Abstract Session
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) including psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Session: Abstracts: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment I: PsA (0775–0780)
0778: The Effect of Probiotic Modulation of Enteral Dysbiosis on Disease Activity in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis - A Randomized Controlled Trial
Sunday, November 12, 2023
2:45 PM - 2:55 PM PT
Location: Ballroom 20A
- MS
Presenting Author(s)
Anirudh Subramanian Muralikrishnan1, Barbara Dreo2, Angelika Lackner1, Rusmir Husic3, Florentine Moazedi-Fuerst3, Josef Hermann4, Philipp Bosch1, Johannes Fessler1, Jens Thiel5 and Martin Stradner1, 1Medical University of Graz, Graz, Austria, 2Division of Rheumatology and Immunology, Medical University of Graz, Graz, Austria, 3Meduni Graz, Graz, Austria, 4Division of Rheumatology and Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical University Graz, Graz, Austria, 5University Hospital Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) is a painful disease of the joints and spine. Recent studies have described enteric dysbiosis as a possible pathological mechanism in PsA and hence could be a target for therapy. In an open label pilot study, probiotic supplementation ameliorated enteric dysbiosis and reduced disease activity of PsA patients. The aim of this study was to test the effect of probiotic supplementation on disease activity in PsA in a larger randomized controlled trial (RCT).
Methods: The study was designed as a single center, double-blind, RCT (NCT04588623) on consecutive patients with PsA in Moderate Disease Activity (MoDA) (Psoriatic ArthritiS Disease Activity Score [PASDAS] >3.2 - < 5.4) under stable treatment. Patients were randomized to either placebo or probiotic containing Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus strains (OMNi-BiOTiC® STRESS Repair, Institut Allergosan, Graz, Austria) for 12 weeks. After week 12 (W12) patients received probiotics, irrespective of the initial grouping and were followed up again at week 24 (W24). The patients enrolled were given a full clinical assessment and samples (stool, serum, and PBMCs) were collected at baseline (BSL), W12, W24. Immune cell composition in the peripheral blood was analyzed using flow cytometry. Stool microbiome was analyzed via 16s rRNA sequencing and levels of Zonulin, Calprotectin and Anti-Trypsin were assayed through ELISA as a measure of gut permeability and intestinal inflammation. The primary end point of the study was the reduction of disease activity to low DA or remission (PASDAS < 3.2) at W12.
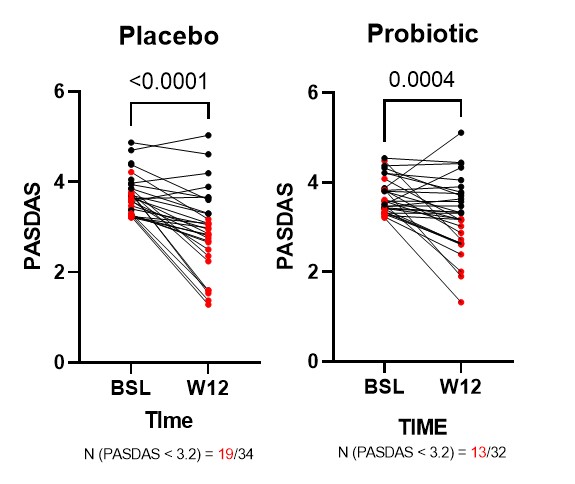
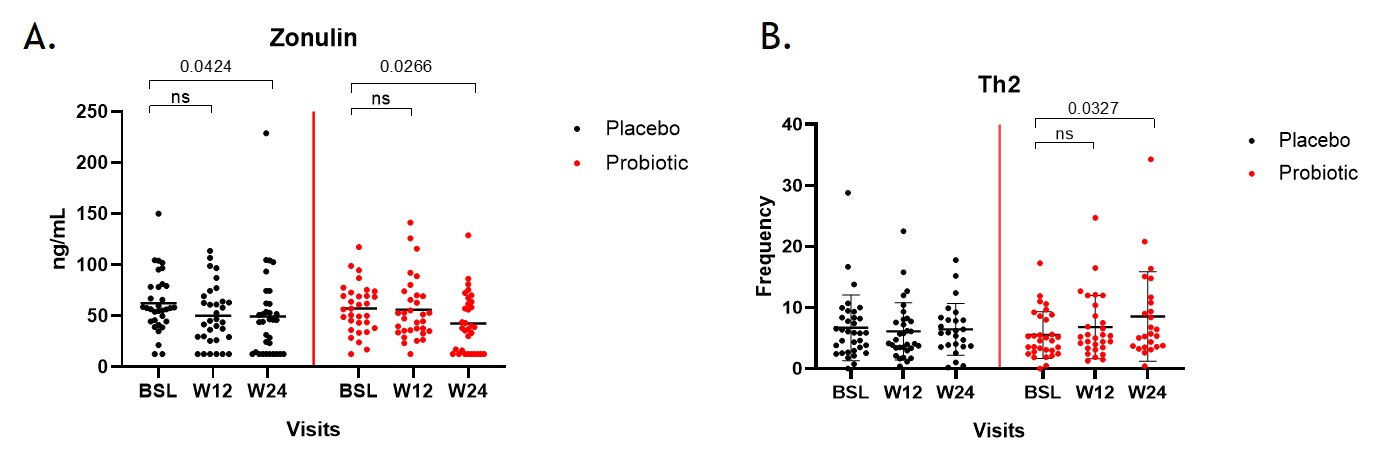
Results: A total of 65 patients were recruited and off these 32 patients were randomized into the probiotic group and 34 patients into the placebo group. A significant reduction in disease activity was observed as measured by the PASDAS score in both groups irrespective of probiotic intervention (Fig1). The proportion of patients reaching low DA or remission was not different between probiotic and placebo (55.8% vs 40.63%). A significant reduction in zonulin levels was observed in the probiotic group at W24 compared to BSL, whereas only a slightly weaker effect was seen in the placebo group (Fig2A). Results from immune cell phenotyping, revealed a significant increase in the frequency of Th2 cells in the probiotic group at W24 (Fig2B). No significant differences were observed in the frequencies of other lymphocyte subsets like Th1, Th17 and Tregs.
Conclusion: In this double-blind RCT, supplementation of probiotics in PsA patients showed limited effects on the dysbiosis of the gut measured by marker Zonulin and also had minor effects on the T-cell composition. However, no difference was seen in the amelioration of disease activity compared to placebo treatment, which could be due to the small samples size and the short recording period of the trial.
A. Muralikrishnan: None; B. Dreo: None; A. Lackner: None; R. Husic: None; F. Moazedi-Fuerst: None; J. Hermann: None; P. Bosch: Janssen, 6, 12, Congress fees, Pfizer, 5; J. Fessler: None; J. Thiel: None; M. Stradner: None.
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) is a painful disease of the joints and spine. Recent studies have described enteric dysbiosis as a possible pathological mechanism in PsA and hence could be a target for therapy. In an open label pilot study, probiotic supplementation ameliorated enteric dysbiosis and reduced disease activity of PsA patients. The aim of this study was to test the effect of probiotic supplementation on disease activity in PsA in a larger randomized controlled trial (RCT).
Methods: The study was designed as a single center, double-blind, RCT (NCT04588623) on consecutive patients with PsA in Moderate Disease Activity (MoDA) (Psoriatic ArthritiS Disease Activity Score [PASDAS] >3.2 - < 5.4) under stable treatment. Patients were randomized to either placebo or probiotic containing Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus strains (OMNi-BiOTiC® STRESS Repair, Institut Allergosan, Graz, Austria) for 12 weeks. After week 12 (W12) patients received probiotics, irrespective of the initial grouping and were followed up again at week 24 (W24). The patients enrolled were given a full clinical assessment and samples (stool, serum, and PBMCs) were collected at baseline (BSL), W12, W24. Immune cell composition in the peripheral blood was analyzed using flow cytometry. Stool microbiome was analyzed via 16s rRNA sequencing and levels of Zonulin, Calprotectin and Anti-Trypsin were assayed through ELISA as a measure of gut permeability and intestinal inflammation. The primary end point of the study was the reduction of disease activity to low DA or remission (PASDAS < 3.2) at W12.
Results: A total of 65 patients were recruited and off these 32 patients were randomized into the probiotic group and 34 patients into the placebo group. A significant reduction in disease activity was observed as measured by the PASDAS score in both groups irrespective of probiotic intervention (Fig1). The proportion of patients reaching low DA or remission was not different between probiotic and placebo (55.8% vs 40.63%). A significant reduction in zonulin levels was observed in the probiotic group at W24 compared to BSL, whereas only a slightly weaker effect was seen in the placebo group (Fig2A). Results from immune cell phenotyping, revealed a significant increase in the frequency of Th2 cells in the probiotic group at W24 (Fig2B). No significant differences were observed in the frequencies of other lymphocyte subsets like Th1, Th17 and Tregs.
Conclusion: In this double-blind RCT, supplementation of probiotics in PsA patients showed limited effects on the dysbiosis of the gut measured by marker Zonulin and also had minor effects on the T-cell composition. However, no difference was seen in the amelioration of disease activity compared to placebo treatment, which could be due to the small samples size and the short recording period of the trial.

Fig1 Changes in PASDAS score in patients grouped by probiotic intervention. Samples in red denote specifically the patients that achieved low DA or remission (PASDAS < 3.2).

Fig2. A. Changes in concentration of zonulin in stool samples at different time points as measured by ELISA (ng/ML). B. Frequency of Th2 cells at different time points in both intervention groups as a frequency of the parent population. In both graphs black dots denote placebo group and red denotes probiotic group.
A. Muralikrishnan: None; B. Dreo: None; A. Lackner: None; R. Husic: None; F. Moazedi-Fuerst: None; J. Hermann: None; P. Bosch: Janssen, 6, 12, Congress fees, Pfizer, 5; J. Fessler: None; J. Thiel: None; M. Stradner: None.



