Poster Session A
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (0380–0422) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
0384: Targeting NET Formation in Early RA Patients; A Spin-off Study from the NORD-STAR
Sunday, November 12, 2023
9:00 AM - 11:00 AM PT
Location: Poster Hall
- MN
Michael T. Nurmohamed, MD, PhD
Amsterdam University Medical Centers & Reade Amsterdam
Kortenhoef, NetherlandsDisclosure information not submitted.
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Bas Dijkshoorn1, Ting Wang2, Gerdur Maria Grondal3, Daisy Vedder4, Anna Rudin5, Dan Nordstrom6, Bjorn Gudbjornsson7, Kristina Lend8, Till Uhlig9, Espen Haavardsholm9, Merete L Hetland10, Marte Schrumpf Heiberg11, Mikkel Østergaard12, Kim Horslev-Petersen13, John Lampa14, Ronald van Vollenhoven15, Christian Lood2 and Michael Nurmohamed16, 1Amsterdam Rheumatology and Immunology Center, Location Reade, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2University of Washington, Seattle, WA, 3Department for Rheumatology, Landspitali University Hospital, Reykjavik, Iceland, 4Reade, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 5Department of Rheumatology and Inflammation Research, Institute of Medicine, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden, 6Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland, 7Centre for Rheumatology Research, University Hospital, Reykjavik, Iceland, 8Amsterdam UMC, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden, 9Center for Treatment of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases (REMEDY), Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, Norway, 10Copenhagen Center for Arthritis Research, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, Denmark, 11Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, Norway, 12Copenhagen Center for Arthritis Research, Center for Rheumatology and Spine Diseases, Centre for Head and Orthopaedics, Rigshospitalet; University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark, 13Danish Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Sønderborg, Denmark, 14Stockholm County, Hãsselby, Sweden, 15Amsterdam University Medical Centers, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 16Amsterdam University Medical Centers, Kortenhoef, Netherlands
Background/Purpose: The formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) with extrusion of nuclear, granular and cytosolic components from a dying neutrophil, has been described extensively in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and linked to generation of autoantigens (e.g. citrullinated proteins), inflammation and organ damage. Thus far there have been very few studies describing the effect of treatment in patients with RA on NET formation, and no studies comparing the effects of treatment strategies in (very) early RA. The objective of the study is to assess the effects of different initial treatments on NET formation in patients with early RA.
Methods: NORD-STAR is an international, multicenter, open-label, assessor-blinded, phase 4 study where patients with newly diagnosed RA started methotrexate (MTX) and were randomized 1:1:1:1 to a) conventional treatment (either prednisolone tapered to 5mg/day, or sulfasalazine combined with hydroxychloroquine and intra-articular corticosteroids), b) certolizumab pegol, c) abatacept, or d) tocilizumab1. This study is a spin-off from the main NORD-STAR study measuring neutrophil biomarkers MPO-DNA (Myeloperoxidase-DNA; NETs) and calprotectin in 24 consecutive Dutch participants and 94 Swedish patients at baseline, 12 weeks and 24 weeks after the start of the treatment. Statistical analysis was done using the Wilcoxon Signed Rank test for paired samples and independent samples median test to compare patients to healthy controls in SPSS version 28.
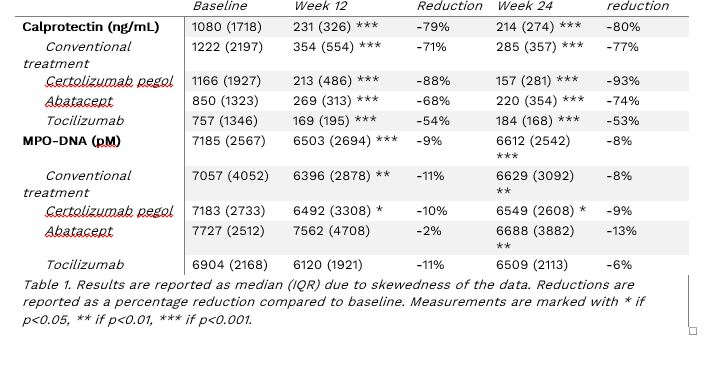
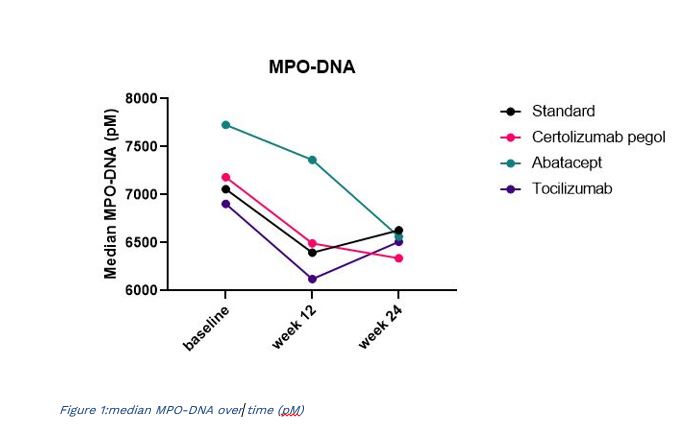
Results: At baseline patients had elevated levels of NETs and neutrophil activation compared to healthy controls as indicated by calprotectin (median 1080ng/ml vs 133ng/ml, p< 0.001) and elevated MPO-DNA (median 7185pM vs 3976pM, p< 0.001). Both of the biomarkers decreased significantly at 12 and 24 weeks after treatment in the total group demonstrating reduced neutrophil activity and NET formation. After 24 weeks of treatment, calprotectin was significantly reduced in all groups by up to 93% (Table 1). MPO-DNA showed a more modest reduction of up to 13%, and was relatively similar in all groups, although the reduction in MPO-DNA did not reach statistical significance in the tocilizumab group.
Conclusion: These results indicate highly elevated neutrophil activation and NET formation in recently diagnosed RA patients. All four treatments studied here reduced these detrimental processes within 3 months. The calprotectin reduction seen in this study is in line with an earlier spin-off study2. The rapid decline in these markers may have contributed to the minimal radiological progression that was seen in the NORD-STAR trial.
References:
[1] Hetland M et al. BMJ. 2020
[2] Stevens D et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022
B. Dijkshoorn: Galapagos, 2, Novartis, 2; T. Wang: None; G. Grondal: None; D. Vedder: None; A. Rudin: AstraZeneca, 12, financial support; D. Nordstrom: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, BMS, 2, Lilly, 2, MSD, 2, Novartis, 2, Pfizer, 2, UCB, 2; B. Gudbjornsson: Nordic-Pharma, 6, Novartis, 2, 6; K. Lend: None; T. Uhlig: Galapagos, 2, 6, Lilly, 2, 6, Novartis, 2, 6, Pfizer, 2, 6, UCB, 2, 6; E. Haavardsholm: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, Boehringer-Ingelheim, 2, Eli Lilly, 2, Gilead, 2, Pfizer, 6, UCB, 6; M. Hetland: AbbVie/Abbott, 1, 5, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 5, Danbio, 12, MLH has chaired the steering committee of the Danish Rheumatology Quality Registry (DANBIO, DRQ), which receives public funding from the hospital owne, Eli Lilly, 5, MEDAC, 6, Novartis, 5, Pfizer, 5, 6, Sandoz, 5, 6; M. Schrumpf Heiberg: Roche, 6; M. Østergaard: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Amgen, 5, Boehringer-Ingelheim, 2, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, 5, 6, Celgene, 2, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 6, Galapagos, 2, 6, Gilead, 2, 6, Hospira, 2, 6, Janssen, 2, 6, MEDAC, 6, Merck, 2, 5, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Novo Nordisk, 2, 6, Orion, 2, 6, Pfizer, 2, 6, Regeneron, 2, 6, Roche, 2, 6, Sandoz, 2, 6, Sanofi, 2, 6, UCB, 2, 6; K. Horslev-Petersen: None; J. Lampa: None; R. van Vollenhoven: AbbVie, 2, 6, AstraZeneca, 2, 5, 6, Biogen, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, 5, 6, Galapagos, 2, 5, 6, GlaxoSmithKline, 6, Janssen, 2, 6, MSD/Merck Sharp and Dohme, 5, Novartis, 5, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, RemeGen, 2, Roche, 5, Sanofi, 5, UCB, 2, 5, 6; C. Lood: Amytryx, 5, Boehringer-Ingelheim, 5, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 5, Citryll, 2, Eli Lilly, 5, Gilead, 5, Horizon Therapeutics, 5, Pfizer, 5, Redd Pharma, 5, 11; M. Nurmohamed: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, 5, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, 5, 6, Celgene, 2, 5, 6, Galapagos, 2, 5, Janssen, 2, 5, 6, Menarini, 2, 5, 6, Merck/MSD, 2, 5, 6, Mundipharma, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, Roche, 2, 5, 6, Sanofi, 2, 5, 6, UCB, 2, 5, 6.
Background/Purpose: The formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) with extrusion of nuclear, granular and cytosolic components from a dying neutrophil, has been described extensively in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and linked to generation of autoantigens (e.g. citrullinated proteins), inflammation and organ damage. Thus far there have been very few studies describing the effect of treatment in patients with RA on NET formation, and no studies comparing the effects of treatment strategies in (very) early RA. The objective of the study is to assess the effects of different initial treatments on NET formation in patients with early RA.
Methods: NORD-STAR is an international, multicenter, open-label, assessor-blinded, phase 4 study where patients with newly diagnosed RA started methotrexate (MTX) and were randomized 1:1:1:1 to a) conventional treatment (either prednisolone tapered to 5mg/day, or sulfasalazine combined with hydroxychloroquine and intra-articular corticosteroids), b) certolizumab pegol, c) abatacept, or d) tocilizumab1. This study is a spin-off from the main NORD-STAR study measuring neutrophil biomarkers MPO-DNA (Myeloperoxidase-DNA; NETs) and calprotectin in 24 consecutive Dutch participants and 94 Swedish patients at baseline, 12 weeks and 24 weeks after the start of the treatment. Statistical analysis was done using the Wilcoxon Signed Rank test for paired samples and independent samples median test to compare patients to healthy controls in SPSS version 28.
Results: At baseline patients had elevated levels of NETs and neutrophil activation compared to healthy controls as indicated by calprotectin (median 1080ng/ml vs 133ng/ml, p< 0.001) and elevated MPO-DNA (median 7185pM vs 3976pM, p< 0.001). Both of the biomarkers decreased significantly at 12 and 24 weeks after treatment in the total group demonstrating reduced neutrophil activity and NET formation. After 24 weeks of treatment, calprotectin was significantly reduced in all groups by up to 93% (Table 1). MPO-DNA showed a more modest reduction of up to 13%, and was relatively similar in all groups, although the reduction in MPO-DNA did not reach statistical significance in the tocilizumab group.
Conclusion: These results indicate highly elevated neutrophil activation and NET formation in recently diagnosed RA patients. All four treatments studied here reduced these detrimental processes within 3 months. The calprotectin reduction seen in this study is in line with an earlier spin-off study2. The rapid decline in these markers may have contributed to the minimal radiological progression that was seen in the NORD-STAR trial.
References:
[1] Hetland M et al. BMJ. 2020
[2] Stevens D et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022


B. Dijkshoorn: Galapagos, 2, Novartis, 2; T. Wang: None; G. Grondal: None; D. Vedder: None; A. Rudin: AstraZeneca, 12, financial support; D. Nordstrom: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, BMS, 2, Lilly, 2, MSD, 2, Novartis, 2, Pfizer, 2, UCB, 2; B. Gudbjornsson: Nordic-Pharma, 6, Novartis, 2, 6; K. Lend: None; T. Uhlig: Galapagos, 2, 6, Lilly, 2, 6, Novartis, 2, 6, Pfizer, 2, 6, UCB, 2, 6; E. Haavardsholm: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, Boehringer-Ingelheim, 2, Eli Lilly, 2, Gilead, 2, Pfizer, 6, UCB, 6; M. Hetland: AbbVie/Abbott, 1, 5, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 5, Danbio, 12, MLH has chaired the steering committee of the Danish Rheumatology Quality Registry (DANBIO, DRQ), which receives public funding from the hospital owne, Eli Lilly, 5, MEDAC, 6, Novartis, 5, Pfizer, 5, 6, Sandoz, 5, 6; M. Schrumpf Heiberg: Roche, 6; M. Østergaard: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Amgen, 5, Boehringer-Ingelheim, 2, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, 5, 6, Celgene, 2, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 6, Galapagos, 2, 6, Gilead, 2, 6, Hospira, 2, 6, Janssen, 2, 6, MEDAC, 6, Merck, 2, 5, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Novo Nordisk, 2, 6, Orion, 2, 6, Pfizer, 2, 6, Regeneron, 2, 6, Roche, 2, 6, Sandoz, 2, 6, Sanofi, 2, 6, UCB, 2, 6; K. Horslev-Petersen: None; J. Lampa: None; R. van Vollenhoven: AbbVie, 2, 6, AstraZeneca, 2, 5, 6, Biogen, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, 5, 6, Galapagos, 2, 5, 6, GlaxoSmithKline, 6, Janssen, 2, 6, MSD/Merck Sharp and Dohme, 5, Novartis, 5, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, RemeGen, 2, Roche, 5, Sanofi, 5, UCB, 2, 5, 6; C. Lood: Amytryx, 5, Boehringer-Ingelheim, 5, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 5, Citryll, 2, Eli Lilly, 5, Gilead, 5, Horizon Therapeutics, 5, Pfizer, 5, Redd Pharma, 5, 11; M. Nurmohamed: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, 5, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, 5, 6, Celgene, 2, 5, 6, Galapagos, 2, 5, Janssen, 2, 5, 6, Menarini, 2, 5, 6, Merck/MSD, 2, 5, 6, Mundipharma, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, Roche, 2, 5, 6, Sanofi, 2, 5, 6, UCB, 2, 5, 6.



