Poster Session C
Metabolic bone disease
Session: (1996–2018) Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic & Clinical Science Poster
1998: How to Tailor Osteoporosis Therapies in Patients with Advanced Liver Disease? Variations of Renal Function by Creatinine and Cystatin C
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- CR
Cristina Rodríguez-Alvear, III, -None- (she/her/hers)
General University Hospital Dr. Balmis-ISABIAL
Alicante, SpainDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Cristina Rodríguez-Alvear1, Mª Carmen López-González2, Elisabet Perea-Martínez3, Antonio Avilés-Hernández3, Eduardo Garín Cascales3, Nuria Buendía Sánchez3, Irene Calabuig-Sais1, Pilar Bernabeu-Gonzálvez3, Agustín Martínez-Sanchís1, Joaquim Esteve-Vives3, PALOMA VELA4, Cayetano Miralles Maciá3, Vega Jovani5 and Mariano Andrés1, 1Dr Balmis Alicante General University Hospital-ISABIAL, Alicante, Spain, 2General University Hospital Dr. Balmis, Alacante, Spain, 3General University Hospital Dr. Balmis, Alicante, Spain, 4Rheumatology, Hospital General Universitario Alicante, Alicante, Spain, 5Department of Rheumatology, Hospital General Universitario Dr. Balmis, Alicante, Spain
Background/Purpose: Rapid bone loss and increased fractures have been described after liver transplantation. Bisphosphonates are restricted in patients with significant kidney disease, as the drugs are excreted by the urine. Evaluating renal function in patients with advanced liver cirrhosis can be challenging and underestimated by standard methods, and this issue may impact the choice of the anti-osteoporosis (OP) agent.
This study analyses variations in renal function across different glomerular filtration rate (GFR) equations in patients with advanced liver disease included in a pre-transplantation assessment to tailor the use of anti-OP agents.
Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional study of patients from a tertiary center selected for a assessment before liver transplantation from February 2019 to December 2022. Sex, age, ethnicity, and serum creatinine and cystatin C (a more sensitive marker than creatinine for estimating GFR in patients with cirrhosis) levels are collected. The indication for anti-OP treatment is established in the presence of T< -1.0 by densitometry (DXA), vertebral radiographic wedging, or a history of a fragility fracture. GFR adjusted by creatinine, cystatin C, and creatinine-cystatin C was calculated using the online calculation tool MediCalc. Results are later categorized as below or above 30ml/min2 (usual cut-off to contraindicate the use of bisphosphonates), finally comparing the rate of patients with GFR < 30 ml/min across three methods. A descriptive study is presented. Comparisons of variables are performed by Fisher's exact test, and P-values of < 0.05 are considered statistically significant.
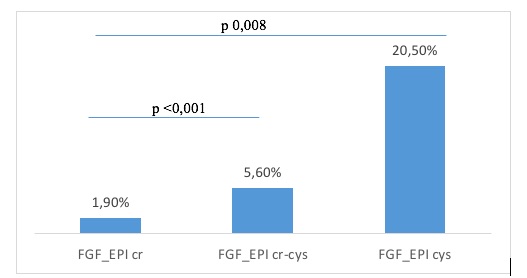
Results: A total of 162 patients (75.9% men) were included, all Caucasian, with a mean age of 60 years (SD 7.6) and a mean BMI of 27.9 (SD 4.9). Seventy-six percent (n=120) were candidates for anti-OP therapy, and 68.5% (n=111) ultimately received it (88% bisphosphonates, 11% denosumab, and 1% teriparatide). Three percent (n=5) presented a fragility fracture, and 9.5% (n=17) showed a radiographic vertebral fracture. Fifty-one percent (n=80) had osteopenia, and 22.9% (n=36) had osteoporosis at DXA scans. Regarding renal function, mean serum creatinine and cystatin C levels were 0.99 mg/dl (SD 1) and 1.7 mg/L (SD 1), respectively. The mean estimated GFR levels using creatinine, cystatin C and creatinine-cystatin were 87 ml/min (SD 24.8), 49.3 (SD 23.4), and 63.9 (SD 23.3), respectively. The percentage of patients with GFR < 30ml/min was 1.9% if measured by creatinine, 20.5% by cystatin, and 5.6% by creatinine-cystatin (figure 1). Differences between rates were statistically significant. In this sense, anti-OP therapy was tailored accordingly in 12 patients (10.9%) with treatment indication, using denosumab instead of bisphosphonates.
Conclusion: In a setting of advanced liver disease eligible for transplantation, renal function estimates significantly varied depending on the GFR equation used, thus largely modifying the rates of patients with a contraindication for using bisphosphonates, despite the high fracture risk. Further studies are necessary to establish the best method to assess renal function in advanced liver disease patients to tailor anti-OP strategies.
C. Rodríguez-Alvear: None; M. López-González: None; E. Perea-Martínez: None; A. Avilés-Hernández: None; E. Garín Cascales: None; N. Buendía Sánchez: None; I. Calabuig-Sais: None; P. Bernabeu-Gonzálvez: None; A. Martínez-Sanchís: None; J. Esteve-Vives: None; P. VELA: AbbVie/Abbott, 5, AstraZeneca, 5, Eli Lilly, 5, 6, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 6, Novartis, 5, Pfizer, 5; C. Miralles Maciá: None; V. Jovani: None; M. Andrés: None.
Background/Purpose: Rapid bone loss and increased fractures have been described after liver transplantation. Bisphosphonates are restricted in patients with significant kidney disease, as the drugs are excreted by the urine. Evaluating renal function in patients with advanced liver cirrhosis can be challenging and underestimated by standard methods, and this issue may impact the choice of the anti-osteoporosis (OP) agent.
This study analyses variations in renal function across different glomerular filtration rate (GFR) equations in patients with advanced liver disease included in a pre-transplantation assessment to tailor the use of anti-OP agents.
Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional study of patients from a tertiary center selected for a assessment before liver transplantation from February 2019 to December 2022. Sex, age, ethnicity, and serum creatinine and cystatin C (a more sensitive marker than creatinine for estimating GFR in patients with cirrhosis) levels are collected. The indication for anti-OP treatment is established in the presence of T< -1.0 by densitometry (DXA), vertebral radiographic wedging, or a history of a fragility fracture. GFR adjusted by creatinine, cystatin C, and creatinine-cystatin C was calculated using the online calculation tool MediCalc. Results are later categorized as below or above 30ml/min2 (usual cut-off to contraindicate the use of bisphosphonates), finally comparing the rate of patients with GFR < 30 ml/min across three methods. A descriptive study is presented. Comparisons of variables are performed by Fisher's exact test, and P-values of < 0.05 are considered statistically significant.
Results: A total of 162 patients (75.9% men) were included, all Caucasian, with a mean age of 60 years (SD 7.6) and a mean BMI of 27.9 (SD 4.9). Seventy-six percent (n=120) were candidates for anti-OP therapy, and 68.5% (n=111) ultimately received it (88% bisphosphonates, 11% denosumab, and 1% teriparatide). Three percent (n=5) presented a fragility fracture, and 9.5% (n=17) showed a radiographic vertebral fracture. Fifty-one percent (n=80) had osteopenia, and 22.9% (n=36) had osteoporosis at DXA scans. Regarding renal function, mean serum creatinine and cystatin C levels were 0.99 mg/dl (SD 1) and 1.7 mg/L (SD 1), respectively. The mean estimated GFR levels using creatinine, cystatin C and creatinine-cystatin were 87 ml/min (SD 24.8), 49.3 (SD 23.4), and 63.9 (SD 23.3), respectively. The percentage of patients with GFR < 30ml/min was 1.9% if measured by creatinine, 20.5% by cystatin, and 5.6% by creatinine-cystatin (figure 1). Differences between rates were statistically significant. In this sense, anti-OP therapy was tailored accordingly in 12 patients (10.9%) with treatment indication, using denosumab instead of bisphosphonates.
Conclusion: In a setting of advanced liver disease eligible for transplantation, renal function estimates significantly varied depending on the GFR equation used, thus largely modifying the rates of patients with a contraindication for using bisphosphonates, despite the high fracture risk. Further studies are necessary to establish the best method to assess renal function in advanced liver disease patients to tailor anti-OP strategies.

Figure 1. Patients with GFR <30 ml/min by different equations
C. Rodríguez-Alvear: None; M. López-González: None; E. Perea-Martínez: None; A. Avilés-Hernández: None; E. Garín Cascales: None; N. Buendía Sánchez: None; I. Calabuig-Sais: None; P. Bernabeu-Gonzálvez: None; A. Martínez-Sanchís: None; J. Esteve-Vives: None; P. VELA: AbbVie/Abbott, 5, AstraZeneca, 5, Eli Lilly, 5, 6, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 6, Novartis, 5, Pfizer, 5; C. Miralles Maciá: None; V. Jovani: None; M. Andrés: None.



