene identities and % somatic hypermutation were determined for B cell receptors (BCR) using IMGT/HighV-QUEST. Seurat was used to merge these outputs with RNA-seq and CITE-seq data to enable integrated analysis of BCRs with transcriptomic and phenotypic profiling. Clonally expanded BCRs were identified and recombinantly expressed as monoclonal antibodies. Total IgG, Jo-1, LPS, dsDNA, and insulin binding were measured by ELISA.
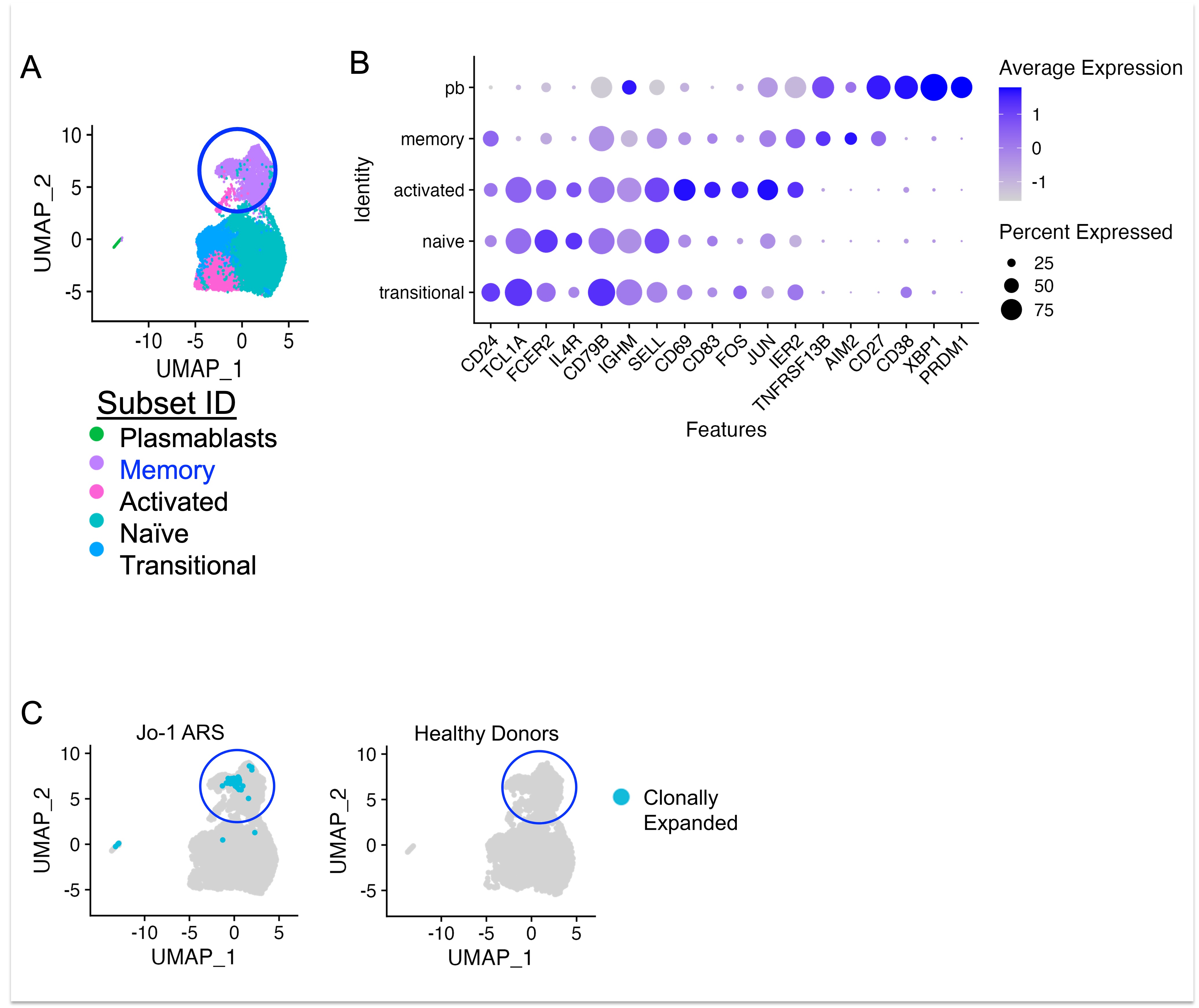
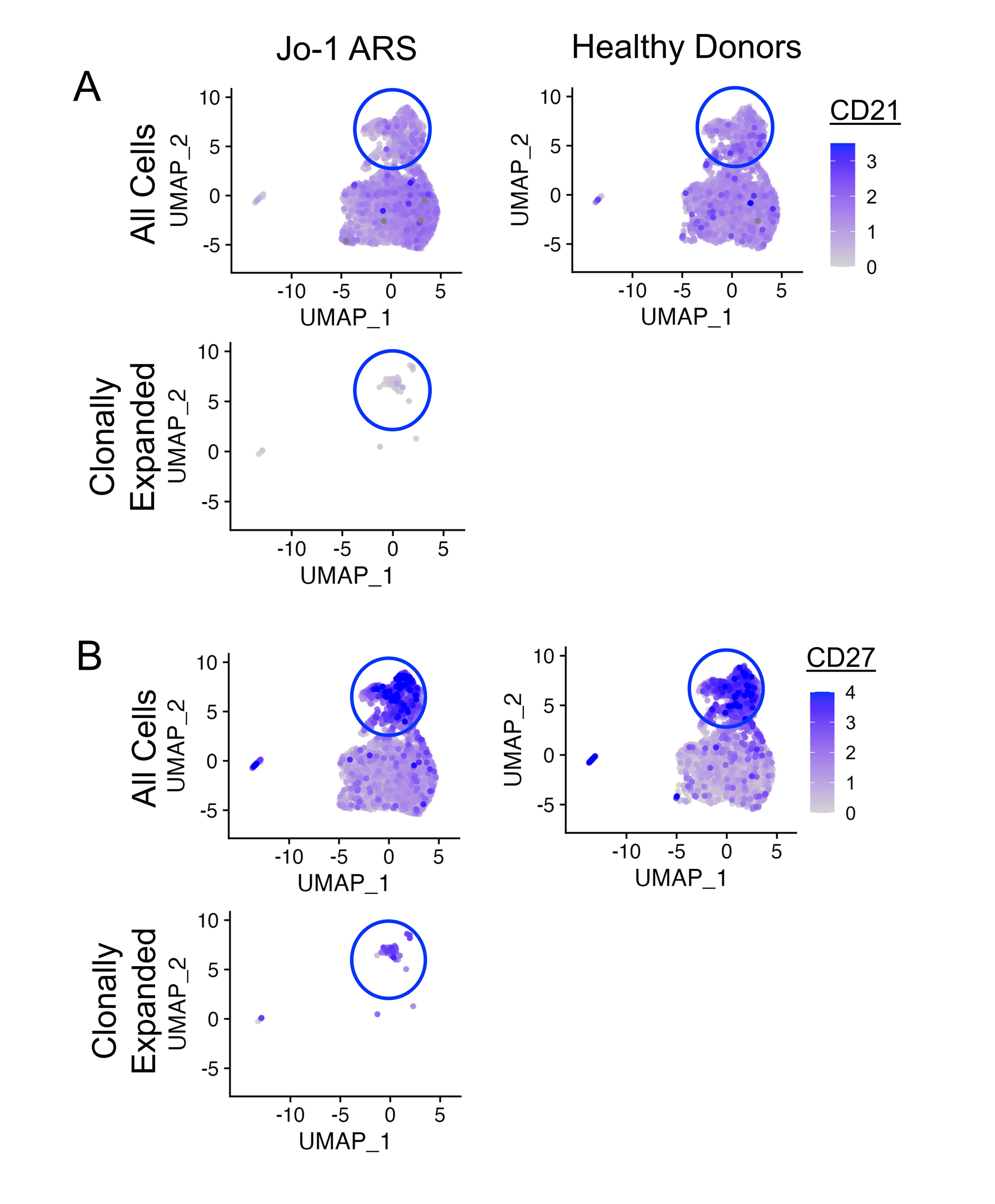
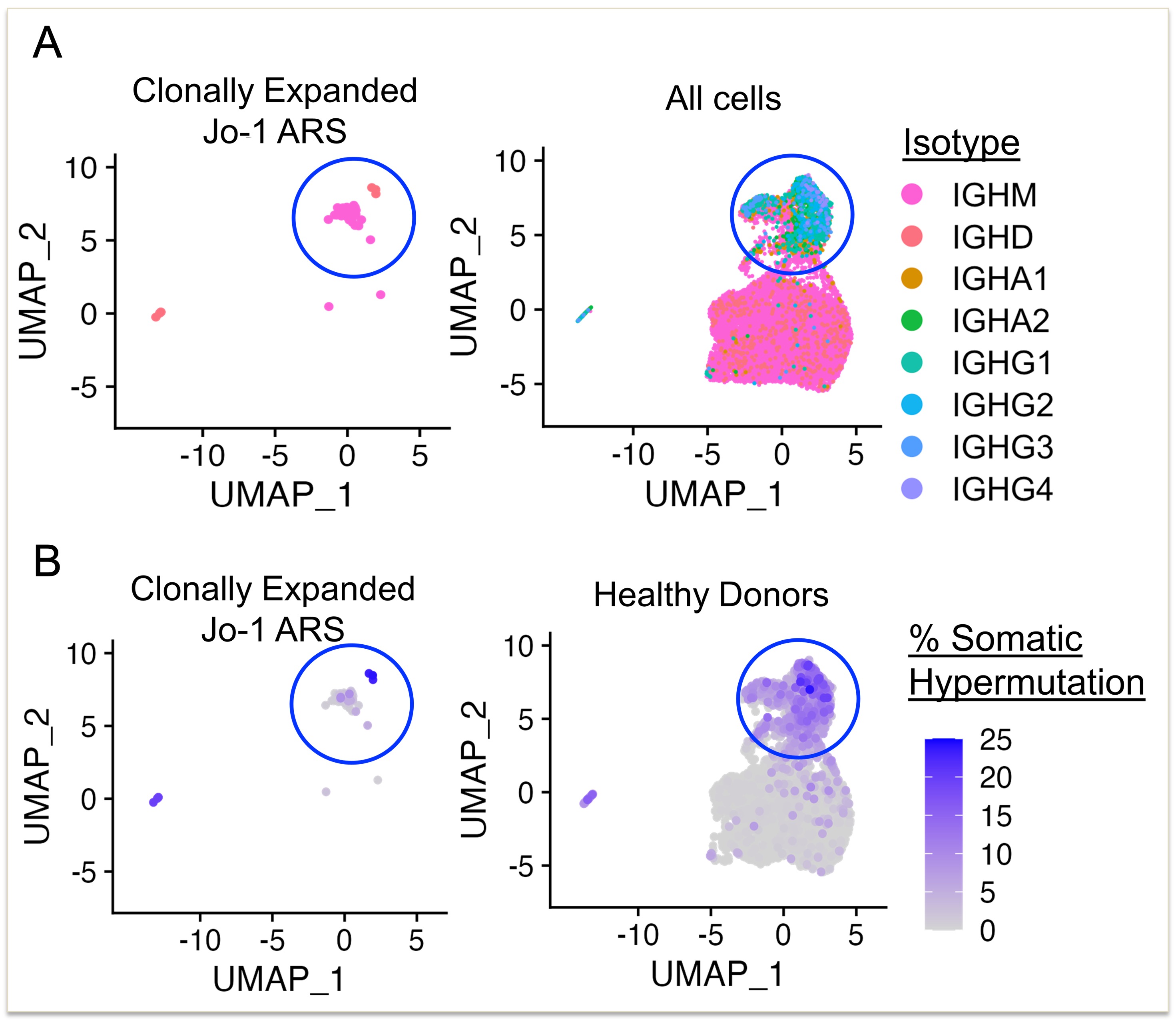
Results: Five B cell subsets (transitional, naïve, activated, memory, plasmablast) were assigned based on isotype switching and gene expression (Fig. 1A-B). We identified 21 expanded clonotypes (defined as n ³ 3 per donor) amongst the five donors (Fig. 1C). Clonally expanded cells were CD27+ and CD21lo (Fig. 2) and were primarily IgM+ (non-class-switched) (Fig. 3A). Somatic hypermutation was highly variable and ranged from germline to very high (25%) (Fig. 3B). Recombinant expression of clonally expanded BCRs as IgG1 antibodies and ELISA binding studies revealed that 5/21 (24%) bound Jo-1. All Jo-1 binding clones exhibited some binding of dsDNA, LPS, or insulin, confirming polyreactivity. Multiple Jo-1 binding B cells expressed the VH4-34 heavy chain gene, which has been previously associated with autoimmunity.
Conclusion: Clonally expanded B cells in patients with Jo-1 ARS are enriched for anti-Jo1 B cells, which display an autoreactive-prone (CD21lo) memory phenotype. Somatic hypermutation analysis shows that germline recognition of Jo-1 autoantigen is possible, and that Jo-1-binding B cells can undergo extensive somatic hypermutation. Future studies will be required to determine if somatic hypermutation is associated with affinity maturation of Jo-1-binding B cells, and presumably enhanced pathogenicity.
L. Bass: None; D. Liu: None; A. Cisneros: None; J. Young-Glazer: Argenx, 5; L. Crofford: None; E. Wilfong: Boehringer-Ingelheim, 1, 5, 6, Cabaletta Bio, 1; R. Bonami: Argenx, 5.
Background/Purpose: Anti-histidyl-tRNA synthetase syndrome (Jo-1 ARS) is defined by the presence of autoantibodies against histidyl tRNA synthetase (Jo-1). Clinically, Jo-1 ARS can involve multiple tissues including muscle, lung, skin, and joints. Previously, we identified that Jo-1 binding B cells show skewing towards specific phenotypic subsets in the peripheral blood of Jo-1 ARS patients, but the mechanisms that promote B cell recognition of Jo-1 autoantigen are unknown.
Methods: Five patients with active anti-Jo-1 ARS were identified from the Vanderbilt MYSTIC cohort (VUMC IRB 141415). We isolated live CD19+ B cells from cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) using fluorescence activated cytometry sorting. Five-thousand cells were targeted for sequencing per sample. Single cell RNA-Seq, V(D)J sequencing, and Cite-Seq were performed using the 10X Chromium platform (5’-RNA, V(D)J, and CITE-Seq) de-multiplexed and processed using the CellRanger pipeline and analyzed with Seurat v4.0.0. V(D)J gene identities and % somatic hypermutation were determined for B cell receptors (BCR) using IMGT/HighV-QUEST. Seurat was used to merge these outputs with RNA-seq and CITE-seq data to enable integrated analysis of BCRs with transcriptomic and phenotypic profiling. Clonally expanded BCRs were identified and recombinantly expressed as monoclonal antibodies. Total IgG, Jo-1, LPS, dsDNA, and insulin binding were measured by ELISA.
Results: Five B cell subsets (transitional, naïve, activated, memory, plasmablast) were assigned based on isotype switching and gene expression (Fig. 1A-B). We identified 21 expanded clonotypes (defined as n ³ 3 per donor) amongst the five donors (Fig. 1C). Clonally expanded cells were CD27+ and CD21lo (Fig. 2) and were primarily IgM+ (non-class-switched) (Fig. 3A). Somatic hypermutation was highly variable and ranged from germline to very high (25%) (Fig. 3B). Recombinant expression of clonally expanded BCRs as IgG1 antibodies and ELISA binding studies revealed that 5/21 (24%) bound Jo-1. All Jo-1 binding clones exhibited some binding of dsDNA, LPS, or insulin, confirming polyreactivity. Multiple Jo-1 binding B cells expressed the VH4-34 heavy chain gene, which has been previously associated with autoimmunity.
Conclusion: Clonally expanded B cells in patients with Jo-1 ARS are enriched for anti-Jo1 B cells, which display an autoreactive-prone (CD21lo) memory phenotype. Somatic hypermutation analysis shows that germline recognition of Jo-1 autoantigen is possible, and that Jo-1-binding B cells can undergo extensive somatic hypermutation. Future studies will be required to determine if somatic hypermutation is associated with affinity maturation of Jo-1-binding B cells, and presumably enhanced pathogenicity.

Figure 1. Transcriptionally defined memory B cell subsets and clonally expanded cells are identified in ARS patients. The 10X Genomics single-cell platform was used to perform transcriptomic (RNA-seq) profiling of purified B lymphocytes isolated from n=5 Jo-1 ARS patients, n=5 non-Jo-1 ARS patients, and n=5 healthy donors (age and sex-matched). A) Transcriptionally defined clusters and B) selected gene expression were identified using Seurat. C) Integrated Seurat/IMGT/HighV-QUEST analysis identified clonally expanded B cells (teal) through single-cell immune repertoire profiling (BCR-seq) in Jo-1 ARS (left) and healthy donors (right).

Figure 2. Clonally expanded B cells isolated from Jo-1 ARS patients exhibit an autoreactive-prone memory (CD21lo CD27+) phenotype. CITE-seq was used to measure A) CD21 and B) CD27 expression in total B cells (top panels) or clonally expanded B cells (bottom panels) in Jo-1 ARS or healthy donors. Heatmaps indicate expression levels.

Figure 3. Clonally expanded B cells isolated from Jo-1 ARS patients underwent limited class switching and ranged from minimally to highly mutated BCRs. Integrated Seurat/IMGT/HighV-QUEST analysis of single-cell RNA-seq/BCR-seq data identified clonally expanded B cells from Jo-1 ARS patients (left) or total cells (right). A) isotype and B) percent variable heavy chain (VH) gene somatic hypermutation is shown. Heatmap indicates % somatic hypermutation.
L. Bass: None; D. Liu: None; A. Cisneros: None; J. Young-Glazer: Argenx, 5; L. Crofford: None; E. Wilfong: Boehringer-Ingelheim, 1, 5, 6, Cabaletta Bio, 1; R. Bonami: Argenx, 5.



