Poster Session B
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (1264–1307) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
1307: Impact of Comorbidities on the First bDMARD Effectiveness and Retention Rate After 2 Years of Follow-up in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Data from the Spanish Registry BIOBADASER
Monday, November 13, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
.jpg)
Clementina Lopez-Medina, MD
Reina Sofia University Hospital
Cordoba, SpainDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Clementina López Medina1, Jerusalem Calvo2, Lucia Otero-Valera3, Alejandro Escudero Contreras2, Rafaela Ortega Castro4, Lourdes Ladehesa Pineda5, Cristina Campos6, Pilar Bernabeu-Gonzálvez7, Cristina Bohorquez8, Alicia Garcia Dorta9, Dolores Ruiz-Montesinos10, Manuel Enrique Pombo Suarez11, Inmaculada Ros12, Fernando Alonso3 and Isabel Castrejon13, 1Rheumatology Department, Cochin Hospital; INSERM (U1153): Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, University of Paris; Rheumatology Department, Reina Sofia Hospital, Cordoba / IMIBIC / University of Cordoba, Cordoba, Spain, 2Reina Sofia University Hospital, Córdoba, Spain, 3Spanish Society of Rheumatology, Madrid, Spain, 4Hospital Reina Sofía, Cordoba, Spain, 5Rheumatology Department Reina Sofia Universitary Hospital, Cordoba, Spain, 6Rheumatology Unit, Hospital General Universitario de Valencia, Valencia, Spain, 7General University Hospital Dr. Balmis, Alicante, Spain, 8Rheumatology Unit, Hospital Universitario Príncipe de Asturias, Alcalá de Henares, Spain, 9Rheumatology Unit, Hospital Universitario de Canarias, Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain, 10Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Sevilla, Spain, 11Hospital Clínico Universitario, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 12Rheumatology Department HUSLL, Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 13Hospital Universitario Gregorio Marañón, Madrid, Spain
Background/Purpose: Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) have a higher prevalence of comorbidities, compared to the general population. The presence of such comorbidities has been directly associated with an increased disease activity. However, little is known about the impact of comorbidities in the therapeutic response and in the retention rate. Objectives: a) To evaluate the effect of comorbidities on the first biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) effectiveness in patients with RA after 2 years of follow-up, and b) to determine the influence of such comorbidities on the first bDMARD retention rate.
Methods: The study population consisted of patients with a diagnosis of RA and exposed to a first bDMARDs, included in BIOBADASER. BIOBADASER is a prospective, large national drug safety registry of patients with rheumatic diseases exposed to b- or tsDMARDs. Patients were classified in two groups at baseline according to the Charlson Comorbidity index (CCI) score: < 3 and ≥3. Patients achieving remission (DAS28< 2.6) at 1 and 2-years timepoints after the anti-TNF initiation were compared between the two groups using chi-square test. The absolute DAS28 score over time was compared between both groups of patients using a linear regression model adjusted for sex and age, and considering the follow-up visit as covariate. Finally, the first bDMARD retention rate was compared between patients < 3 and ≥3 using Log-Rank test and Kaplan-Meier curve.
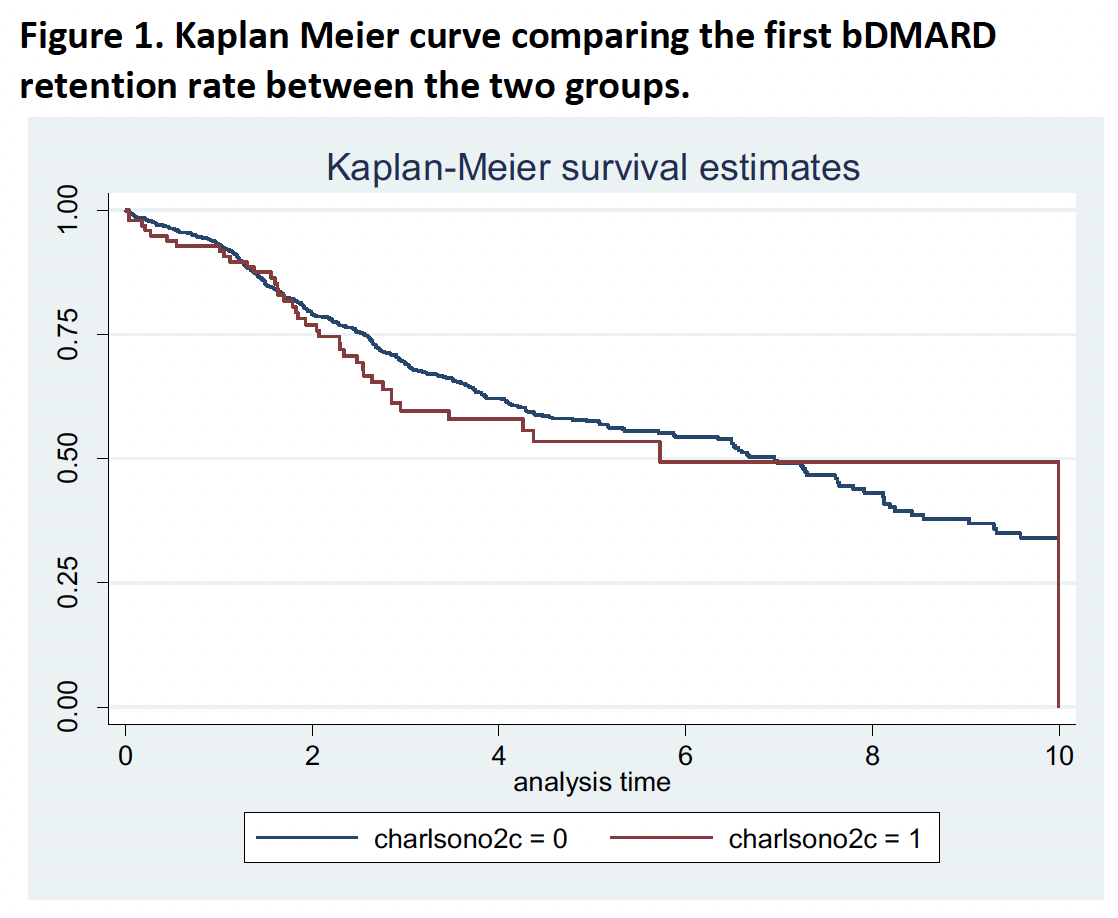
Results: A total of 1253 patients initiating bDMARD were included (76.6% female and mean age 56 years at the beginning of therapy). Overall, 107 (9%) patients had a CCI ≥3, being diabetes the most frequent comorbidity (5.0%). No differences were found in DAS28< 2.6 between patients with CCI< 3 and CCI≥3 after 1 year of follow-up (48.2% vs. 44.2%, p-value=0.457), nor after 2 years (50.8% vs. 40.7%, p-value=0.135). The linear regression model showed significant higher scores in DAS28 over the two years in patients with a CCI ≥3 after adjusting for age and sex (beta coefficient 0.27, 95%CI: 0.02-0.51; p-value=0.034). Finally, no differences in the bDMARD retention rate were found between both groups (median 2.6 years [IQR: 1.5-4.1] in CCI< 3 vs. 2.1 years [IQR: 0.6-3.7] in CCI≥3; log rank test p-value 0.467) (Figure).
Conclusion: These data suggest that a higher CCI in patients with RA is associated with greater DAS28 scores during the first two years after bDMARD initiation, although no differences in remission status were found. In addition, a slightly shorter retention rate was found in patients with CCI≥3, although the difference was non-significant. These results suggest a lower probability of disease activity control in patients with comorbidities after the initiation of bDMARD.
C. López Medina: AbbVie, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, 6, Janssen, 6, MSD, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, UCB Pharma, 2, 5, 6; J. Calvo: None; L. Otero-Valera: None; A. Escudero Contreras: None; R. Ortega Castro: None; L. Ladehesa Pineda: None; C. Campos: None; P. Bernabeu-Gonzálvez: None; C. Bohorquez: None; A. Garcia Dorta: None; D. Ruiz-Montesinos: None; M. Pombo Suarez: Janssen, 6, MSD Spain, 6; I. Ros: Janssen, 6, novartis, 6, Pfizer, 6; F. Alonso: None; I. Castrejon: Bristol Myers Squibb, 1, 6, Galapagos, 2, GlaxoSmithKline, 1, 6, Lilly, 1, 6, Merck Sharp & Dohme, 6, Pfizer, 1, 2, 6.
Background/Purpose: Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) have a higher prevalence of comorbidities, compared to the general population. The presence of such comorbidities has been directly associated with an increased disease activity. However, little is known about the impact of comorbidities in the therapeutic response and in the retention rate. Objectives: a) To evaluate the effect of comorbidities on the first biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) effectiveness in patients with RA after 2 years of follow-up, and b) to determine the influence of such comorbidities on the first bDMARD retention rate.
Methods: The study population consisted of patients with a diagnosis of RA and exposed to a first bDMARDs, included in BIOBADASER. BIOBADASER is a prospective, large national drug safety registry of patients with rheumatic diseases exposed to b- or tsDMARDs. Patients were classified in two groups at baseline according to the Charlson Comorbidity index (CCI) score: < 3 and ≥3. Patients achieving remission (DAS28< 2.6) at 1 and 2-years timepoints after the anti-TNF initiation were compared between the two groups using chi-square test. The absolute DAS28 score over time was compared between both groups of patients using a linear regression model adjusted for sex and age, and considering the follow-up visit as covariate. Finally, the first bDMARD retention rate was compared between patients < 3 and ≥3 using Log-Rank test and Kaplan-Meier curve.
Results: A total of 1253 patients initiating bDMARD were included (76.6% female and mean age 56 years at the beginning of therapy). Overall, 107 (9%) patients had a CCI ≥3, being diabetes the most frequent comorbidity (5.0%). No differences were found in DAS28< 2.6 between patients with CCI< 3 and CCI≥3 after 1 year of follow-up (48.2% vs. 44.2%, p-value=0.457), nor after 2 years (50.8% vs. 40.7%, p-value=0.135). The linear regression model showed significant higher scores in DAS28 over the two years in patients with a CCI ≥3 after adjusting for age and sex (beta coefficient 0.27, 95%CI: 0.02-0.51; p-value=0.034). Finally, no differences in the bDMARD retention rate were found between both groups (median 2.6 years [IQR: 1.5-4.1] in CCI< 3 vs. 2.1 years [IQR: 0.6-3.7] in CCI≥3; log rank test p-value 0.467) (Figure).
Conclusion: These data suggest that a higher CCI in patients with RA is associated with greater DAS28 scores during the first two years after bDMARD initiation, although no differences in remission status were found. In addition, a slightly shorter retention rate was found in patients with CCI≥3, although the difference was non-significant. These results suggest a lower probability of disease activity control in patients with comorbidities after the initiation of bDMARD.

C. López Medina: AbbVie, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, 6, Janssen, 6, MSD, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, UCB Pharma, 2, 5, 6; J. Calvo: None; L. Otero-Valera: None; A. Escudero Contreras: None; R. Ortega Castro: None; L. Ladehesa Pineda: None; C. Campos: None; P. Bernabeu-Gonzálvez: None; C. Bohorquez: None; A. Garcia Dorta: None; D. Ruiz-Montesinos: None; M. Pombo Suarez: Janssen, 6, MSD Spain, 6; I. Ros: Janssen, 6, novartis, 6, Pfizer, 6; F. Alonso: None; I. Castrejon: Bristol Myers Squibb, 1, 6, Galapagos, 2, GlaxoSmithKline, 1, 6, Lilly, 1, 6, Merck Sharp & Dohme, 6, Pfizer, 1, 2, 6.



