Abstract Session
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: Abstracts: RA – Treatments II: RA Treatment Safety (1675–1680)
1679: Effects of Janus Kinase Inhibitor on TNF-a and IL-6-Induced Osteoclasts and RANKL-Induced Osteoclasts in Peripheral Blood Monocytes from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Monday, November 13, 2023
5:00 PM - 5:10 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall A-B
- KY
Kazuhiro Yokota, MD, PhD
Department of Rheumatology and Applied Immunology, Faculty of Medicine, Saitama Medical University
Iruma-gun, JapanDisclosure information not submitted.
Presenting Author(s)
Kazuhiro Yokota1, Yoshimi Aizaki2, Takuma Tsuzuki Wada1, Hiroshi Kajiyama1, Yasuto Araki2, Hiroaki Yazawa2, Yuji Akiyama2 and Toshihide Mimura1, 1Department of Rheumatology and Applied Immunology, Faculty of Medicine, Saitama Medical University, Iruma-gun, Japan, 2Department of Rheumatology and Applied Immunology, Faculty of Medicine, Saitama Medical University, Saitama, Japan
Background/Purpose: We have previously demonstrated that a combination of TNF-a and IL-6 induces mouse osteoclast-like cells with bone resorption activity both in vitro and in vivo [Arthritis & Rheumatology (A&R), 2014]. Recently, we have shown that the combination of TNF-a and IL-6 induces osteoclasts (OCs) derived from human peripheral blood monocytes (PBMs) via RANKL-independent pathways in vitro. In particular, the number of TNF-a and IL-6-induced OCs differentiated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with RA had a significant positive correlation with the modified total Sharp score. On the other hand, the number of RANKL-induced OCs had a significant negative correlation with whole-body bone mineral density (A&R, 2021). We undertook the present study to clarify the effects of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor on TNF-a and IL-6-induced OCs and RANKL-induced OCs in PBMs derived from patients with RA or healthy donors (HDs).
Methods: PBMs derived from 5 RA patients and HDs were stimulated by TNF-α and IL-6 or RANKL with or without 100-1000 nM filgotinib, a JAK inhibitor. The number of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase-positive multinucleated cells and bone resorption activity using a pit formation assay were assessed. Quantitative RT-PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression levels of IL-1b and IL-8. Furthermore, the number of TNF-α and IL-6-induced or RANKL-induced OCs differentiated from PBMs in RA patients before and 6 months after treatment with filgotinib was examined.
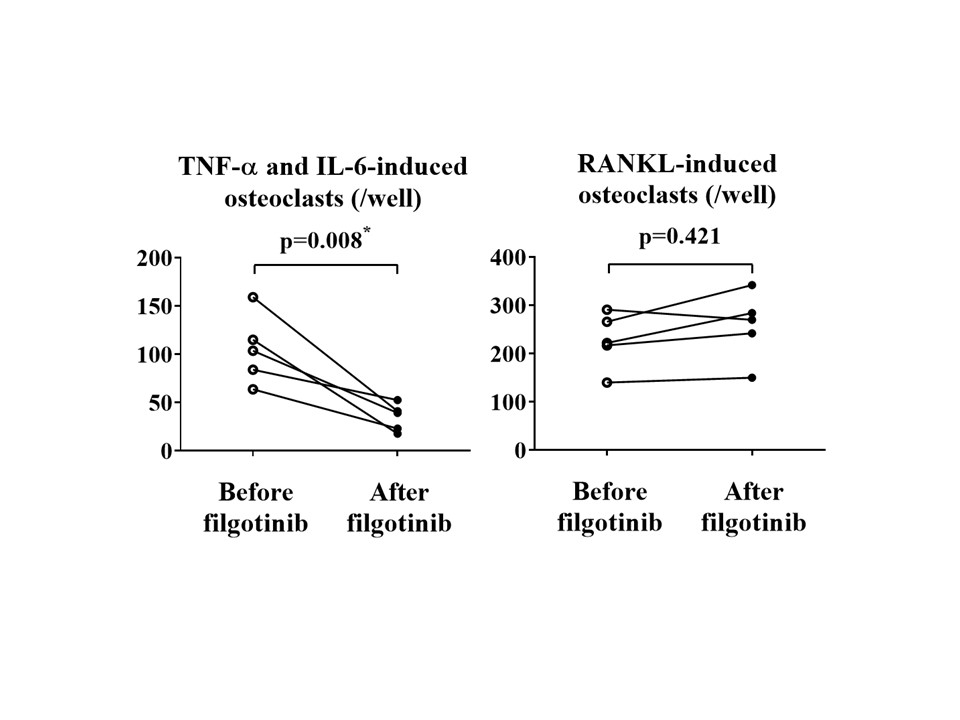
Results: The number of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs and RANKL-induced OCs derived from PBMs in RA patients was significantly increased compared to that in HDs (each n=5, p< 0.05). Filgotinib significantly inhibited the differentiation of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs derived from PBMs of RA patients in a dose-dependent manner (n=4, all p< 0.05). On the other hand, the same concentrations of filgotinib did not inhibit osteoclastogenesis induce by RANKL (n=4, all p >0.05). Resorption pits generated by TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs derived from HDs in the presence of filgotinib was reduced comparing with those without filgotinib. In contrast, filgotinib did not inhibit generation of resorption pits by RANKL-induced OCs (n=4). Levels of IL-1b and IL-8 mRNA expressed by TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs from RA patients, but not RANKL-induced OCs, were significantly reduced by filgotinib (each n=3, p< 0.05). Six months after treatment with filgotinib, the number of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs differentiated from PBMs was significantly decreased compared with those of before the treatment (n=5, p=0.008) (Figure). In contrast, no significant change in the number of RANKL-induced OCs by the six-months administration of the JAK inhibitor was observed in the same patients (n = 5, p=0.421).
Conclusion: Filgotinib inhibits TNF-α and IL-6-induced osteoclast differentiation in vitro. Administration of filgotinib reduces differentiation potential of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs in PBMs from RA patients. Our results suggest that the inhibitory mechanism of filgotinib on joint destruction in RA may be related to its inhibition of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs, presumed pathogenic OCs.
K. Yokota: None; Y. Aizaki: None; T. Wada: None; H. Kajiyama: None; Y. Araki: None; H. Yazawa: None; Y. Akiyama: None; T. Mimura: Gilead, 5.
Background/Purpose: We have previously demonstrated that a combination of TNF-a and IL-6 induces mouse osteoclast-like cells with bone resorption activity both in vitro and in vivo [Arthritis & Rheumatology (A&R), 2014]. Recently, we have shown that the combination of TNF-a and IL-6 induces osteoclasts (OCs) derived from human peripheral blood monocytes (PBMs) via RANKL-independent pathways in vitro. In particular, the number of TNF-a and IL-6-induced OCs differentiated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with RA had a significant positive correlation with the modified total Sharp score. On the other hand, the number of RANKL-induced OCs had a significant negative correlation with whole-body bone mineral density (A&R, 2021). We undertook the present study to clarify the effects of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor on TNF-a and IL-6-induced OCs and RANKL-induced OCs in PBMs derived from patients with RA or healthy donors (HDs).
Methods: PBMs derived from 5 RA patients and HDs were stimulated by TNF-α and IL-6 or RANKL with or without 100-1000 nM filgotinib, a JAK inhibitor. The number of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase-positive multinucleated cells and bone resorption activity using a pit formation assay were assessed. Quantitative RT-PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression levels of IL-1b and IL-8. Furthermore, the number of TNF-α and IL-6-induced or RANKL-induced OCs differentiated from PBMs in RA patients before and 6 months after treatment with filgotinib was examined.
Results: The number of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs and RANKL-induced OCs derived from PBMs in RA patients was significantly increased compared to that in HDs (each n=5, p< 0.05). Filgotinib significantly inhibited the differentiation of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs derived from PBMs of RA patients in a dose-dependent manner (n=4, all p< 0.05). On the other hand, the same concentrations of filgotinib did not inhibit osteoclastogenesis induce by RANKL (n=4, all p >0.05). Resorption pits generated by TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs derived from HDs in the presence of filgotinib was reduced comparing with those without filgotinib. In contrast, filgotinib did not inhibit generation of resorption pits by RANKL-induced OCs (n=4). Levels of IL-1b and IL-8 mRNA expressed by TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs from RA patients, but not RANKL-induced OCs, were significantly reduced by filgotinib (each n=3, p< 0.05). Six months after treatment with filgotinib, the number of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs differentiated from PBMs was significantly decreased compared with those of before the treatment (n=5, p=0.008) (Figure). In contrast, no significant change in the number of RANKL-induced OCs by the six-months administration of the JAK inhibitor was observed in the same patients (n = 5, p=0.421).
Conclusion: Filgotinib inhibits TNF-α and IL-6-induced osteoclast differentiation in vitro. Administration of filgotinib reduces differentiation potential of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs in PBMs from RA patients. Our results suggest that the inhibitory mechanism of filgotinib on joint destruction in RA may be related to its inhibition of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs, presumed pathogenic OCs.

Figure. Administration of filgotinib, a JAK inhibitor, for six months inhibits the differentiation of TNF-α and IL-6-induced osteoclasts in peripheral blood monocytes from patients with RA. Left; Six months after treatment with filgotinib, the number of TNF-α and IL-6-induced osteoclasts differentiated from peripheral blood monocytes was significantly decreased compared with those of before the treatment. Right; No significant change in the number of RANKL-induced osteoclasts was observed in the same patients (each n = 5). * = p < 0.05 between groups, Wilcoxon's signed rank test.
K. Yokota: None; Y. Aizaki: None; T. Wada: None; H. Kajiyama: None; Y. Araki: None; H. Yazawa: None; Y. Akiyama: None; T. Mimura: Gilead, 5.




