Abstract Session
Vasculitis
Session: Abstracts: Vasculitis – ANCA-Associated II (2491–2496)
2496: HXB-319, a New Generation Mesenchymal Stromal Cell (MSC) Therapy, Alleviates Neutrophilic Inflammation, and End-organ Damage in Pulmonary Renal Syndromes by Inducing FoxP3+ Tregs, and by Promoting TNFα-stimulated gene-6 (TSG-6) over Expression
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
3:15 PM - 3:25 PM PT
Location: Ballroom 20A
- HB
Hulya Bukulmez, MD (she/her/hers)
MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University
Cleveland, OH, United StatesDisclosure information not submitted.
Presenting Author(s)
Hulya Bukulmez1, Adrienne Dennis1, Jane Reese-Koc2, Scott Sieg2 and Steven Emancipator2, 1MetroHealth Medical Center, Department of Pediatrics, Cleveland, OH, 2Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH
Background/Purpose: Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) have been shown to be safe therapies in more than 100 human clinical trials. However, MSCs clinical efficacy is variable, and has been dependent on the severity of the inflammatory disease activity. MSC therapies have NOT been FDA approved for any disease indication, mostly due to lack of uniform potency and lack of specificity targeting the varying aspects of autoimmune diseases.
We developed a novel MSC-based cell therapy (HXB-319) that potently reduces inflammation and potentially halts organ damage in autoimmune pulmonary renal syndromes.
Methods: Using a combination of cytokines and growth factors that mimicked severe autoimmune disease microenvironment, we engineered a novel bone marrow derived MSC based cell therapy (HXB-319). We then verified its anti-inflammatory activity by flow cytometry, RT-PCR, and mass spectrophotometry in vitro. Next, In vivo efficacy was assessed by treating autoimmune induced DAH in C57Bl/6 mice by intraperitoneal (IP) injection of pristane. Seven days later, some mice were treated with either MSCs or HXB-319 (2X106 cells, IP). At day 14, peritoneal lavage fluid and lung tissue were sampled.
Results: HXB-319 cells showed significantly increased expression of anti-inflammatory genes (indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), TSG-6 and CD-274), and markers of angiogenesis (vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and CD-146).
Protein pathway analysis of HXB-319 culture media (secretome) showed significant upregulation of protein pathways that reduce inflammation (IL1RN, IDO), and fibrosis with upregulation of HGF, c-MET signaling, matrix metalloproteinase secretion (MMP1, MMP13), and downregulation of TGF-β via Activin pathway, while inducing vascularization (VEGF).
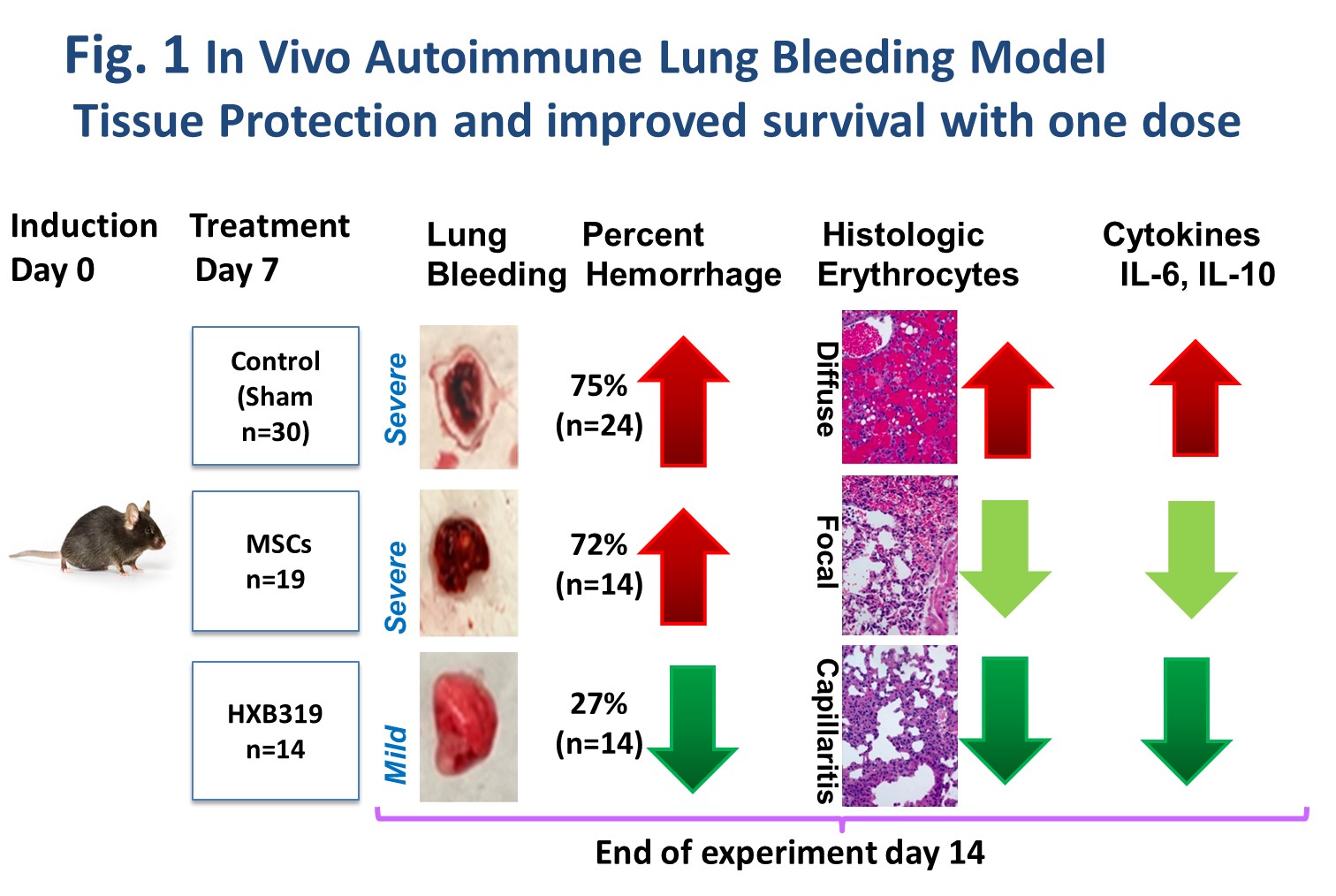
Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH) model (C57bl/6 mouse induced by 0.5 cc IP pristane injection) was utilized for proof-of-concept in vivo studies. In the DAH model, the mortality is typically above 75% beyond 14 days after pristane injection.
When delivered in vivo to the DAH mice,HXB-319 significantly reduced lung inflammation and alveolar hemorrhage (27.2%) vs. naked MSC treatment (75%) (Fig.1). Pulmonary gene expression of IL-6 and 1L-10, and serum IL-1β levels were significantly reduced by HXB-319 when measured at day 14.
Peritoneal lavage fluid from DAH mice treated with HXB-319 showed reductions in total cells recovered, neutrophils, monocytes, and NK cells compared to mice given MSCs or untreated DAH mice, the reduction in neutrophils was the most statistically significant result (Table 1). DAH mouse treatment with HXB-319 cells, also significantly decreased the proportion of RORγT cells (Th17) in both CD4+ and CD8+ populations, and significantly increased the proportion of FoxP3+ cells among CD4+ cells (Tregs).
Conclusion: Novel HXB-319 cell therapy, phenotypically engineered to control inflammation, is a potent anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and angiogenic cell therapy. HXB-319 may suppress severe autoimmune disease activity, and end organ damage in DAH, particularly by excessive induction of anti inflammatory activity via IDO, and over expression of TSG-6, increased CD4+ Tregs and significant suppressive effects on neutrophil population.
.jpg)
H. Bukulmez: None; A. Dennis: None; J. Reese-Koc: None; S. Sieg: None; S. Emancipator: None.
Background/Purpose: Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) have been shown to be safe therapies in more than 100 human clinical trials. However, MSCs clinical efficacy is variable, and has been dependent on the severity of the inflammatory disease activity. MSC therapies have NOT been FDA approved for any disease indication, mostly due to lack of uniform potency and lack of specificity targeting the varying aspects of autoimmune diseases.
We developed a novel MSC-based cell therapy (HXB-319) that potently reduces inflammation and potentially halts organ damage in autoimmune pulmonary renal syndromes.
Methods: Using a combination of cytokines and growth factors that mimicked severe autoimmune disease microenvironment, we engineered a novel bone marrow derived MSC based cell therapy (HXB-319). We then verified its anti-inflammatory activity by flow cytometry, RT-PCR, and mass spectrophotometry in vitro. Next, In vivo efficacy was assessed by treating autoimmune induced DAH in C57Bl/6 mice by intraperitoneal (IP) injection of pristane. Seven days later, some mice were treated with either MSCs or HXB-319 (2X106 cells, IP). At day 14, peritoneal lavage fluid and lung tissue were sampled.
Results: HXB-319 cells showed significantly increased expression of anti-inflammatory genes (indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), TSG-6 and CD-274), and markers of angiogenesis (vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and CD-146).
Protein pathway analysis of HXB-319 culture media (secretome) showed significant upregulation of protein pathways that reduce inflammation (IL1RN, IDO), and fibrosis with upregulation of HGF, c-MET signaling, matrix metalloproteinase secretion (MMP1, MMP13), and downregulation of TGF-β via Activin pathway, while inducing vascularization (VEGF).
Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH) model (C57bl/6 mouse induced by 0.5 cc IP pristane injection) was utilized for proof-of-concept in vivo studies. In the DAH model, the mortality is typically above 75% beyond 14 days after pristane injection.
When delivered in vivo to the DAH mice,HXB-319 significantly reduced lung inflammation and alveolar hemorrhage (27.2%) vs. naked MSC treatment (75%) (Fig.1). Pulmonary gene expression of IL-6 and 1L-10, and serum IL-1β levels were significantly reduced by HXB-319 when measured at day 14.
Peritoneal lavage fluid from DAH mice treated with HXB-319 showed reductions in total cells recovered, neutrophils, monocytes, and NK cells compared to mice given MSCs or untreated DAH mice, the reduction in neutrophils was the most statistically significant result (Table 1). DAH mouse treatment with HXB-319 cells, also significantly decreased the proportion of RORγT cells (Th17) in both CD4+ and CD8+ populations, and significantly increased the proportion of FoxP3+ cells among CD4+ cells (Tregs).
Conclusion: Novel HXB-319 cell therapy, phenotypically engineered to control inflammation, is a potent anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and angiogenic cell therapy. HXB-319 may suppress severe autoimmune disease activity, and end organ damage in DAH, particularly by excessive induction of anti inflammatory activity via IDO, and over expression of TSG-6, increased CD4+ Tregs and significant suppressive effects on neutrophil population.

In vivo validation of HXB-319 mechanism of action
.jpg)
Table 1: Flow cytometry analysis of post mortem peritoneal lavage fluid of DAH model
H. Bukulmez: None; A. Dennis: None; J. Reese-Koc: None; S. Sieg: None; S. Emancipator: None.



