Abstract Session
Myopathic rheumatic diseases (polymyositis, dermatomyositis, inclusion body myositis)
Session: Abstracts: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science I (2461–2466)
2463: Efficacy and Safety of Car-T-Cell Treatment in Refractory Antisynthetase Syndrome – Data of the First Three Patients
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
2:30 PM - 2:40 PM PT
Location: Room 25A-C
- JT
Jule Taubmann, MD, BSc
Universitätsklinikum Erlangen
Erlangen, GermanyDisclosure information not submitted.
Presenting Author(s)
Jule Taubmann1, Johannes Knitza2, Fabian Müller3, Sebastian Boeltz1, Simon Voelkl4, Michael Aigner4, Arnd Kleyer5, Ioanna Minnopoulou1, Regina Gary4, Sascha kretschmann4, Andreas Mackensen4 and Georg Schett6, 1Department of Internal Medicine 3, Rheumatology and Immunology, Universitätsklinikum Erlangen and Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany, 2Department of Internal Medicine 3 Rheumatology and Immunology, Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nürnberg, University Hospital Erlangen, Erlangen, Germany, 3Friedrich Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg and Universitätsklinikum Erlangen, Erlangen, Germany, 4Department of Internal Medicine 5, Hematology and Oncology, Universitätsklinikum Erlangen and Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany, 5University Hospital Erlangen, Erlangen, Germany, 6Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany
Background/Purpose: Antisynthetase syndrome (ASS) can be very severe affecting the lungs, the skin and the joints next to the muscles. ASS can take a refractory life-threatening course, necessitating the development of new treatment strategies. We recently reported the first case of successful rescue therapy of ASS with CD19-targeted CAR-T-cells [1]. Herein, we present efficacy and safety data for the first three patients with refractory ASS treated with autologous CD19 CAR-T-cells. The objective of this study was to test whether administration of CD19 CAR-T-cells is tolerable and effective in patients with severe refractory ASS.
Methods: Autologous CD19 CAR-T-cells were prepared and given as described previously [1,2,3]. All immunosuppressive treatments were stopped before CD19 CAR-T-cell administration. Tolerability was assessed by monitoring for Cytokine-Release Syndrome (CRS) and Immune-related effector Cell Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS). Efficacy was assessed by CK levels, good response according 2016 ACR/EULAR total improvement score (TIS), imaging of muscles and lungs and successful cessation of all immunosuppressive treatments including glucocorticoids.
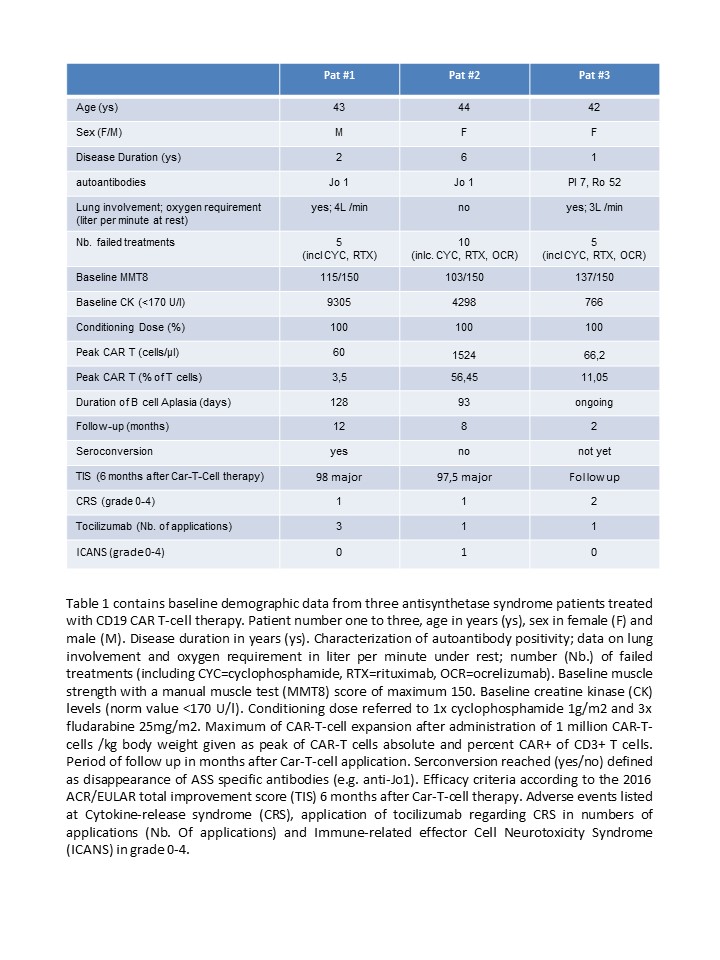
Results: Three ASS patients were treated with CD19 CAR-T-cells (table 1). All patients presented with active myositis and elevated CK levels. Patient 1 showed involvement of the muscles, skin and lungs, patient 2 showed involvement of muscles, skin, joints and lungs, patient 3 showed involvement of muscles and lungs. All patients did not respond to a minimum of 5 different immunosuppressive treatments (table 1). CAR-T-cell treatment was well-tolerated. Mild CRS (grade I) was observed in the first two patients. Patient 3 showed signs off increased O2 requirement (temporarily 10l/min by mask), chills and fever (39.0°C) defined as CRS grade II. All patients were treated with tocilizumab and CRS resolved quickly. Patient 2 had signs of mild self-limited ICANS (grade I discrete ataxia for a few days) two weeks after CAR-T treatment. Expansion of CAR-T-cells paralleled with the complete depletion of circulating B cells. The first two patients experienced normalization of CK levels (patient 1: CK+150 days: 70 U/l, patient 2: CK+150 days: 99 U/l), major clinical improvement according to the 2016 TIS and could stop all immunosuppressive therapy. Follow-up CT scans of the lung done in patient 1 showed resolution of alveolar inflammation. Follow-up MRI of patient 1 and 2 revealed abrogation of inflammatory changes in the thigh muscles and hamstrings. At the latest follow up (365days and 150days) both patients were in drug-free remission, while patient 3 awaits follow up assessment.
Conclusion: Taken together, these data suggest that CD19 CAR-T-cell therapy provides a possibility to intercept with severe ASS leading to drug-free remission and resolution of muscle and lung inflammation.
J. Taubmann: None; J. Knitza: None; F. Müller: AbbVie, 6, AstraZeneca, 1, 5, 6, Bristol Myers Squibb, 1, 6, Janssen, 6, KITE, 1, 6, Miltenyi Biomedicine, 1, 6, Novartis, 1, 6, Sobi, 6; S. Boeltz: None; S. Voelkl: None; M. Aigner: Kosmas Therapuetics, 8, Kyverna, 5, Miltenyi Biomedicine, 2, 7, Miltenyi Biotec, 6; A. Kleyer: None; I. Minnopoulou: None; R. Gary: None; S. kretschmann: None; A. Mackensen: BioNTech, 1, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 1, KITE/Gilead, 1, 6, Kyverna, 5, Miltenyi Biotech, 5; G. Schett: None.
Background/Purpose: Antisynthetase syndrome (ASS) can be very severe affecting the lungs, the skin and the joints next to the muscles. ASS can take a refractory life-threatening course, necessitating the development of new treatment strategies. We recently reported the first case of successful rescue therapy of ASS with CD19-targeted CAR-T-cells [1]. Herein, we present efficacy and safety data for the first three patients with refractory ASS treated with autologous CD19 CAR-T-cells. The objective of this study was to test whether administration of CD19 CAR-T-cells is tolerable and effective in patients with severe refractory ASS.
Methods: Autologous CD19 CAR-T-cells were prepared and given as described previously [1,2,3]. All immunosuppressive treatments were stopped before CD19 CAR-T-cell administration. Tolerability was assessed by monitoring for Cytokine-Release Syndrome (CRS) and Immune-related effector Cell Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS). Efficacy was assessed by CK levels, good response according 2016 ACR/EULAR total improvement score (TIS), imaging of muscles and lungs and successful cessation of all immunosuppressive treatments including glucocorticoids.
Results: Three ASS patients were treated with CD19 CAR-T-cells (table 1). All patients presented with active myositis and elevated CK levels. Patient 1 showed involvement of the muscles, skin and lungs, patient 2 showed involvement of muscles, skin, joints and lungs, patient 3 showed involvement of muscles and lungs. All patients did not respond to a minimum of 5 different immunosuppressive treatments (table 1). CAR-T-cell treatment was well-tolerated. Mild CRS (grade I) was observed in the first two patients. Patient 3 showed signs off increased O2 requirement (temporarily 10l/min by mask), chills and fever (39.0°C) defined as CRS grade II. All patients were treated with tocilizumab and CRS resolved quickly. Patient 2 had signs of mild self-limited ICANS (grade I discrete ataxia for a few days) two weeks after CAR-T treatment. Expansion of CAR-T-cells paralleled with the complete depletion of circulating B cells. The first two patients experienced normalization of CK levels (patient 1: CK+150 days: 70 U/l, patient 2: CK+150 days: 99 U/l), major clinical improvement according to the 2016 TIS and could stop all immunosuppressive therapy. Follow-up CT scans of the lung done in patient 1 showed resolution of alveolar inflammation. Follow-up MRI of patient 1 and 2 revealed abrogation of inflammatory changes in the thigh muscles and hamstrings. At the latest follow up (365days and 150days) both patients were in drug-free remission, while patient 3 awaits follow up assessment.
Conclusion: Taken together, these data suggest that CD19 CAR-T-cell therapy provides a possibility to intercept with severe ASS leading to drug-free remission and resolution of muscle and lung inflammation.

J. Taubmann: None; J. Knitza: None; F. Müller: AbbVie, 6, AstraZeneca, 1, 5, 6, Bristol Myers Squibb, 1, 6, Janssen, 6, KITE, 1, 6, Miltenyi Biomedicine, 1, 6, Novartis, 1, 6, Sobi, 6; S. Boeltz: None; S. Voelkl: None; M. Aigner: Kosmas Therapuetics, 8, Kyverna, 5, Miltenyi Biomedicine, 2, 7, Miltenyi Biotec, 6; A. Kleyer: None; I. Minnopoulou: None; R. Gary: None; S. kretschmann: None; A. Mackensen: BioNTech, 1, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 1, KITE/Gilead, 1, 6, Kyverna, 5, Miltenyi Biotech, 5; G. Schett: None.



