Poster Session C
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Session: (L01–L14) Late-Breaking Poster
L13: An Open-label, Multicenter, Phase 1/2 Study to Assess Safety, Efficacy and Cellular Kinetics of YTB323, a Rapid Manufacturing CAR-T Cell Therapy Targeting CD19 on B Cells, for Severe Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Preliminary Results
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- GC
Late-Breaking Poster Presenter(s)
Josefina Cortés Hernández1, Pere Barba2, Mònica Linares Alberich3, Ozana Fischer4, Beata Kovacs4, Thomas Calzascia4, David Pearson4, Ana-Laura Jordán Garrote5, Tiina Kirsilä4, Richard Siegel4, Tamas Shisha4, Giulio Cavalli4 and Peter Gergely4, 1Vall d'Hebron Institute of Research (VHIR) and Hospital Universitari Vall d'Hebron, Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain, 2Vall d'Hebron Institute of Oncology and Hospital Universitari Vall d'Hebron, Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain, 3Banc de Sang i Teixits, Hospital Universitari Vall d'Hebron, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain, 4Novartis Biomedical Research, Basel, Basel-Stadt, Switzerland, 5Novartis Farmacéutica, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is characterized by pathogenic autoreactive B cells producing autoantibodies against multiple self-antigens. Recently, a series of clinical cases suggested that traditionally manufactured anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T cell) therapies show potential to promote full clinical remission in severe refractory SLE (srSLE).1,2 This is the first clinical trial to evaluate the preliminary safety and efficacy of anti-CD19 CAR-T cell therapy in patients with srSLE. YTB323 is a novel, rapidly manufactured, autologous CAR-T cell therapy that has shown preserved T cell stemness and enhanced CAR-T cell efficacy in hematological malignancies.3
Methods: An open-label, single-arm, multicenter phase 1/2 study, CYTB323G12101 (NCT05798117), to assess the safety, efficacy and cellular kinetics of YTB323 in participants with srSLE is currently ongoing. A sentinel cohort of patients with srSLE (n=3), dosed with 12.5x106 cells at least 28 days apart, was enrolled. The primary endpoint was safety as measured by vital signs, adverse events, laboratory parameters and ECG evaluation. CAR-T cell kinetics were monitored by quantitative PCR and flow cytometry. Further relevant endpoints included changes from baseline levels in circulating B and T cells, autoantibody and complement levels, disease activity scores and renal outcome measures.
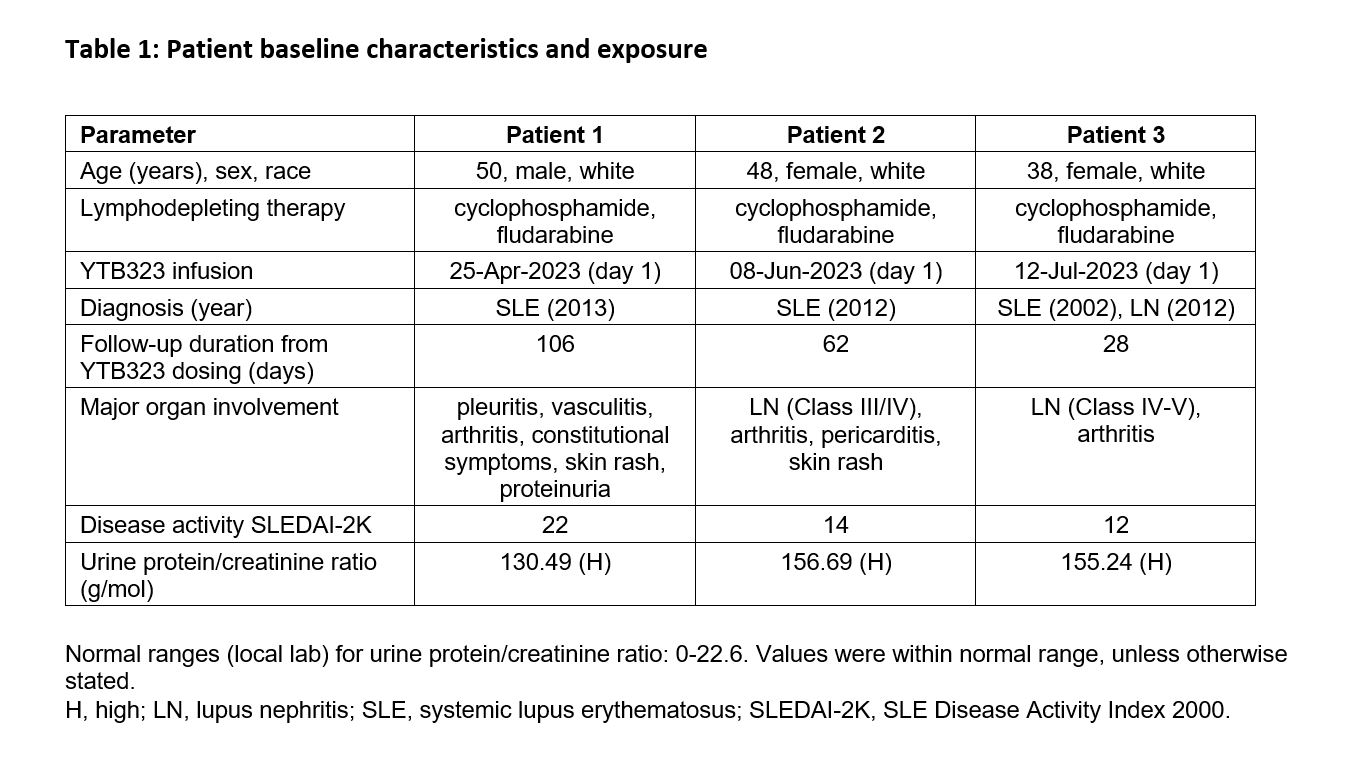
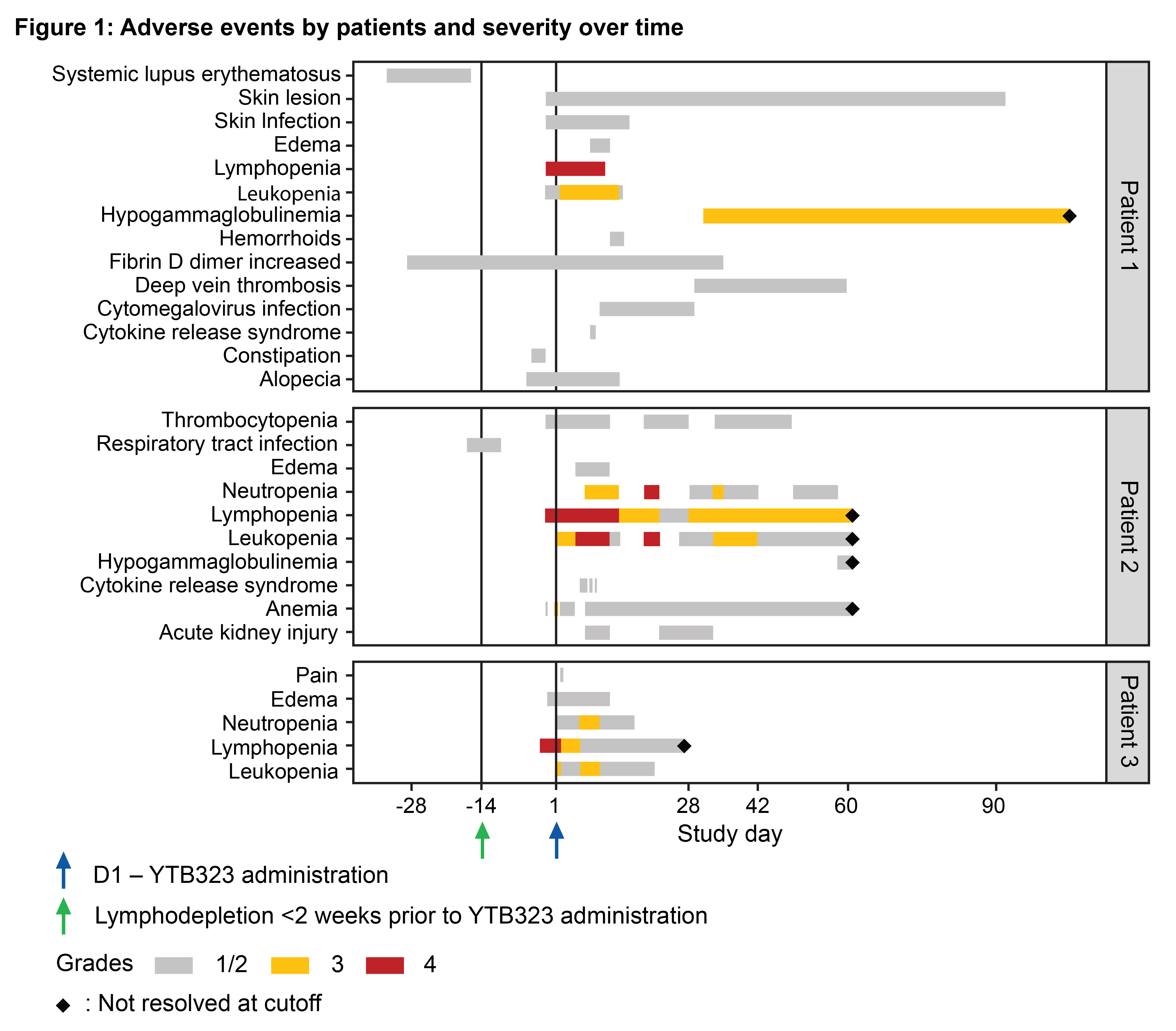
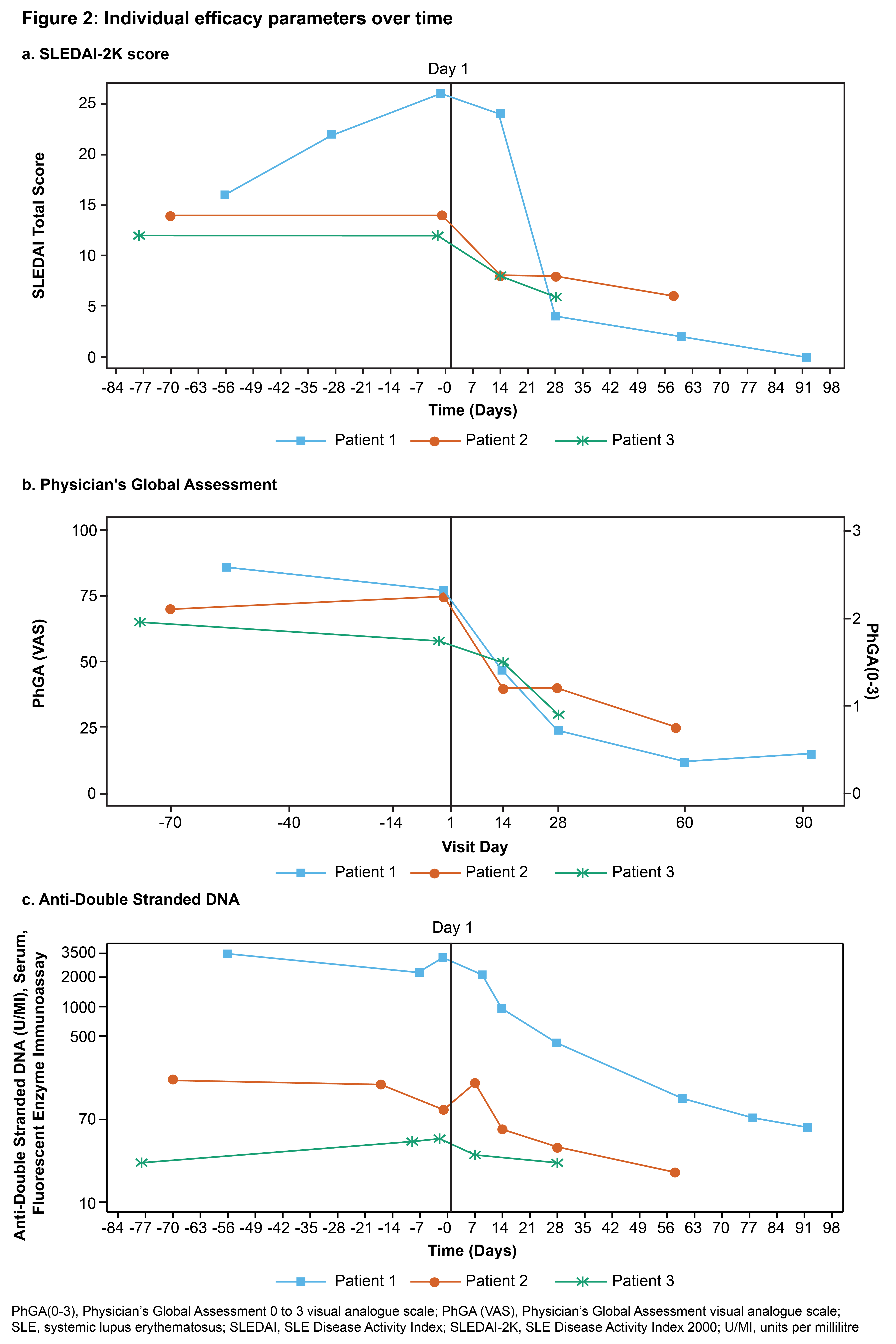
Results: Baseline characteristics of patients are summarized in Table 1. Adverse events are shown in Figure 1. No serious adverse events or deaths were reported. Following screening, the first patient experienced a worsening of disease during immunosuppressant washout prior to receiving lymphodepletion therapy. No immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) occurred. A grade 1 cytomegalovirus reactivation occurred in one patient, which was subsequently resolved. Two patients had cytokine release syndrome (grade 1 or 2); both responded well to tocilizumab treatment and fully recovered. As expected, grade 3 and 4 transient lymphodepletion-related cytopenias were observed in all patients. Grade 2 or 3 hypogammaglobulinemia was observed in two patients; neither event required intravenous immunoglobulin treatment. Cellular kinetics studies showed peak expansion (Tmax) at 13 and 18 days post-infusion for the two patients with available data characterizing the expansion phase. Transient T cell and sustained B cell depletion were observed in all patients. Preliminary efficacy data (Figure 2) suggest substantial decreases in SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) (Figure 2a) and Physician's Global Assessment (PhGA) (Figure 2b), in line with improvements in relevant disease biomarkers such as dsDNA (Figure 2c), complement levels and proteinuria.
Conclusion: Preliminary data from this clinical trial including the first three sentinel patients suggest favorable safety, CAR-T cell expansion, B cell depletion and initial efficacy, supporting continuation of the study to evaluate YTB323 in srSLE.
References
1. Mackensen et al. Nat Med (2022) 28:2124-32.
2. Schett et al. The EULAR Journal (2023) 93.
3. Dickinson et al. Cancer Discov (2023) 13:1982-1997.
An Open-label, Multicenter, Phase 1/2 Study to Assess Safety, Efficacy and Cellular Kinetics of YTB323, a Rapid Manufacturing CAR-T Cell Therapy Targeting CD19 on B Cells, for Severe Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Preliminary Results
J. Cortés Hernández: GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 6; P. Barba: Allogene, 1, 2, Amgen, 1, 2, BMS/Celgene, 1, 2, Incite, 1, 2, Kite/Gilead, 1, 2, Miltenyi Biomedicine, 1, 2, Nektar, 1, 2, Novartis, 1, 2, Pfizer, 1, 2, Pierre Fabre, 1, 2; M. Linares Alberich: None; O. Fischer: Novartis, 3; B. Kovacs: Novartis, 3; T. Calzascia: Novartis, 3; D. Pearson: Novartis, 3; A. Jordán Garrote: Novartis, 3; T. Kirsilä: Novartis, 3; R. Siegel: Novartis, 3; T. Shisha: Novartis, 3; G. Cavalli: Novartis, 3; P. Gergely: Novartis, 3.
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is characterized by pathogenic autoreactive B cells producing autoantibodies against multiple self-antigens. Recently, a series of clinical cases suggested that traditionally manufactured anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T cell) therapies show potential to promote full clinical remission in severe refractory SLE (srSLE).1,2 This is the first clinical trial to evaluate the preliminary safety and efficacy of anti-CD19 CAR-T cell therapy in patients with srSLE. YTB323 is a novel, rapidly manufactured, autologous CAR-T cell therapy that has shown preserved T cell stemness and enhanced CAR-T cell efficacy in hematological malignancies.3
Methods: An open-label, single-arm, multicenter phase 1/2 study, CYTB323G12101 (NCT05798117), to assess the safety, efficacy and cellular kinetics of YTB323 in participants with srSLE is currently ongoing. A sentinel cohort of patients with srSLE (n=3), dosed with 12.5x106 cells at least 28 days apart, was enrolled. The primary endpoint was safety as measured by vital signs, adverse events, laboratory parameters and ECG evaluation. CAR-T cell kinetics were monitored by quantitative PCR and flow cytometry. Further relevant endpoints included changes from baseline levels in circulating B and T cells, autoantibody and complement levels, disease activity scores and renal outcome measures.
Results: Baseline characteristics of patients are summarized in Table 1. Adverse events are shown in Figure 1. No serious adverse events or deaths were reported. Following screening, the first patient experienced a worsening of disease during immunosuppressant washout prior to receiving lymphodepletion therapy. No immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) occurred. A grade 1 cytomegalovirus reactivation occurred in one patient, which was subsequently resolved. Two patients had cytokine release syndrome (grade 1 or 2); both responded well to tocilizumab treatment and fully recovered. As expected, grade 3 and 4 transient lymphodepletion-related cytopenias were observed in all patients. Grade 2 or 3 hypogammaglobulinemia was observed in two patients; neither event required intravenous immunoglobulin treatment. Cellular kinetics studies showed peak expansion (Tmax) at 13 and 18 days post-infusion for the two patients with available data characterizing the expansion phase. Transient T cell and sustained B cell depletion were observed in all patients. Preliminary efficacy data (Figure 2) suggest substantial decreases in SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) (Figure 2a) and Physician's Global Assessment (PhGA) (Figure 2b), in line with improvements in relevant disease biomarkers such as dsDNA (Figure 2c), complement levels and proteinuria.
Conclusion: Preliminary data from this clinical trial including the first three sentinel patients suggest favorable safety, CAR-T cell expansion, B cell depletion and initial efficacy, supporting continuation of the study to evaluate YTB323 in srSLE.
References
1. Mackensen et al. Nat Med (2022) 28:2124-32.
2. Schett et al. The EULAR Journal (2023) 93.
3. Dickinson et al. Cancer Discov (2023) 13:1982-1997.



An Open-label, Multicenter, Phase 1/2 Study to Assess Safety, Efficacy and Cellular Kinetics of YTB323, a Rapid Manufacturing CAR-T Cell Therapy Targeting CD19 on B Cells, for Severe Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Preliminary Results
J. Cortés Hernández: GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 6; P. Barba: Allogene, 1, 2, Amgen, 1, 2, BMS/Celgene, 1, 2, Incite, 1, 2, Kite/Gilead, 1, 2, Miltenyi Biomedicine, 1, 2, Nektar, 1, 2, Novartis, 1, 2, Pfizer, 1, 2, Pierre Fabre, 1, 2; M. Linares Alberich: None; O. Fischer: Novartis, 3; B. Kovacs: Novartis, 3; T. Calzascia: Novartis, 3; D. Pearson: Novartis, 3; A. Jordán Garrote: Novartis, 3; T. Kirsilä: Novartis, 3; R. Siegel: Novartis, 3; T. Shisha: Novartis, 3; G. Cavalli: Novartis, 3; P. Gergely: Novartis, 3.



